This article needs additional citations for verification .(January 2019) |
Delaware House of Representatives | |
|---|---|
| Delaware General Assembly | |
 | |
| Type | |
| Type | |
Term limits | None |
| History | |
New session started | January 10, 2023 |
| Leadership | |
Speaker | |
Majority Leader | |
Minority Leader | |
| Structure | |
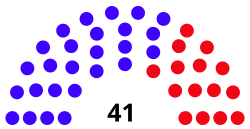
| Seats | 41 |
Political groups | Majority
Minority
|
Length of term | 2 years |
| Authority | Article III, Section 1, Delaware Constitution |
| Salary | $48,237/year [1] |
| Elections | |
Last election | November 5, 2024 (41 seats) |
Next election | November 3, 2026 (41 seats) |
| Redistricting | Legislative Control |
| Meeting place | |
 | |
| House of Representatives Chamber Delaware Legislative Hall Dover, Delaware | |
| Website | |
| Delaware House of Representatives | |
The Delaware State House of Representatives is the lower house of the Delaware General Assembly, the state legislature of the U.S. state of Delaware. It is composed of 41 Representatives from an equal number of constituencies, each of whom is elected to a two-year term. Its members are not subject to term limits, and their terms start the day after the election. [2] The House meets at the Delaware Legislative Hall in Dover.