Characteristics
The Geoffroy's cat is about the size of a domestic cat, but has numerous black spots and dark bands on the cheeks, head and neck as well as on the tail and limbs. The background colour of its fur varies from a brownish-yellow coat in the northern part of its range to a more grayish coat in the south. The underbelly hair is cream-coloured or even white. The backs of the ears are black with white spots. Black individuals are common. [6]
Its size is about 60 cm (24 in) in head and body with a relatively short tail of about 31 cm (12 in). It weighs between 2 and 5 kg (4.4 and 11.0 lb), though individuals up to 7.8 kg (17 lb) have been reported. Males are usually larger than females, and Geoffroy's cat in the south are larger than those from the north. [6] It has a bite force quotient at the canine tip of 106.3. [7]
Distribution and habitat
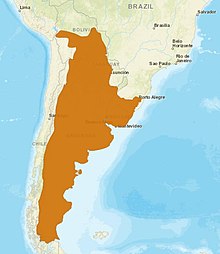
The Geoffroy's cat is distributed in Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Chile, Paraguay and Uruguay. It inhabits pampas and savanna landscapes in the Gran Chaco from southern Bolivia to the Straits of Magellan ranging at elevations from sea level up to 3,800 m (12,500 ft) in the Andes. It prefers open woodland or scrubland with plenty of cover, but also occurs in grasslands and marshy areas. [1] It is thought to be rare in Chile. [8]
Ecology and behaviour
The Geoffroy's cat is nocturnal and a solitary hunter that contacts conspecifics only during the mating season. Geoffroy's cats have been observed to stand up on their hind legs to scan the surrounding landscape and use their tail as a support, an unusual behaviour among cats. It is able to climb trees but rarely does, except to leave faeces to scent mark its territory. [6] It preys primarily on rodents, hares, other small mammals, birds, snakes, small lizards, insects, and occasionally frogs and fish. [6] Females maintain home ranges about 2 to 6 km2 (0.77 to 2.32 sq mi) in size, while males range over up to 12 km2 (4.6 sq mi). [6]
Reproduction
The breeding season for Geoffroy's cats lasts from October to March. During this time, the female comes into estrus for periods of up to twelve days, between three and five weeks apart. Mating during this time is brief and frequent, often taking place on a high ledge or similar site. [6]
Gestation lasts for 72–78 days. [9] Most births occur between December and May. Litters consist of one to three kittens, and one or two is more common. [10]
The kittens are born blind and helpless, weighing about 65 to 95 g (2.3 to 3.4 oz), and develop rather slowly compared to the domestic cat. The eyes open after eight to nineteen days, and they begin to eat solid food at six or seven weeks. [6] Kittens become independent of their mother at around eight months, but are generally not sexually mature until 18 months for females and 24 months for males. [10]
Conservation
From the 1960s to the 1980s, Geoffroy's cats were hunted extensively for their pelts for the international fur trade, but little trade took place after 1988 and the species was upgraded to CITES Appendix I status in 1992. [10] [1] Legislation introduced in the late 1980s made hunting and domestic trade of Geoffroy's cat's pelts illegal in Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Chile, Paraguay, and Uruguay. International trade in Cites Appendix I listed species is now prohibited, except for non-commercial purposes. [11]
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.