
Fayette County is a county located in the U.S. state of Alabama. As of the 2020 census, the population was 16,321. Its county seat is Fayette. Its name is in honor of the Marquis de Lafayette, who aided General George Washington in the American Revolutionary War.

Seminole County is a county located in the U.S. state of Oklahoma. As of the 2020 census, the population was 23,556. Its county seat is Wewoka. Most of the county was a reservation for the Seminole Nation of Oklahoma which still retains jurisdiction over some land in the county. A small portion of land at the eastern end of the county belonged to the Muscogee (Creek) Nation.

Choctaw County is a county located in the U.S. state of Oklahoma. As of the 2020 census, the population was 14,204. Its county seat is Hugo.

Lee County is a county located in the U.S. state of Kentucky. As of the 2020 census, the population was 7,395. Its county seat is Beattyville. The county was formed in 1870 from parts of Breathitt, Estill, Owsley and Wolfe counties. The county was named for Robert E. Lee. The area of Kentucky where Lee County is located was a pro-union region of Kentucky but the legislature that created the county was controlled by former Confederates. The town of Proctor, named for the Rev. Joseph Proctor, was the first county seat. The first court was held on April 25, 1870, in the old Howerton House. The local economy at the time included coal mining, salt gathering, timber operations, and various commercial operations. It had a U.S. post office from 1843 until 1918.

Summit County is a county located in the U.S. state of Colorado. As of the 2020 census, the population was 31,055. The county seat and largest town is Breckenridge.

Preventive healthcare, or prophylaxis, is the application of healthcare measures to prevent diseases. Disease and disability are affected by environmental factors, genetic predisposition, disease agents, and lifestyle choices, and are dynamic processes that begin before individuals realize they are affected. Disease prevention relies on anticipatory actions that can be categorized as primal, primary, secondary, and tertiary prevention.
Healthy People is a program of a nationwide health-promotion and disease-prevention goals set by the United States Department of Health and Human Services. The goals were first set in 1979 "in response to an emerging consensus among scientists and health authorities that national health priorities should emphasize disease prevention". The Healthy People program was originally issued by the Department of Health, Education and Welfare. This first issue contained "a report announcing goals for a ten-year plan to reduce controllable health risks. In its section on nutrition, the report recommended diets with fewer calories; less saturated fat, cholesterol, salt, and sugar; relatively more complex carbohydrates, fish and poultry; and less red meat." Though this recommended diet consisted of more processed foods rather than fresh produce, the report advised for consumers to "be wary of processed foods". The goals were subsequently updated for Healthy People 2000, Healthy People 2010, Healthy People 2020 and Healthy People 2030.
Australia is a high income country, and this is reflected in the good status of health of the population overall. In 2011, Australia ranked 2nd on the United Nations Development Programme's Human Development Index, indicating the level of development of a country. Despite the overall good status of health, the disparities occurring in the Australian healthcare system are a problem. The poor and those living in remote areas as well as indigenous people are, in general, less healthy than others in the population, and programs have been implemented to decrease this gap. These include increased outreach to the indigenous communities and government subsidies to provide services for people in remote or rural areas.
Chronic, non-communicable diseases account for an estimated 80% of total deaths and 70% of disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) lost in China. Cardiovascular diseases, chronic respiratory disease, and cancer are the leading causes of both death and of the burden of disease, and exposure to risk factors is high: more than 300 million men smoke cigarettes and 160 million adults are hypertensive, most of whom are not being treated. An obesity epidemic is imminent, with more than 20% of children aged 7–17 years in big cities now overweight or obese. Rates of death from chronic disease in middle-aged people are higher in China than in some high-income countries.

The healthcare system in Turkey has improved in terms of health status especially after implementing the Health Transformation Program (HP) in 2003. "Health for All" was the slogan for this transformation, and HP aimed to provide and finance health care efficiently, effectively, and equitably. By covering most of the population, the General Health Insurance Scheme is financed by employers, employees, and government contributions through the Social Security Institution. Even though HP aimed to be equitable, after 18 years of implementation, there are still disparities between the regions in Turkey. These discrepancies can be seen in terms of infant mortality between rural and urban areas and different parts of the country, although these have been declining over the years. While the under-5 mortality rate in Western Marmara is 7.9, the under-5 mortality rate in Southeastern Asia is two times higher than Western Marmara, with the rate of 16.3 in 2021.
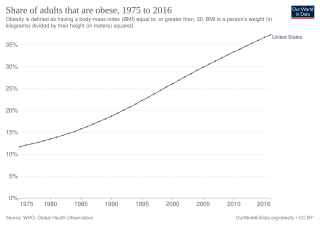
Obesity is common in the United States and is a major health issue associated with numerous diseases, specifically an increased risk of certain types of cancer, coronary artery disease, type 2 diabetes, stroke, and cardiovascular disease, as well as significant increases in early mortality and economic costs.
Health in Egypt refers to the overall health of the population of Egypt.

America's Health Rankings started in 1990 and is the longest-running annual assessment of the nation's health on a state-by-state basis. It is founded on the World Health Organization holistic definition of health, which says health is a state of complete physical, mental, and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity. America's Health Rankings is a partnership of the United Health Foundation, and the American Public Health Association.

The Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) is a public health research institute of the University of Washington in Seattle. Its research fields are global health statistics and impact evaluation.
Health in Malta has seen improvements in recent years, with one of the highest life expectancies in Europe. Malta has a good overall quality of health and has seen rapid growth and improvement in key health indicators. Malta has seen significant development in the practice of mental health which has been supported by new infrastructure and increased government health spending. The introduction of health-focused government initiatives, particularly around nutrition, alcohol, smoking, and health will likely contribute to the further improvement of overall health nationwide.
Montenegro is a country with an area of 13,812 square kilometres and a population of 620,029, according to the 2011 census. The country is bordered by Croatia, the Adriatic Sea, Bosnia, Herzegovina, Serbia, Kosovo and Albania. The most common health issues faced are non-communicable diseases accounting for 95% of all deaths. This is followed by 4% of mortality due to injury, and 1% due to communicable, maternal, perinatal and nutritional conditions. Other health areas of interest are alcohol consumption, which is the most prevalent disease of addiction within Montenegro and smoking. Montenegro has one of the highest tobacco usage rates across Europe. Life expectancy for men is 74 years, and life expectancy for women is 79.









