
Cannabinoids are several structural classes of compounds found in the cannabis plant primarily and most animal organisms or as synthetic compounds. The most notable cannabinoid is the phytocannabinoid tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) (delta-9-THC), the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis. Cannabidiol (CBD) is also a major constituent of temperate cannabis plants and a minor constituent in tropical varieties. At least 100 distinct phytocannabinoids have been isolated from cannabis, although only four have been demonstrated to have a biogenetic origin. It was reported in 2020 that phytocannabinoids can be found in other plants such as rhododendron, licorice and liverwort, and earlier in Echinacea.

Tetrahydrocannabivarin is a homologue of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) having a propyl (3-carbon) side chain instead of pentyl (5-carbon), making it non-psychoactive in lower doses. It has been shown to exhibit neuroprotective activity, appetite suppression, glycemic control and reduced side effects compared to THC, making it a potential treatment for management of obesity and diabetes. THCV was studied by Roger Adams as early as 1942.

Dimethylheptylpyran (DMHP) is a synthetic cannabinoid and analogue of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). It was invented in 1949 during attempts to elucidate the structure of Δ9-THC, one of the active components of cannabis. DMHP is a pale yellow, viscous oil which is insoluble in water but dissolves in alcohol or non-polar solvents.

O-2545 is an analgesic cannabinoid derivative created by Organix Inc. for use in scientific research. Unlike most cannabinoids discovered to date, it is water-soluble, which gives it considerable advantages over many related cannabinoids. It has high affinity for both CB1 and CB2 receptors, with Ki values of 1.5 nM at CB1 and 0.32 nM at CB2.

O-1057 is an analgesic cannabinoid derivative created by Organix Inc., Newburyport, Massachusetts, for use in scientific research. Unlike most cannabinoids discovered to date, it is water-soluble, which gives it considerable advantages over many related cannabinoids. It has moderate affinity for both CB1 and CB2 receptors, with Ki values of 8.36 nM at CB1 and 7.95 nM at CB2

AM-411 is an analgesic drug that is a cannabinoid agonist. It is a derivative of Δ8-THC substituted with an adamantyl group at the 3-position, demonstrating that the binding pocket for the alkyl chain at this position can accommodate significant bulk.
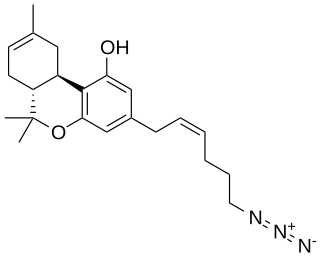
O-1238 is a drug which is a cannabinoid derivative that is used in scientific research. It is a partial agonist at the cannabinoid receptor CB1, producing a maximal stimulation of 58.3% with a Ki of 8.45 nM.
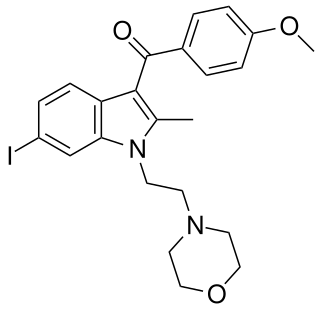
AM-630 (6-Iodopravadoline) is a drug that acts as a potent and selective inverse agonist for the cannabinoid receptor CB2, with a Ki of 32.1 nM at CB2 and 165x selectivity over CB1, at which it acted as a weak partial agonist. It is used in the study of CB2 mediated responses and has been used to investigate the possible role of CB2 receptors in the brain. AM-630 is significant as one of the first indole derived cannabinoid ligands substituted on the 6-position of the indole ring, a position that has subsequently been found to be important in determining affinity and efficacy at both the CB1 and CB2 receptors, and has led to the development of many related derivatives.

AM-2389 is a classical cannabinoid derivative which acts as a potent and reasonably selective agonist for the CB1 receptor, with a Ki of 0.16 nM, and 26× selectivity over the related CB2 receptor. It has high potency in animal tests of cannabinoid activity, and a medium duration of action. Replacing the 1',1'-dimethyl substitution of the dimethylheptyl side chain of classical cannabinoids with cyclopropyl or cyclopentyl results in higher potency than cyclobutyl, but only the cyclobutyl derivatives show selectivity for CB1 over CB2. High selectivity for CB1 over CB2 is difficult to achieve (cf. AM-906, AM-1235), as almost all commonly used CB1 agonists have similar or greater affinity for CB2 than CB1, and the only truly highly selective CB1 agonists known as of 2012 are eicosanoid derivatives such as O-1812.

PTI-2 (SGT-49) is an indole-based synthetic cannabinoid. It is one of few synthetic cannabinoids containing a thiazole group and is closely related to PTI-1. These compounds may be viewed as simplified analogues of indole-3-heterocycle compounds originally developed by Organon and subsequently further researched by Merck.

