Related Research Articles

Mandarin is a group of Chinese (Sinitic) dialects that are natively spoken across most of northern and southwestern China. The group includes the Beijing dialect, the basis of the phonology of Standard Chinese, the official language of China. Because Mandarin originated in North China and most Mandarin dialects are found in the north, the group is sometimes referred to as Northern Chinese. Many varieties of Mandarin, such as those of the Southwest and the Lower Yangtze, are not mutually intelligible with the standard language. Nevertheless, Mandarin as a group is often placed first in lists of languages by number of native speakers.
Tone is the use of pitch in language to distinguish lexical or grammatical meaning – that is, to distinguish or to inflect words. All verbal languages use pitch to express emotional and other paralinguistic information and to convey emphasis, contrast and other such features in what is called intonation, but not all languages use tones to distinguish words or their inflections, analogously to consonants and vowels. Languages that have this feature are called tonal languages; the distinctive tone patterns of such a language are sometimes called tonemes, by analogy with phoneme. Tonal languages are common in East and Southeast Asia, Africa, the Americas and the Pacific.

Yue is a group of similar Sinitic languages spoken in Southern China, particularly in Liangguang.
Tone sandhi is a phonological change occurring in tonal languages, in which the tones assigned to individual words or morphemes change based on the pronunciation of adjacent words or morphemes. It usually simplifies a bidirectional tone into a one-direction tone. It is a type of sandhi, or fusional change, from the Sanskrit word for "joining".

Middle Chinese or the Qieyun system (QYS) is the historical variety of Chinese recorded in the Qieyun, a rime dictionary first published in 601 and followed by several revised and expanded editions. The Swedish linguist Bernard Karlgren believed that the dictionary recorded a speech standard of the capital Chang'an of the Sui and Tang dynasties. However, based on the more recently recovered preface of the Qieyun, most scholars now believe that it records a compromise between northern and southern reading and poetic traditions from the late Northern and Southern dynasties period. This composite system contains important information for the reconstruction of the preceding system of Old Chinese phonology.

Chinese, also known as Sinitic, is a branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family consisting of hundreds of local varieties, many of which are not mutually intelligible. Variation is particularly strong in the more mountainous southeast of mainland China. The varieties are typically classified into several groups: Mandarin, Wu, Min, Xiang, Gan, Hakka and Yue, though some varieties remain unclassified. These groups are neither clades nor individual languages defined by mutual intelligibility, but reflect common phonological developments from Middle Chinese.
Taishanese, alternatively romanized in Cantonese as Toishanese or Toisanese, in local dialect as Hoisanese or Hoisan-wa, is a dialect of Yue Chinese native to Taishan, Guangdong. Although it is related to Cantonese, Taishanese has little mutual intelligibility with the latter. Taishanese is also spoken throughout Sze Yup, located on the western fringe of the Pearl River Delta in Guangdong China. In the late 19th century and early 20th century, most of the Chinese emigration to North America originated from Sze Yup, the area where this variety is natively spoken. Thus, up to the mid-20th century, Taishanese was the dominant variety of the Chinese language spoken in Chinatowns in Canada and the United States. It was formerly the lingua franca of the overseas Chinese residing in the United States.
A pitch-accent language, when spoken, has word accents in which one syllable in a word or morpheme is more prominent than the others, but the accentuated syllable is indicated by a contrasting pitch rather than by loudness, as in many languages, like English. Pitch-accent also contrasts with fully tonal languages like Vietnamese and Standard Chinese, in which each syllable can have an independent tone. Some have claimed that the term "pitch accent" is not coherently defined and that pitch-accent languages are just a sub-category of tonal languages in general.
A tone contour, or contour tone, is a tone in a tonal language which shifts from one pitch to another over the course of the syllable or word. Tone contours are especially common in East, Southeast Asia, West Africa, Nilo-Saharan languages, Khoisan languages, Oto-Manguean languages and some languages of South America.
The Shanghainese language, also known as the Shanghai dialect, or Hu language, is a variety of Wu Chinese spoken in the central districts of the City of Shanghai and its surrounding areas. It is classified as part of the Sino-Tibetan language family. Shanghainese, like the rest of the Wu language group, is mutually unintelligible with other varieties of Chinese, such as Mandarin.

Penang Hokkien is a local variant of Hokkien spoken in Penang, Malaysia. It is spoken as a mother tongue by 63.9% of Penang's Chinese community, and also by some Penangite Indians and Penangite Malays as a third language spoken by these two other ethnic groups.
The phonology of Vietnamese features 19 consonant phonemes, with 5 additional consonant phonemes used in Vietnamese's Southern dialect, and 4 exclusive to the Northern dialect. Vietnamese also has 14 vowel nuclei, and 6 tones that are integral to the interpretation of the language. Older interpretations of Vietnamese tones differentiated between "sharp" and "heavy" entering and departing tones. This article is a technical description of the sound system of the Vietnamese language, including phonetics and phonology. Two main varieties of Vietnamese, Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City, which are slightly different to each other, are described below.

