
Masovian Voivodeship or Mazowieckie Province or Mazowieckie Voivodeship or Mazovian Voivodeship or Mazovian Province, etc. is a voivodeship (province) in east-central Poland, containing Poland's capital Warsaw.

Łódź Voivodeship is a voivodeship (province) of Poland. The province is named after its capital and largest city, Łódź, pronounced.

Tadeusz Mazowiecki was a Polish author, journalist, philanthropist and politician, formerly one of the leaders of the Solidarity movement, and the first non-communist Polish prime minister since 1946, having held the post from 1989 to 1991.

Parliamentary elections were held in Poland on 21 September 1997. All 460 members of the Sejm and 100 senators of the Senate were elected. The liberal conservative party Solidarity Electoral Action won the most seats in both chambers of parliament and formed a coalition government with the Freedom Union, another liberal party. The elections were a major setback for the Democratic Left Alliance and the Polish People's Party, which were forced out of government.

Members of the European Parliament (MEPs) are elected by the population of the member states of the European Union (EU). The European Electoral Act 2002 allows member states the choice to allocate electoral subdivisions or constituencies for the European Parliament elections in several different ways.

Parliamentary elections were held in Poland on 4 June 1989 to elect members of the Sejm and the recreated Senate, with a second round on 18 June. They were the first elections in the country since the communist government abandoned its monopoly of power in April 1989 and the first elections in the Eastern Bloc that resulted in the communist government losing power.

Maków County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Masovian Voivodeship, east-central Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Maków Mazowiecki, which lies 73 kilometres (45 mi) north of Warsaw. The only other town in the county is Różan, lying 20 km (12 mi) east of Maków Mazowiecki.

Warsaw Voivodeship was a voivodeship of Poland in the years 1919–1939. Its capital and biggest city was Warsaw.

Congress Poland was subdivided several times from its creation in 1815 until its dissolution in 1918. Congress Poland was divided into departments, a relic from the times of the French-dominated Duchy of Warsaw. In 1816 the administrative divisions were changed to forms that were more traditionally Polish: voivodeships, obwóds and powiats. Following the November Uprising, the subdivisions were again changed in 1837 to bring the subdivisions closer to the structure of the Russian Empire when guberniyas (governorates) were introduced. In this way, Congress Poland was gradually transformed into the "Vistulan Country". Over the next several decades, various smaller reforms were carried out, either changing the smaller administrative units or merging/splitting various guberniyas.
This is a list of coats of arms of Poland.
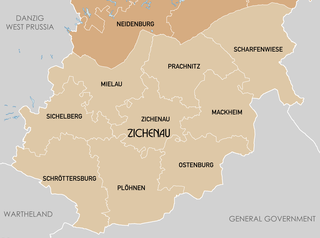
Regierungsbezirk Zichenau was a Regierungsbezirk, or administrative region, of the Nazi German Province of East Prussia in 1939–45, established in German-occupied Polish territory during World War II. The regional capital was Zichenau (Ciechanów). It was also referred to under the designation of South East Prussia which, however, was later sometimes also applied to Bialystok District, although the latter was not incorporated into, but merely attached to East Prussia.

The 2009 European Parliament election in Poland was the election of the delegation from Poland to the European Parliament in 2009 which took place on 7 June 2009. On 13 February the Sejm accepted a proposal for an amendment to the electoral court act to allow voting for the European Parliament election of 2009 to take place over 2 days i.e. the 6 and 7 June 2009. However, on 5 March, the proposal was referred to the Constitutional Tribunal of the Republic of Poland by the Polish President, Lech Kaczyński. The Polish electorate elected 50 MEPs. In the 27 EU Member States, at total of 736 MEPs were elected from 4–7 June 2009.

Masovian Railways, in Polish Koleje Mazowieckie, is a regional rail operator in the Masovian Voivodeship of Poland.

Mazovia or Masovia is a historical region in mid-north-eastern Poland. It spans the North European Plain, roughly between Łódź and Białystok, with Warsaw being the unofficial capital and largest city. Throughout the centuries, Mazovia developed a separate sub-culture featuring diverse folk songs, architecture, dress and traditions different from those of other Poles.

The 2014 European Parliament election in Poland elected the delegation from Poland to the European Parliament. It took place on 25 May 2014. The Polish electorate will elect 51 MEPs, compared to 50 in the 2009 election.. The number of MEPs is a result of the 2013 reapportionment of seats in the European Parliament. This means that Poland will have 6% of the total seats in the European Parliament.

On Sunday 26 May 2019, a vote was held to elect the Polish delegation to the European Parliament. Polish voters elected 52 MEPs, compared to 51 in the 2014 election. The increased number of MEPs is a result of the 2018 reapportionment of seats in the European Parliament. Following the United Kingdom's announcement, that it will participate in elections to the European Parliament on May 23, Poland will continue to be represented by 51 MEPs. The 52nd MEP will take up their mandate immediately after the UK leaves the European Union. Following the announcement of the election results, the National Electoral Commission indicated Dominik Tarczyński from Lesser Poland and Świętokrzyskie will take up the 52nd seat.

LGBT-free zones were municipalities and regions of Poland that have declared themselves unwelcoming of LGBT rights, in order to ban equality marches and other LGBT events. By June 2020, some 100 municipalities (map) and five voivodeships, encompassing a third of the country, had adopted resolutions which have been characterized as "LGBT-free zones". On 6 February 2024, Warsaw Voivodship Administrative Court repealed the last "LGBT-free zone" in Poland.

The Warsaw Voivodeship was a voivodeship (province) of the Polish People's Republic, with capital in Warsaw, that was located in Masovia. It was established on 22 August 1944, and until 28 June 1945, it remained under the administration of the Provisional Government of the Republic of Poland, which then was replaced by the Provisional Government of National Unity. On, 19 February 1947, the provisional government was replaced by the Polish People's Republic. It existed until 31 May 1975, when it was partitioned into the voivodeships of Biała Podlaska, Białystok, Ciechanów, Lublin, Łomża, Ostrołęka, Płock, Radom, Siedlce, Skierniewice, and Warsaw Capital.

Rafał Romanowski is a Polish politician who has served as a Member of the European Parliament since 2023. He was undersecretary of state at the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development from 2015 to 2020 and 2021 to 2022. From 2022 to 2023, he served as secretary of state in the same ministry. Romanowski was a member of the Sejm from 2019 to 2023 and became a Member of the European Parliament of the 9th term in November 2023.























