
Severe acute respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus is a species of virus consisting of many known strains phylogenetically related to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 1 (SARS-CoV-1) that have been shown to possess the capability to infect humans, bats, and certain other mammals. These enveloped, positive-sense single-stranded RNA viruses enter host cells by binding to the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor. The SARSr-CoV species is a member of the genus Betacoronavirus and of the subgenus Sarbecovirus.
An epitope, also known as antigenic determinant, is the part of an antigen that is recognized by the immune system, specifically by antibodies, B cells, or T cells. The part of an antibody that binds to the epitope is called a paratope. Although epitopes are usually non-self proteins, sequences derived from the host that can be recognized are also epitopes.

Rubella virus (RuV) is the pathogenic agent of the disease rubella, transmitted only between humans via the respiratory route, and is the main cause of congenital rubella syndrome when infection occurs during the first weeks of pregnancy.
Metaviridae is a family of viruses which exist as Ty3-gypsy LTR retrotransposons in a eukaryotic host's genome. They are closely related to retroviruses: members of the family Metaviridae share many genomic elements with retroviruses, including length, organization, and genes themselves. This includes genes that encode reverse transcriptase, integrase, and capsid proteins. The reverse transcriptase and integrase proteins are needed for the retrotransposon activity of the virus. In some cases, virus-like particles can be formed from capsid proteins.
Virus-like particles (VLPs) are molecules that closely resemble viruses, but are non-infectious because they contain no viral genetic material. They can be naturally occurring or synthesized through the individual expression of viral structural proteins, which can then self assemble into the virus-like structure. Combinations of structural capsid proteins from different viruses can be used to create recombinant VLPs. Both in-vivo assembly and in-vitro assembly have been successfully shown to form virus-like particles. VLPs derived from the Hepatitis B virus (HBV) and composed of the small HBV derived surface antigen (HBsAg) were described in 1968 from patient sera. VLPs have been produced from components of a wide variety of virus families including Parvoviridae, Retroviridae, Flaviviridae, Paramyxoviridae and bacteriophages. VLPs can be produced in multiple cell culture systems including bacteria, mammalian cell lines, insect cell lines, yeast and plant cells.
Alphavirus is a genus of RNA viruses, the sole genus in the Togaviridae family. Alphaviruses belong to group IV of the Baltimore classification of viruses, with a positive-sense, single-stranded RNA genome. There are 32 alphaviruses, which infect various vertebrates such as humans, rodents, fish, birds, and larger mammals such as horses, as well as invertebrates. Alphaviruses that could infect both vertebrates and arthropods are referred dual-host alphaviruses, while insect-specific alphaviruses such as Eilat virus and Yada yada virus are restricted to their competent arthropod vector. Transmission between species and individuals occurs mainly via mosquitoes, making the alphaviruses a member of the collection of arboviruses – or arthropod-borne viruses. Alphavirus particles are enveloped, have a 70 nm diameter, tend to be spherical, and have a 40 nm isometric nucleocapsid.
Baltimore classification is a system used to classify viruses based on their manner of messenger RNA (mRNA) synthesis. By organizing viruses based on their manner of mRNA production, it is possible to study viruses that behave similarly as a distinct group. Seven Baltimore groups are described that take into consideration whether the viral genome is made of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) or ribonucleic acid (RNA), whether the genome is single- or double-stranded, and whether the sense of a single-stranded RNA genome is positive or negative.
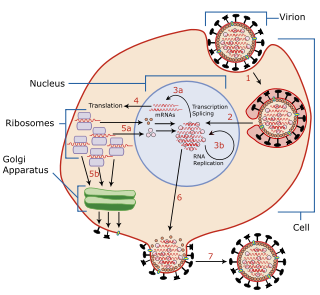
Viral entry is the earliest stage of infection in the viral life cycle, as the virus comes into contact with the host cell and introduces viral material into the cell. The major steps involved in viral entry are shown below. Despite the variation among viruses, there are several shared generalities concerning viral entry.
Cowpea chlorotic mottle virus, known by the abbreviation CCMV, is a virus that specifically infects the cowpea plant, or black-eyed pea. The leaves of infected plants develop yellow spots, hence the name "chlorotic". Similar to its "brother" virus, Cowpea mosaic virus (CPMV), CCMV is produced in high yield in plants. In the natural host, viral particles can be produced at 1–2 mg per gram of infected leaf tissue. Belonging to the bromovirus genus, cowpea chlorotic mottle virus (CCMV) is a small spherical plant virus. Other members of this genus include the brome mosaic virus (BMV) and the broad bean mottle virus (BBMV).
Rubivirus is a genus of viruses. It contains three species.

