Class members
Dihydropyridine class L-type calcium channel blockers include, in alphabetical order (brand names vary in different countries):
| Name | Image | Brand name | Citations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amlodipine |  | Norvasc, Istin, Normodipine, Tenox, Cordi Cor | [4] |
| Aranidipine |  | Sapresta (サプレスタ) | [5] |
| Azelnidipine | 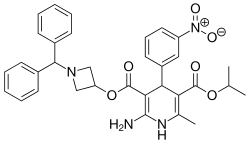 | CalBlock (カルブロック) | [6] |
| Barnidipine |  | Vasexten, Libradin, Cyress, HypoCa | [7] |
| Benidipine |  | Coniel | [8] |
| Cilnidipine |  | Atelec (アテレック), Cilacar, Cinalong, Siscard | [9] |
| Clevidipine |  | Cleviprex | [10] |
| Cronidipine |  | [11] | |
| Darodipine |  | [12] | |
| Dexniguldipine |  | [13] | |
| Efonidipine |  | Landel (ランデル) | [14] |
| Elgodipine |  | [15] | |
| Elnadipine |  | [16] | |
| Felodipine |  | Renedil, Plendil | [17] |
| Flordipine |  | [18] | |
| Furnidipine |  | [19] | |
| Iganidipine |  | [20] | |
| Isradipine |  | DynaCirc CR | [21] |
| Lacidipine |  | Lacipil, Motens, Sakure | |
| Lemildipine |  | ||
| Lercanidipine |  | Zanidip, Zanidip-Recordati | |
| Levamlodipine |  | EsCordi Cor | |
| Levniguldipine |  | ||
| Manidipine |  | Manyper, Caslot, Madipine | |
| Nicardipine | 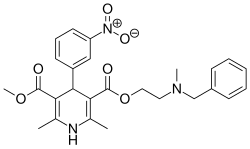 | Cardene, Cardene SR | |
| Nifedipine |  | Adalat, Nifedical, Procardia, Corinfar, Cordaflex | |
| Niguldipine |  | ||
| Niludipine |  | ||
| Nilvadipine |  | Nivadil | |
| Nimodipine |  | Nimotop | |
| Nisoldipine |  | Sular, Baymycard, Syscor | |
| Nitrendipine |  | Baypress, Cardif, Nitrepin, Baylotensin | |
| Olradipine |  | ||
| Oxodipine |  | ||
| Palonidipine |  | ||
| Pranidipine |  | Acalas | |
| Ryodipine |  | ||
| Sagandipine |  | ||
| Sornidipine |  | ||
| Teludipine |  | ||
| Tiamdipine |  | ||
| Trombodipine |  | ||
| Vatanidipine |  | ||
The pharmaceutical drug finerenone is also a dihydrophyridine derivative, but does not act as a calcium channel blocker but as an antimineralocorticoid. [22]