Anion exchange transporter is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC26A7 gene. [5] [6] [7] [8]
Anion exchange transporter is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC26A7 gene. [5] [6] [7] [8]
This gene is one member of a family of sulfate/anion transporter genes. Family members are well conserved in their genomic (number and size of exons) and protein (aa length among species) structures yet have markedly different tissue expression patterns. This gene has abundant and specific expression in the kidney. Splice variants that use both alternate transcription initiation and polyadenylation sites have been described for this gene. [8]

Prestin is a protein that is critical to sensitive hearing in mammals. It is encoded by the SLC26A5 gene.
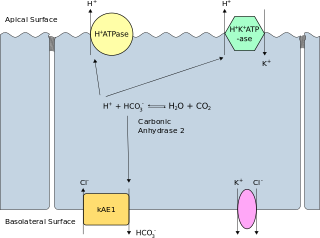
Band 3 anion transport protein, also known as anion exchanger 1 (AE1) or band 3 or solute carrier family 4 member 1 (SLC4A1), is a protein that is encoded by the SLC4A1 gene in humans.
Pendrin is an anion exchange protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC26A4 gene . Pendrin was initially identified as a sodium-independent chloride-iodide exchanger with subsequent studies showing that it also accepts formate and bicarbonate as substrates. Pendrin is similar to the Band 3 transport protein found in red blood cells. Pendrin is the protein which is mutated in Pendred syndrome, which is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by sensorineural hearing loss, goiter and a partial organification problem detectable by a positive perchlorate test.

The sulfate transporter is a solute carrier family protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC26A2 gene. SLC26A2 is also called the diastrophic dysplasia sulfate transporter (DTDST), and was first described by Hästbacka et al. in 1994. A defect in sulfate activation described by Superti-Furga in achondrogenesis type 1B was subsequently also found to be caused by genetic variants in the sulfate transporter gene. This sulfate (SO42−) transporter also accepts chloride, hydroxyl ions (OH−), and oxalate as substrates. SLC26A2 is expressed at high levels in developing and mature cartilage, as well as being expressed in lung, placenta, colon, kidney, pancreas and testis.

GLUT5 is a fructose transporter expressed on the apical border of enterocytes in the small intestine. GLUT5 allows for fructose to be transported from the intestinal lumen into the enterocyte by facilitated diffusion due to fructose's high concentration in the intestinal lumen. GLUT5 is also expressed in skeletal muscle, testis, kidney, fat tissue (adipocytes), and brain.
A urea transporter is a membrane transport protein, transporting urea. Humans and other mammals have two types of urea transport proteins, UT-A and UT-B. The UT-A proteins are important for renal urea handling and are produced by alternative splicing of the SLC14A2 gene. Urea transport in the kidney is regulated by vasopressin.

Electrogenic sodium bicarbonate cotransporter 1, sodium bicarbonate cotransporter is a membrane transport protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC4A4 gene.

Anion exchange protein 2 (AE2) is a membrane transport protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC4A2 gene. AE2 is functionally similar to the Band 3 Cl−/HCO3− exchange protein.

Chloride anion exchanger, also known as down-regulated in adenoma, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC26A3 gene.

Anion exchange protein 3 is a membrane transport protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC4A3 gene. AE3 is functionally similar to the Band 3 Cl−/HCO3− exchange protein but it is expressed primarily in brain neurons and in the heart. Like AE2 its activity is sensitive to pH. AE3 mutations have been linked to seizures.

Solute carrier family 26 member 6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC26A6 gene. It is an anion-exchanger expressed in the apical membrane of the kidney proximal tubule, the apical membranes of the duct cells in the pancreas, and the villi of the duodenum.

Solute carrier family 22 member 8, or organic anion transporter 3 (OAT3), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC22A8 gene.
Electroneutral sodium bicarbonate exchanger 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC4A8 gene.

Solute carrier family 22 member 7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the gene SLC22A7.

Solute carrier family 22 member 9 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC22A9 gene.

Electrogenic sodium bicarbonate cotransporter 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC4A5 gene.

Testis anion transporter 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC26A8 gene.

The organic anion transporter 1 (OAT1) also known as solute carrier family 22 member 6 (SLC22A6) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC22A6 gene. It is a member of the organic anion transporter (OAT) family of proteins. OAT1 is a transmembrane protein that is expressed in the brain, the placenta, the eyes, smooth muscles, and the basolateral membrane of proximal tubular cells of the kidneys. It plays a central role in renal organic anion transport. Along with OAT3, OAT1 mediates the uptake of a wide range of relatively small and hydrophilic organic anions from plasma into the cytoplasm of the proximal tubular cells of the kidneys. From there, these substrates are transported into the lumen of the nephrons of the kidneys for excretion. OAT1 homologs have been identified in rats, mice, rabbits, pigs, flounders, and nematodes.
The anion exchanger family is a member of the large APC superfamily of secondary carriers. Members of the AE family are generally responsible for the transport of anions across cellular barriers, although their functions may vary. All of them exchange bicarbonate. Characterized protein members of the AE family are found in plants, animals, insects and yeast. Uncharacterized AE homologues may be present in bacteria. Animal AE proteins consist of homodimeric complexes of integral membrane proteins that vary in size from about 900 amino acyl residues to about 1250 residues. Their N-terminal hydrophilic domains may interact with cytoskeletal proteins and therefore play a cell structural role. Some of the currently characterized members of the AE family can be found in the Transporter Classification Database.
The sulfate permease (SulP) family is a member of the large APC superfamily of secondary carriers. The SulP family is a large and ubiquitous family of proteins derived from archaea, bacteria, fungi, plants and animals. Many organisms including Bacillus subtilis, Synechocystis sp, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Arabidopsis thaliana and Caenorhabditis elegans possess multiple SulP family paralogues. Many of these proteins are functionally characterized, and most are inorganic anion uptake transporters or anion:anion exchange transporters. Some transport their substrate(s) with high affinities, while others transport it or them with relatively low affinities. Others may catalyze SO2−
4:HCO−
3 exchange, or more generally, anion:anion antiport. For example, the mouse homologue, SLC26A6, can transport sulfate, formate, oxalate, chloride and bicarbonate, exchanging any one of these anions for another. A cyanobacterial homologue can transport nitrate. Some members can function as channels. SLC26A3 and SLC26A6 can function as carriers or channels, depending on the transported anion. In these porters, mutating a glutamate, also involved in transport in the CIC family, created a channel out of the carrier. It also changed the stoichiometry from 2Cl−/HCO−
3 to 1Cl−/HCO−
3.
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.