A peccary is a pig-like ungulate of the family Tayassuidae. They are found throughout Central and South America, Trinidad in the Caribbean, and in the southwestern area of North America. They usually measure between 90 and 130 cm in length, and a full-grown adult usually weighs about 20 to 40 kg. They represent the closest relatives of the family Suidae, which contains pigs and relatives. Together Tayassuidae and Suidae are grouped in the suborder Suina within the order Artiodactyla.
The year 1975 in science and technology involved some significant events, listed below.

Suina is a suborder of omnivorous, non-ruminant artiodactyl mammals that includes the domestic pig and peccaries. A member of this clade is known as a suine. Suina includes the family Suidae, termed suids, known in English as pigs or swine, as well as the family Tayassuidae, termed tayassuids or peccaries. Suines are largely native to Africa, South America, and Southeast Asia, with the exception of the wild boar, which is additionally native to Europe and Asia and introduced to North America and Australasia, including widespread use in farming of the domestic pig subspecies. Suines range in size from the 55 cm (22 in) long pygmy hog to the 210 cm (83 in) long giant forest hog, and are primarily found in forest, shrubland, and grassland biomes, though some can be found in deserts, wetlands, or coastal regions. Most species do not have population estimates, though approximately two billion domestic pigs are used in farming, while several species are considered endangered or critically endangered with populations as low as 100. One species, Heude's pig, is considered by the International Union for Conservation of Nature to have gone extinct in the 20th century.

The Gran Chaco or Dry Chaco is a sparsely populated, hot and semiarid lowland tropical dry broadleaf forest natural region of the Río de la Plata basin, divided among eastern Bolivia, western Paraguay, northern Argentina, and a portion of the Brazilian states of Mato Grosso and Mato Grosso do Sul, where it is connected with the Pantanal region. This land is sometimes called the Chaco Plain.

Entelodontidae is an extinct family of pig-like artiodactyls which inhabited the Northern Hemisphere from the late Eocene to the early Miocene epochs, about 38-19 million years ago. Their large heads, low snouts, narrow gait, and proposed omnivorous diet inspires comparisons to suids and tayassuids (peccaries), and historically they have been considered closely related to these families purely on a morphological basis. However, studies which combine morphological and molecular (genetic) data on artiodactyls instead suggest that entelodonts are cetancodontamorphs, more closely related to hippos and cetaceans through their resemblance to Pakicetus, than to basal pigs like Kubanochoerus and other ungulates.

The collared peccary is a species of artiodactyl (even-toed) mammal in the family Tayassuidae found in North, Central, and South America. It is the only member of the genus Dicotyles. They are commonly referred to as javelina, saíno, taitetu, or báquiro, although these terms are also used to describe other species in the family. The species is also known as the musk hog. In Trinidad, it is colloquially known as quenk.

The white-lipped peccary is a species of peccary found in Central and South America and the only member of the genus Tayassu. Multiple subspecies have been identified. White-lipped peccaries are similar in appearance to pigs, but covered in dark hair. The range of T. pecari, which extends from Mexico to Argentina, has become fragmented, and the species's population is declining overall. They can be found in a variety of habitats. Social animals, white-lipped peccaries typically forage in large groups, which can have as many as 300 peccaries.

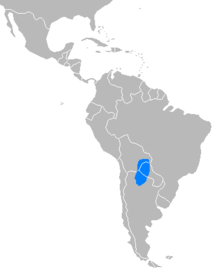
Catagonus is a genus of peccaries that contains the living Chacoan peccary, C. wagneri, and several extinct species. The genus has always been restricted to South America.

The Chacoan mara or Chacoan cavy is a relatively large South American rodent of the cavy family. They are a close relative of the better known Patagonian mara. The Chacoan mara is the sole member of the genus Pediolagus.

Archaeotherium is an extinct genus of entelodont artiodactyl endemic to North America during the Eocene and Oligocene epochs (35—28 mya), existing for approximately 9.1 million years. Archaeotherium fossils are most common in the White River Formation of the Great Plains, but it has also been found in the John Day Basin of Oregon and the Trans-Pecos area of Texas.

Platygonus is an extinct genus of herbivorous peccaries of the family Tayassuidae, endemic to North and South America from the Miocene through Pleistocene epochs, existing for about 10.289 million years. P. compressus stood 2.5 feet tall.
The Gran Chaco is a plain of about 1.000.000 km2. It covers parts of Bolivia, Paraguay, Brazil and Argentina.
Kaa-Iya del Gran Chaco National Park and Integrated Management Natural Area is the biggest national park in Bolivia and one of the largest in South America. It is a protected area in the region of the Gran Chaco and has a larger surface area than Belgium. It is situated in the south of Santa Cruz Department on the border with Paraguay in the Cordillera Province and Chiquitos Province.

The chacoan gracile opossum is a species of opossum in the family Didelphidae. It is native to Argentina, Brazil and Paraguay. Its habitat is seasonally flooded grasslands and forests in and near the Gran Chaco.

Platygonus compressus, the flat-headed peccary, is an extinct mammal species from the Tayassuidae family that lived in North and South America during the Pleistocene. It was first described in 1848 by John L. Leconte.
Brasiliochoerus stenocephalus is an extinct species of peccary that lived in South America during the Late Pleistocene. Fossils have been found in Brazil, Argentina and Bolivia. It is commonly known as the narrow-headed peccary due to its long and markedly convex rostrum.
Catagonus metropolitanus is an extinct species of peccary known from the Pleistocene of Argentina.
Catagonus carlesi, or Parachoerus carlesi, is an extinct species of peccary that lived in Argentina during the Late Pleistocene.