Related Research Articles
Berkelium is a synthetic chemical element; it has symbol Bk and atomic number 97. It is a member of the actinide and transuranium element series. It is named after the city of Berkeley, California, the location of the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory where it was discovered in December 1949. Berkelium was the fifth transuranium element discovered after neptunium, plutonium, curium and americium.

Einsteinium is a synthetic chemical element; it has symbol Es and atomic number 99. It is named after Albert Einstein and is a member of the actinide series and is the seventh transuranium element.
Terbium(III) iodide (TbI3) is an inorganic chemical compound.

Few compounds of californium have been made and studied. The only californium ion that is stable in aqueous solutions is the californium(III) cation. The other two oxidation states are IV (strong oxidizing agents) and II (strong reducing agents). The element forms a water-soluble chloride, nitrate, perchlorate, and sulfate and is precipitated as a fluoride, oxalate or hydroxide. If problems of availability of the element could be overcome, then CfBr2 and CfI2 would likely be stable.

Einsteinium triiodide is an iodide of the synthetic actinide einsteinium which has the molecular formula EsI3. This crystalline salt is an amber-coloured solid. It glows red in the dark due to einsteinium's intense radioactivity.

Neodymium(II) iodide or neodymium diiodide is an inorganic salt of iodine and neodymium the formula NdI2. Neodymium uses the +2 oxidation state in the compound.
Einsteinium compounds are compounds that contain the element einsteinium (Es). These compounds largely have einsteinium in the +3 oxidation state, or in some cases in the +2 and +4 oxidation states. Although einsteinium is relatively stable, with half-lives ranging from 20 days upwards, these compounds have not been studied in great detail.

Praseodymium(III) iodide is an inorganic salt, consisting of the rare-earth metal praseodymium and iodine, with the chemical formula PrI3. It forms green crystals. It is soluble in water.

Lanthanum(III) iodide is an inorganic compound containing lanthanum and iodine with the chemical formula LaI
3.
Europium(III) iodide is an inorganic compound containing europium and iodine with the chemical formula EuI3.

Lutetium(III) iodide or lutetium iodide is an inorganic compound consisting of iodine and lutetium, with the chemical formula of LuI3.
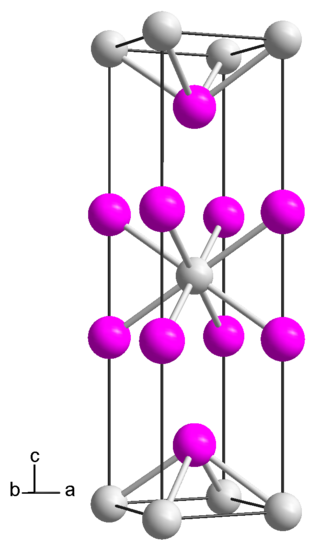
Cerium diiodide is an iodide of cerium, with the chemical formula of CeI2.

Holmium(III) iodide is an iodide of holmium, with the chemical formula of HoI3. It is used as a component of metal halide lamps.
Einsteinium fluoride is a binary inorganic chemical compound of einsteinium and fluorine with the chemical formula EsF3.
Einsteinium tetrafluoride is a binary inorganic chemical compound of einsteinium and fluorine with the chemical formula EsF4. The compound was observed by thermochromatography.

Einsteinium hexafluoride is a binary inorganic chemical compound of einsteinium and fluorine with the chemical formula EsF6. This is a hypothetical compound—its existence has been predicted theoretically, but the compound has yet to be isolated.
Einsteinium(II) chloride is a binary inorganic chemical compound of einsteinium and chlorine with the chemical formula EsCl2.
Einsteinium oxychloride is an inorganic chemical compound of einsteinium, oxygen, and chlorine with the chemical formula EsClO.
Einsteinium(II) bromide is a binary inorganic chemical compound of einsteinium and bromine with the chemical formula EsBr2.
Protactinium tetraiodide is a binary inorganic compound of protactinium metal and iodine with the chemical formula PaI4.
References
- ↑ "WebElements Periodic Table » Einsteinium » einsteinium diiodide". webelements.com. Archived from the original on 25 January 2024. Retrieved 25 January 2024.
- ↑ Young, J. P.; Haire, R. G.; Peterson, J. R.; Ensor, D. D.; Fellow, R. L. (November 1981). "Chemical consequences of radioactive decay. 2. Spectrophotometric study of the ingrowth of berkelium-249 and californium-249 into halides of einsteinium-253". Inorganic Chemistry . 20 (11): 3979–3983. doi:10.1021/ic50225a076. Archived from the original on 25 January 2024. Retrieved 25 January 2024.
- 1 2 Macintyre, Jane E. (23 July 1992). Dictionary of Inorganic Compounds. CRC Press. p. 3121. ISBN 978-0-412-30120-9. Archived from the original on 28 May 2024. Retrieved 25 January 2024.
- ↑ Edelstein, Norman M. (11 September 2013). Actinides in Perspective: Proceedings of the Actinides—1981 Conference, Pacific Grove, California, USA, 10-15 September 1981. Elsevier. p. 322. ISBN 978-1-4831-9051-8. Archived from the original on 28 May 2024. Retrieved 26 January 2024.