The Fuzhou language, also Foochow, Hokchew, Hok-chiu, or Fuzhounese, is the prestige variety of the Eastern Min branch of Min Chinese spoken mainly in the Mindong region of Eastern Fujian Province. As it is mutually unintelligible to neighbouring varieties in the province, under a technical linguistic definition Fuzhou is a language and not a dialect. Thus, while Fuzhou may be commonly referred to as a 'dialect' by laypersons, this is colloquial usage and not recognised in academic linguistics. Like many other varieties of Chinese, the Fuzhou dialect is dominated by monosyllabic morphemes that carry lexical tones, and has a mainly analytic syntax. While the Eastern Min branch it belongs to is relatively closer to Southern Min or Hokkien than to other Sinitic branches such as Mandarin, Wu Chinese or Hakka, they are still not mutually intelligible.
In linguistics, intonation is variation in pitch used to indicate the speaker's attitudes and emotions, to highlight or focus an expression, to signal the illocutionary act performed by a sentence, or to regulate the flow of discourse. For example, the English question "Does Maria speak Spanish or French?" is interpreted as a yes-or-no question when it is uttered with a single rising intonation contour, but is interpreted as an alternative question when uttered with a rising contour on "Spanish" and a falling contour on "French". Although intonation is primarily a matter of pitch variation, its effects almost always work hand-in-hand with other prosodic features. Intonation is distinct from tone, the phenomenon where pitch is used to distinguish words or to mark grammatical features.

Sichuanese or Szechwanese (simplified Chinese: 四川话; traditional Chinese: 四川話; Sichuanese Pinyin: Si4cuan1hua4; pinyin: Sìchuānhuà; Wade–Giles: Szŭ4-ch'uan1-hua4), also called Sichuanese/Szechwanese Mandarin (simplified Chinese: 四川官话; traditional Chinese: 四川官話; pinyin: Sìchuān Guānhuà) is a branch of Southwestern Mandarin spoken mainly in Sichuan and Chongqing, which was part of Sichuan Province until 1997, and the adjacent regions of their neighboring provinces, such as Hubei, Guizhou, Yunnan, Hunan and Shaanxi. Although "Sichuanese" is often synonymous with the Chengdu-Chongqing dialect, there is still a great amount of diversity among the Sichuanese dialects, some of which are mutually unintelligible with each other. In addition, because Sichuanese is the lingua franca in Sichuan, Chongqing and part of Tibet, it is also used by many Tibetan, Yi, Qiang and other ethnic minority groups as a second language.
The Xuzhou dialect is a Mandarin dialect spoken in the city of Xuzhou in Jiangsu province, China.
This article summarizes the phonology of Standard Chinese.
The standard pronunciation of Cantonese is that of Guangzhou, also known as Canton, the capital of Guangdong Province. Hong Kong Cantonese is related to the Guangzhou dialect, and the two diverge only slightly. Yue dialects in other parts of Guangdong and Guangxi provinces, such as Taishanese, may be considered divergent to a greater degree.
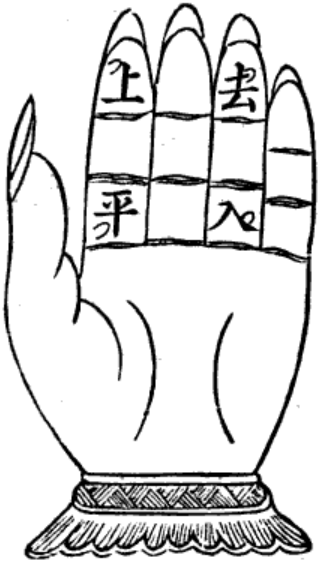
The four tones of Chinese poetry and dialectology are four traditional tone classes of Chinese words. They play an important role in Chinese poetry and in comparative studies of tonal development in the modern varieties of Chinese, both in traditional Chinese and in Western linguistics. They correspond to the phonology of Middle Chinese, and are named even or level, rising, departing or going, and entering or checked. They were reconstructed as mid, mid rising, high falling, and mid with a final stop consonant respectively. Due to historic splits and mergers, none of the modern varieties of Chinese have the exact four tones of Middle Chinese, but they are noted in rhyming dictionaries.
The Fuqing dialect, or Hokchia, is an Eastern Min dialect. It is spoken in the county-level city of Fuqing, China, situated within the prefecture-level city of Fuzhou. It is not completely mutually intelligible with the Fuzhou dialect.
References
- ↑ Wurm, S.; Li, R.; Baumann, T. (1987). Language Atlas of China. London: Longman Group.
- ↑ Jiang, L. (2006). The research on Weihai dialect kinship terminology. Wuhan, China: Central China Normal University.
- ↑ Yan, M. M. (2006). Introduction to Chinese Dialectology. Munich: Lincom Europa.
- ↑ Deng, J.; Fulop, S. (2016). Interactions between stop aspiration and tonal pitch in Weihai Chinese. Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics 171. Vol. 26. p. 060011. doi: 10.1121/2.0000551 .
