 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC names Einsteinium sesquioxide Dieinsteinium trioxide Einsteinium(III) oxide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Es2O3 | |
| Molar mass | 554 g/mol (253Es) |
| Appearance | colourless solid [1] |
| Structure | |
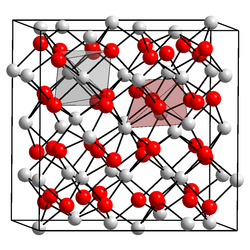
| Hexagonal | |
| Ia3 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Einsteinium(III) oxide is an oxide of the synthetic actinide einsteinium which has the molecular formula Es2O3. It is a colourless solid. [1]
Three modifications are known. The body-centered cubic form has lattice parameter a = 1076.6 ± 0.6 pm; this allows the ionic radius of the Es3+ ion to be calculated as 92.8 pm. [3] The other two forms are monoclinic and hexagonal: the hexagonal form has the lanthanum(III) oxide structure. [4]
Einsteinium(III) oxide can be obtained by annealing einsteinium(III) nitrate in sub-microgram quantities. [3]