| |||
| Identifiers | |||
|---|---|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| Br3Np | |||
| Molar mass | 477 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | green solid [1] | ||
| Density | 6.62 g·cm−3 [2] | ||
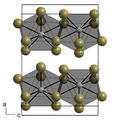
| Structure | |||
| α-NpBr3: hexagonal β-NpBr3: orthorhombic | |||
| α-NpBr3: P63/m (No. 176) β-NpBr3: Ccmm (No. 63) | |||
a = 791.7 pm (α), 411 pm (β), b = 791.7 pm (α), 1265 pm (β), c = 438.2 pm (α), 915 pm (β) | |||
| Related compounds | |||
Other anions | neptunium(III) fluoride neptunium(III) chloride neptunium(III) iodide | ||
Other cations | uranium(III) bromide plutonium(III) bromide | ||
Related compounds | neptunium(IV) bromide | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
Neptunium(III) bromide is a bromide of neptunium, with the chemical formula of NpBr3.