| Chinkara | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Chinkara in Thar Desert, Rajasthan | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Artiodactyla |
| Family: | Bovidae |
| Subfamily: | Antilopinae |
| Tribe: | Antilopini |
| Genus: | Gazella |
| Species: | G. bennettii [2] |
| Binomial name | |
| Gazella bennettii [2] (Sykes, 1831) | |
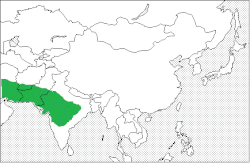 | |
| Distribution map of chinkara | |
The chinkara (Gazella bennettii), also known as the Indian gazelle, is a gazelle species native to India, Iran, Afghanistan and Pakistan. [1]




