
Liliales is an order of monocotyledonous flowering plants in the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group and Angiosperm Phylogeny Web system, within the lilioid monocots. This order of necessity includes the family Liliaceae. The APG III system (2009) places this order in the monocot clade. In APG III, the family Luzuriagaceae is combined with the family Alstroemeriaceae and the family Petermanniaceae is recognized. Both the order Lililiales and the family Liliaceae have had a widely disputed history, with the circumscription varying greatly from one taxonomist to another. Previous members of this order, which at one stage included most monocots with conspicuous tepals and lacking starch in the endosperm are now distributed over three orders, Liliales, Dioscoreales and Asparagales, using predominantly molecular phylogenetics. The newly delimited Liliales is monophyletic, with ten families. Well known plants from the order include Lilium (lily), tulip, the North American wildflower Trillium, and greenbrier.

Smilacaceae, the greenbriers, is a family of flowering plants. While they were often assigned to a more broadly defined family Liliaceae, most recent botanists have accepted the two as distinct families, diverging around 55 million years ago during the Early Paleogene. One characteristic that distinguishes Smilacaceae from most of the other members of the Liliaceae-like Liliales is that it has true vessels in its conducting tissue. Another is that the veins of the leaves, between major veins, are reticulate (net-shaped), rather than parallel as in most monocots.

Hemerocallidoideae is the a subfamily of flowering plants, part of the family Asphodelaceae sensu lato in the monocot order Asparagales according to the APG system of 2016. Earlier classification systems treated the group as a separate family, the Hemerocallidaceae. The name is derived from the generic name of the type genus, Hemerocallis. The largest genera in the group are Dianella, Hemerocallis (15), and Caesia (11).

Elaeocarpus is a genus of nearly five hundred species of flowering plants in the family Elaeocarpaceae native to the Western Indian Ocean, Tropical and Subtropical Asia, and the Pacific. Plants in the genus Elaeocarpus are trees or shrubs with simple leaves, flowers with four or five petals usually, and usually blue fruit.

Austrobaileya is the sole genus consisting of a single species that constitutes the entire flowering plant family Austrobaileyaceae. The species Austrobaileya scandens grows naturally only in the Wet Tropics rainforests of northeastern Queensland, Australia.

Myoporum is a genus of flowering plants in the figwort family, Scrophulariaceae. There are 30 species in the genus, eighteen of which are endemic to Australia although others are endemic to Pacific Islands, including New Zealand, and one is endemic to two Indian Ocean islands. They are shrubs or small trees with leaves that are arranged alternately and have white, occasionally pink flowers and a fruit that is a drupe.

Cordyline is a genus of about 24 species of woody monocotyledonous flowering plants in family Asparagaceae, subfamily Lomandroideae. The subfamily has previously been treated as a separate family Laxmanniaceae, or Lomandraceae. Other authors have placed the genus in the Agavaceae. Cordyline is native to the western Pacific Ocean region, from New Zealand, eastern Australia, southeastern Asia and Polynesia, with one species found in southeastern South America.

Craspedia is a genus of flowering plants in the family Asteraceae commonly known as billy buttons, billy balls, and woollyheads. They are native to Australia and New Zealand where they grow in a variety of habitats from sea level to the Alps. The genus is found in every state of Australia but not in the Northern Territory. In New Zealand, Craspedia is found from East Cape on the North Island south to Stewart Island. It also occurs on Campbell Island and the Chatham Islands.

Acronychia is a genus of about fifty species of plants in the rue family Rutaceae. The leaves are simple or pinnate, and the flowers bisexual with four sepals, four petals and eight stamens. They have a broad distribution including in India, Malesia, Australia and the islands of the western Pacific Ocean. About twenty species are endemic to Australia.
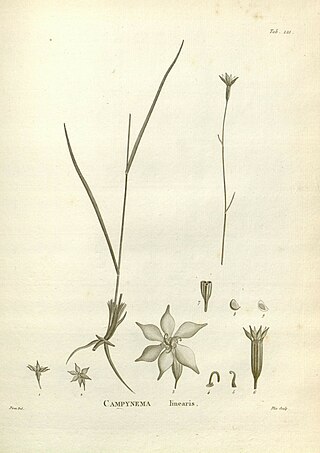
Campynemataceae (Campynemaceae) is a family of flowering plants. The family consists of two genera and four species of perennial herbaceous plants endemic to New Caledonia and Tasmania.
Supplejack is a common name for several plants and may refer to:

Gahnia is a genus of sedges native to China, Southeast Asia, New Guinea, Australia, New Zealand and a number of Pacific Islands. The common name is due to the toothed margins. It often forms tussocks.

Ripogonum discolor, known as the prickly supplejack, is a common rainforest vine, found in eastern Australia. The original specimen was collected at the Clarence River.

Borya is a genus of flowering plants in the family Boryaceae, endemic to Australia.

Ripogonum scandens, is a common rainforest vine native to New Zealand. It can also grow in areas of swamp.

Ripogonum brevifolium, commonly known as small–leaved supplejack, is a vine, or sometimes a shrub, native to Australia.

Ripogonum elseyanum, commonly known as hairy supplejack, is a climbing vine, or sometimes a shrub, native to coastal rainforests of New South Wales and Queensland, Australia.

Ripogonum fawcettianum, commonly known as small supplejack, is a small climbing vine, or sometimes a shrub, native to coastal rainforests of New South Wales and Queensland, Australia.

Synima is a genus of tropical rainforest trees, constituting part of the plant family Sapindaceae.

Coronariae is a term used historically to refer to a group of flowering plants, generally including the lilies (Liliaceae), and later replaced by the order Liliales. First used in the 17th century by John Ray, it referred to flowers used to insert in garlands. Coronariae soon came to be associated with Liliaceae in the Linnaean system. The term was abandoned at the end of the 19th century, being replaced with Liliiflorae and then Liliales.



















