
Jacob Ludwig Karl Grimm, also known as Ludwig Karl, was a German author, linguist, philologist, jurist, and folklorist. He formulated Grimm's law of linguistics, and was the co-author of the Deutsches Wörterbuch, the author of Deutsche Mythologie, and the editor of Grimms' Fairy Tales. He was the older brother of Wilhelm Grimm; together, they were the literary duo known as the Brothers Grimm.
Philology is the study of language in oral and written historical sources; it is the intersection of textual criticism, literary criticism, history, and linguistics with strong ties to etymology. Philology is also defined as the study of literary texts and oral and written records, the establishment of their authenticity and their original form, and the determination of their meaning. A person who pursues this kind of study is known as a philologist. In older usage, especially British, philology is more general, covering comparative and historical linguistics.
Verner's law describes a historical sound change in the Proto-Germanic language whereby consonants that would usually have been the voiceless fricatives *f, *þ, *s, *h, *hʷ, following an unstressed syllable, became the voiced fricatives *β, *ð, *z, *ɣ, *ɣʷ. The law was formulated by Karl Verner, and first published in 1877.

Ēostre is a West Germanic spring goddess. The name is reflected in Old English: *Ēastre, Old High German: *Ôstara, and Old Saxon: *Āsteron. By way of the Germanic month bearing her name, she is the namesake of the festival of Easter in some languages. The Old English deity Ēostre is attested solely by Bede in his 8th-century work The Reckoning of Time, where Bede states that during Ēosturmōnaþ, pagan Anglo-Saxons had held feasts in Ēostre's honour, but that this tradition had died out by his time, replaced by the Christian Paschal month, a celebration of the resurrection of Jesus.
Etymology is the scientific study of the origin and evolution of a word's semantic meaning across time, including its constituent morphemes and phonemes. It is a subfield of historical linguistics, philology, and semiotics, and draws upon comparative semantics, morphology, pragmatics, and phonetics in order to construct a comprehensive and chronological catalogue of all meanings that a morpheme, phoneme, word, or sign has carried across time.

Karl Viktor Müllenhoff was a German philologist who specialized in Germanic studies.
German studies is the field of humanities that researches, documents and disseminates German language and literature in both its historic and present forms. Academic departments of German studies often include classes on German culture, German history, and German politics in addition to the language and literature component. Common German names for the field are Germanistik, Deutsche Philologie, and Deutsche Sprachwissenschaft und Literaturwissenschaft. In English, the terms Germanistics or Germanics are sometimes used, but the subject is more often referred to as German studies, German language and literature, or German philology.

Jacob WackernagelGerman:[ˈvakərˌnaːɡəl] was a Swiss linguist, Indo-Europeanist and scholar of Sanskrit. He was born in Basel, son of the philologist Wilhelm Wackernagel (1806–1869).

Winfred Philip Lehmann was an American linguist who specialized in historical, Germanic, and Indo-European linguistics. He was for many years a professor and head of departments for linguistics at the University of Texas at Austin, and served as president of both the Linguistic Society of America and the Modern Language Association. Lehmann was also a pioneer in machine translation. He lectured a large number of future scholars at Austin, and was the author of several influential works on linguistics.

Eduard Sievers was a German philologist of the classical and Germanic languages. Sievers was one of the Junggrammatiker of the so-called "Leipzig School". He was one of the most influential historical linguists of the late nineteenth century. He is known for his recovery of the poetic traditions of Germanic languages such as Anglo-Saxon and Old Saxon, as well as for his discovery of Sievers' law.
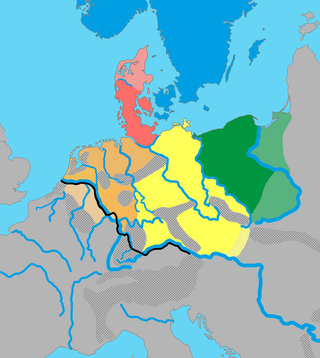
Elbe Germanic, also called Irminonic or Erminonic, is a term introduced by the German linguist Friedrich Maurer (1898–1984) in his book, Nordgermanen und Alemanen, to describe the unattested proto-language, or dialectal grouping, ancestral to the later Lombardic, Alemannic, Bavarian and Thuringian dialects. During late antiquity and the Middle Ages, its supposed descendants had a profound influence on the neighboring West Central German dialects and, later, in the form of Standard German, on the German language as a whole.

Rudolf Simek is an Austrian philologist and religious studies scholar who is Professor and Chair of Ancient German and Nordic Studies at the University of Bonn. Simek specializes in Germanic studies, and is the author of several notable works on Germanic religion and mythology, Germanic peoples, Vikings, Old Norse literature, and the culture of Medieval Europe.
Erika Timm is a German linguist, the author of works that have made fundamental contributions to Yiddish historical linguistics and philology.

Gustav Neckel was a German philologist who specialized in Germanic studies.

Germanic heroic legend is the heroic literary tradition of the Germanic-speaking peoples, most of which originates or is set in the Migration Period. Stories from this time period, to which others were added later, were transmitted orally, traveled widely among the Germanic speaking peoples, and were known in many variants. These legends typically reworked historical events or personages in the manner of oral poetry, forming a heroic age. Heroes in these legends often display a heroic ethos emphasizing honor, glory, and loyalty above other concerns. Like Germanic mythology, heroic legend is a genre of Germanic folklore.

Friedrich Maurer was a German philologist who specialized in Germanic studies.

Helmut Birkhan is an Austrian philologist who is Professor Emeritus of Ancient German Language and Literature and the former Managing Director of the Institute for Germanic Studies at the University of Vienna.

Hugo Gering was a German philologist who specialized in Germanic studies.

Johannes Alphonsus Huisman, also known as J. A. Huisman, was a Dutch philologist who specialized in Germanic studies.