PTI-1 (SGT-48) is an indole-based synthetic cannabinoid. It is one of few synthetic cannabinoids containing a thiazole group and is closely related to PTI-2. These compounds may be viewed as simplified analogues of indole-3-heterocycle compounds originally developed by Organon and subsequently further researched by Merck.

Tetrahydrocannabiphorol (THCP) is a potent phytocannabinoid, a CB1 and CB2 receptor agonist which was known as a synthetic homologue of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), but for the first time in 2019 was isolated as a natural product in trace amounts from Cannabis sativa.

Δ-8-tetrahydrocannabinol is a psychoactive cannabinoid found in the cannabis plant. It is an isomer of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol, the compound commonly known as THC, with which it co-occurs in hemp; natural quantities of ∆8-THC found in hemp are low. Psychoactive effects are similar to that of Δ9-THC, with central effects occurring by binding to cannabinoid receptors found in various regions of the brain.
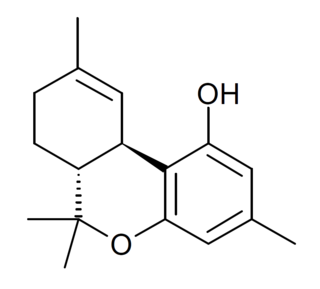
Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabiorcol (Δ9-THCC, (C1)-Δ9-THC) is a phytocannabinoid found in Cannabis pollen. It is a homologue of THC and THCV with the alkyl side chain replaced by a smaller methyl group. Unlike THC and THCV, THCC has negligible affinity for the CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors because of the smaller methyl group and does not have psychoactive effects as a result, but conversely it is significantly more potent than THC or THCV as an activator of the TRPA1 calcium channel which plays an important role in pain perception, and it has been shown to produce analgesic effects via activation of spinal TRPA1 channels. THCC was studied by Roger Adams as early as 1942.

Hexahydrocannabinol (HHC) is a hydrogenated derivative of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). It is a naturally occurring phytocannabinoid that has rarely been identified as a trace component in Cannabis sativa, but can also be produced synthetically by firstly acid cyclization of cannabidiol and then hydrogenation of tetrahydrocannabinol. The synthesis and bioactivity of HHC was first reported in 1940 by Roger Adams.

Tetrahydrocannabihexol is a phytocannabinoid, the hexyl homologue of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) which was first isolated from Cannabis plant material in 2020 along with the corresponding hexyl homologue of cannabidiol, though it had been known for several decades prior to this as an isomer of the synthetic cannabinoid parahexyl. Another isomer Δ8-THCH is also known as a synthetic cannabinoid under the code number JWH-124, though it is unclear whether this occurs naturally in Cannabis, but likely is due to Δ8-THC itself being a degraded form of Δ9-THC. THC-Hexyl can be synthesized from 4-hexylresorcinol and was studied by Roger Adams as early as 1942.
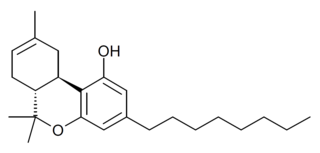
JWH-138 (THC-Octyl, Δ8-THC-C8) is a synthetic cannabinoid first synthesized by Roger Adams and studied heavily by John W. Huffman, with a Ki of 8.5nM at the CB1 cannabinoid receptor. THC-Octyl and its hydrogenated analog HHC-Octyl was synthesized and studied by Roger Adams as early as 1942.
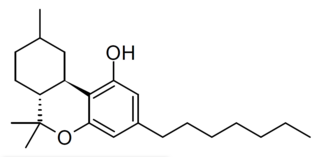
Hexahydrocannabiphorol is a semi-synthetic cannabinoid derivative which has been marketed since around 2021. It is believed to be made from the hydrogenation of tetrahydrocannabiphorol (THCP). THCP is only reported as a trace component of cannabis in 2019. HHCP was studied by Roger Adams as early as 1942.

Hexahydrocannabihexol (HHCH) is a semi-synthetic cannabinoid derivative. It was first synthesised by Roger Adams in 1942 and found to be more potent than either the pentyl or heptyl homologues, or the unsaturated tetrahydrocannabinol analogue. HHCH was first identified as a designer drug in Sweden in September 2023.
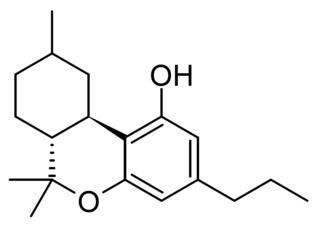
Hexahydrocannabivarin is a semi-synthetic cannabinoid derivative, the hydrogenated derivative of tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV). It was first synthesised by Roger Adams in 1942 and produces only weak cannabinoid-like effects in animals. More recently it has been sold as an ingredient in grey-market cannabinoid products. It has been investigated for potential antineoplastic activity in vitro.




















