The Bovidae comprise the biological family of cloven-hoofed, ruminant mammals that includes cattle, yaks, bison, buffalo, antelopes, sheep and goats. A member of this family is called a bovid. With 143 extant species and 300 known extinct species, the family Bovidae consists of 11 major subfamilies and thirteen major tribes. The family evolved 20 million years ago, in the early Miocene.

An ibex is any of several species of wild goat , distinguished by the male's large recurved horns, which are transversely ridged in front. Ibex are found in Eurasia, North Africa and East Africa.

The markhor is a large wild Capra (goat) species native to South Asia and Central Asia, mainly within Pakistan, India, the Karakoram range, parts of Afghanistan, and the Himalayas. It is listed on the IUCN Red List as Near Threatened since 2015.

The kri-kri, sometimes called the Cretan goat, Agrimi, or Cretan Ibex, is a feral goat inhabiting the Eastern Mediterranean, previously considered a subspecies of wild goat. The kri-kri today is found only in Greece: specifically on Crete and on three small islands off its coast ; as well as on the island of Sapientza off the southwestern coast of Peloponnese, where it was brought in great numbers in order to protect the species from extinction.

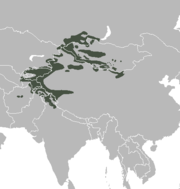
The wild goat is a wild goat species, inhabiting forests, shrublands and rocky areas ranging from Turkey and the Caucasus in the west to Turkmenistan, Afghanistan and Pakistan in the east. It has been listed as near threatened on the IUCN Red List and is threatened by destruction and degradation of habitat.

The Iberian ibex, also known as the Spanish ibex, Spanish wild goat and Iberian wild goat, is a species of ibex endemic to the Iberian Peninsula. Four subspecies have been described; two are now extinct. The Portuguese ibex became extinct in 1892, and the Pyrenean ibex became extinct in 2000. A project to clone the Pyrenean ibex resulted in one clone being born alive in July 2003, making it the first taxon to become "un-extinct", although the clone died several minutes after birth due to physical defects in its lungs.

The Nubian ibex is a desert-dwelling goat species found in mountainous areas of northern and northeast Africa, and the Middle East. It was historically considered to be a subspecies of the Alpine ibex, but is now considered a distinct species. The wild population is estimated at 4,500 mature individuals, and it is classified as vulnerable.

The Caucasus mixed forests is a temperate broadleaf and mixed forests ecoregion in the Caucasus Mountains, as well as the adjacent Lesser Caucasus range and the eastern end of the Pontic Mountains.
Afghanistan has long been known for diverse wildlife. Many of the larger mammals in the country are categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature as globally threatened. These include the snow leopard, Marco Polo sheep, Siberian musk deer, markhor, urial, and the Asiatic black bear. Other species of interest are the ibex, the gray wolf, and the brown bear, striped hyenas, and numerous bird of prey species. Most of the Marco Polo sheep and ibex are being poached for food, whereas wolves, snow leopards and bears are being killed for damage prevention.

Shahdag National Park — is a national park of Azerbaijan. It was established on an area of 115,900 hectares (1,159 km2) in the Quba Rayon, Qusar Rayon, İsmayıllı Rayon, Qəbələ Rayon, Oğuz Rayon and Şamaxı Rayon administrative districts on December 8, 2006. It was enlarged by presidential decree on July 8, 2010 from 115,900 hectares (1,159 km2) to 130,508.1 hectares (1,305.081 km2).

The bezoar ibex is a wild goat subspecies that is native to the montane forested areas in the Caucasus and the Zagros Mountains.
The Chiltan ibex or Chiltan goat is a wild goat endemic to Chiltan, Balochistan, Pakistan.
Sarcocystis is a genus of parasitic Apicomplexan alveolates. Species in this genus infect reptiles, birds and mammals. The name is derived from Greek: sarkos = flesh and kystis = bladder.

Bovidae in Chinese mythology include various myths and legends about a group of biologically distinct animals which form important motifs within Chinese mythology. There are many myths about the animals modernly classified as Bovidae, referring to oxen, sheep, goats, and mythological types such as "unicorns". Chinese mythology refers to those myths found in the historical geographic area of China, a geographic area which has evolved or changed somewhat through history. Thus this includes myths in Chinese and other languages, as transmitted by Han Chinese as well as other ethnic groups. There are various motifs of animals of the Bovidae biological family in Chinese mythology. These have often served as allusions in poetry and other literature. Some species are also used in the traditional Chinese calendar and time-keeping system.

Goat evolution is the process by which domestic goats came to exist through evolution by natural selection. Wild goats — medium-sized mammals which are found in noticeably harsh environments, particularly forests and mountains, in the Middle East and Central Asia — were one of the first species domesticated by modern humans, with the date of domestication generally considered to be 8,000 BC. Goats are part of the family Bovidae, a broad and populous group which includes a variety of ruminants such as bison, cows and sheep. Bovids all share many traits, such as hooves and a herbivorous diet and all males, along with many females, have horns. Bovids began to diverge from deer and giraffids during the early Miocene epoch. The subfamily Caprinae, which includes goats, ibex and sheep, are considered to have diverged from the rest of Bovidae as early as the late Miocene, with the group reaching its greatest diversity in the ice ages.