Double-stranded RNA viruses are a polyphyletic group of viruses that have double-stranded genomes made of ribonucleic acid. The double-stranded genome is used as a template by the viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) to transcribe a positive-strand RNA functioning as messenger RNA (mRNA) for the host cell's ribosomes, which translate it into viral proteins. The positive-strand RNA can also be replicated by the RdRp to create a new double-stranded viral genome.

Tupanvirus is a genus of viruses first described in 2018. The genus is composed of two species of virus that are in the giant virus group. Researchers discovered the first isolate in 2012 from deep water sediment samples taken at 3000m depth off the coast of Brazil. The second isolate was collected from a soda lake in Southern Nhecolândia, Brazil in 2014. They are named after Tupã (Tupan), a Guaraní thunder god, and the places they were found. These are the first viruses reported to possess genes for amino-acyl tRNA synthetases for all 20 standard amino acids.
Yokose virus (YOKV) is in the genus Flavivirus of the family Flaviviridae. Flaviviridae are often found in arthropods, such as mosquitoes and ticks, and may also infect humans. The genus Flavivirus includes over 50 known viruses, including Yellow Fever, West Nile Virus, Zika Virus, and Japanese Encephalitis. Yokose virus is a new member of the Flavivirus family that has only been identified in a few bat species. Bats have been associated with several emerging zoonotic diseases such as Ebola and SARS.

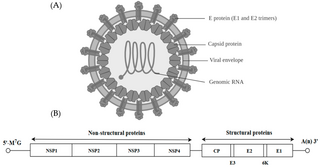
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2) is a strain of coronavirus that causes COVID-19, the respiratory illness responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic. The virus previously had a provisional name, 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV), and has also been called the human coronavirus 2019. First identified in the city of Wuhan, Hubei, China, the World Health Organization declared the outbreak a public health emergency of international concern from January 30, 2020, to May 5, 2023. SARS‑CoV‑2 is a positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus that is contagious in humans.

Duplodnaviria is a realm of viruses that includes all double-stranded DNA viruses that encode the HK97 fold major capsid protein. The HK97 fold major capsid protein is the primary component of the viral capsid, which stores the viral deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Viruses in the realm also share a number of other characteristics, such as an icosahedral capsid, an opening in the viral capsid called a portal, a protease enzyme that empties the inside of the capsid prior to DNA packaging, and a terminase enzyme that packages viral DNA into the capsid.

Varidnaviria is a realm of viruses that includes all DNA viruses that encode major capsid proteins that contain a vertical jelly roll fold. The major capsid proteins (MCP) form into pseudohexameric subunits of the viral capsid, which stores the viral deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), and are perpendicular, or vertical, to the surface of the capsid. Apart from this, viruses in the realm also share many other characteristics, such as minor capsid proteins (mCP) with the vertical jelly roll fold, an ATPase that packages viral DNA into the capsid, and a DNA polymerase that replicates the viral genome.
Bat coronavirus RaTG13 is a SARS-like betacoronavirus identified in the droppings of the horseshoe bat Rhinolophus affinis. It was discovered in 2013 in bat droppings from a mining cave near the town of Tongguan in Mojiang county in Yunnan, China. In February 2020, it was identified as the closest known relative of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, sharing 96.1% nucleotide identity. However, in 2022, scientists found three closer matches in bats found 530 km south, in Feuang, Laos, designated as BANAL-52, BANAL-103 and BANAL-236.
Rustrela virus, scientific name Rubivirus strelense, is a species of virus in the genus Rubivirus.
Rc-o319 is a bat-derived strain of severe acute respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus collected in Little Japanese horseshoe bats from sites in Iwate, Japan. Its has 81% similarity to SARS-CoV-2 and is the earliest strain branch of the SARS-CoV-2 related coronavirus.
In the management of HIV/AIDS, HIV capsid inhibitors are antiretroviral medicines that target the capsid shell of the virus. Most current antiretroviral drugs used to treat HIV do not directly target the viral capsid. These have also been termed "Capsid-targeting Antivirals", "Capsid Effectors", and "Capsid Assembly Modulators (CAMs)". Because of this, drugs that specifically inhibit the HIV capsid are being developed in order to reduce the replication of HIV, and treat infections that have become resistant to current antiretroviral therapies.









