
The long-tailed planigale, also known as Ingram's planigale or the northern planigale, is the smallest of all marsupials, and one of the smallest of all mammals. It is rarely seen but is a quite common inhabitant of the blacksoil plains, clay-soiled woodlands, and seasonally flooded grasslands of Australia's Top End.

The Kimberley is the northernmost of the nine regions of Western Australia. It is bordered on the west by the Indian Ocean, on the north by the Timor Sea, on the south by the Great Sandy and Tanami deserts in the region of the Pilbara, and on the east by the Northern Territory.

The Victoria Highway links the Great Northern Highway in Western Australia with the Stuart Highway in the Northern Territory. The highway is a part of the Perth - Darwin National Highway link. It is signed as National Highway 1, and is part of Highway 1, a circular route around the country. It is 555 kilometres (345 mi) long, and most of the route – some 470 kilometres (290 mi) – lies within the Northern Territory. In some areas it runs in parallel with the Northern Territory's Victoria River, from which its name originates.

Lake Argyle is Western Australia's largest and Australia's second largest freshwater man-made reservoir by volume. The reservoir is part of the Ord River Irrigation Scheme and is located near the East Kimberley town of Kununurra. The lake flooded large parts of the Shire of Wyndham-East Kimberley on the Kimberley Plateau about 80 kilometres (50 mi) inland from the Joseph Bonaparte Gulf, close to the border with the Northern Territory.

The Ord River is a 651-kilometre long (405 mi) river in the Kimberley region of Western Australia. The river's catchment covers 55,100 square kilometres (21,274 sq mi).

The unofficial geographic term Northern Australia includes those parts of Queensland and Western Australia north of latitude 26° and all of the Northern Territory. Those local government areas of Western Australia and Queensland that lie partially in the north are included.
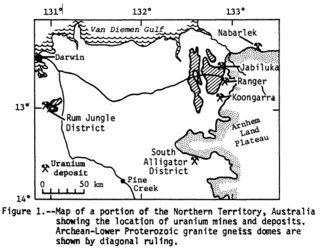
Alligator Rivers is the name of an area in an Arnhem Land region of the Northern Territory of Australia, containing three rivers, the East, West, and South Alligator Rivers. It is regarded as one of the richest biological regions in Australia, with part of the region in the Kakadu National Park. It is an Important Bird Area (IBA), lying to the east of the Adelaide and Mary River Floodplains IBA. It also contains mineral deposits, especially uranium, and the Ranger Uranium Mine is located there. The area is also rich in Australian Aboriginal art, with 1500 sites. The Kakadu National Park is one of the few World Heritage sites on the list because of both its natural and human heritage values. They were explored by Lieutenant Phillip Parker King in 1820, who named them in the mistaken belief that the crocodiles in the estuaries were alligators.

The Georgina River is the north-westernmost of the three major rivers of the Channel Country in Central West Queensland, that also flows through a portion of the Northern Territory, in central Australia. Part of the Lake Eyre basin, the Georgina flows in extremely wet years into Lake Eyre.
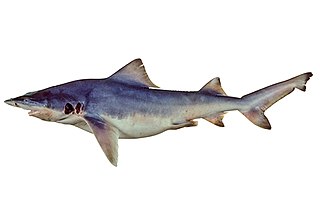
The northern river shark or New Guinea river shark is a species of requiem shark, in the family Carcharhinidae, found in scattered tidal rivers and associated coastal waters in northern Australia and in Papua New Guinea. This species inhabits areas with poor visibility, soft bottoms, and large tides, with immature sharks ranging into fresh and brackish water. It is similar to other river sharks in having a stocky grey body with a high back, tiny eyes, and broad fins. It measures up to 2.5 m (8.2 ft) long.
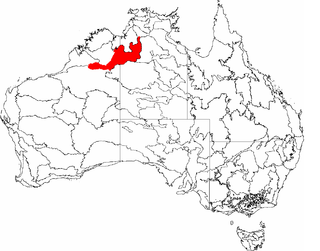
The Ord Victoria Plain, an interim Australian bioregion, is located in the Northern Territory and Western Australia, comprising 12,540,703 hectares.

The purple-crowned fairywren is a species of bird in the Australasian wren family, Maluridae. It is the largest of the eleven species in the genus Malurus and is endemic to northern Australia. The species name is derived from the Latin word cǒrōna meaning "crown", owing to the distinctive purple circle of crown feathers sported by breeding males. Genetic evidence shows that the purple-crowned fairywren is most closely related to the superb fairywren and splendid fairywren. Purple-crowned fairywrens can be distinguished from other fairywrens in northern Australia by the presence of cheek patches and the deep blue colour of their perky tails.

Cambridge Gulf is a gulf on the north coast of the Kimberley region of Western Australia. Many rivers flow into the gulf, including the Ord River, Pentecost River, Durack River, King River and the Forrest River, making the environment an estuarine one.
The Yalgar River is a 185-kilometre-long tributary of the Murchison River, located in the Shire of Meekatharra in central Western Australia. It rises in the Glengarry Range 25 km southeast of Mooloogool Station homestead, about 80 kilometres northeast of Meekatharra, flowing 145 kilometres westward to a junction with the Hope River. From there it flows north-northwesterly for about 40 kilometres, emptying into the upper reaches of the Murchison River, near Moorarie Station homestead on the Carnarvon-Meekatharra Road.

The buff-sided robin is a small, diurnal, insectivorous, perching (passerine) bird in the family Petroicidae, a group commonly known as the Australo-Papuan or Australasian robins. It is also known as the buff-sided fly-robin, buff-sided shrike-robin and Isabellflankenschnäpper (German). The buff-sided robin is endemic to northern Australia, where it primarily occurs in riparian forests and monsoon vine thickets from the Kimberly region of Western Australia to the north-west Queensland Gulf of Carpentaria. The plumage of the adult birds is characterised by a dark hood and back with a prominent white stripe on the supercilium; a white throat, white wing and tail bars, and a striking buff to orange patch on the flank below the wings. Adult birds are not sexually dimorphic; however, males are generally larger and can be separated from females based on morphological measurements. Buff-sided robins predominantly take insects from the ground by sallying from an observational perch. Insect prey are also occasionally taken by hawking on the wing or by gleaning from the trunk or foliage of riparian vegetation.

The Victoria Plains tropical savanna is a tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands ecoregion in northwestern Australia.
The Behn River or Behm River is a river in the Kimberley region of Western Australia.

The Keep River is a river located in the Victoria Bonaparte bioregion of Western Australia and the Northern Territory in Australia.
The Nicholson River is a river located in the Northern Territory and the state of Queensland, Australia.
The Malngin are an Aboriginal Australian people of the Kimberley region of Western Australia. The Malngin language was a dialect of Gurindj.















