
Holmium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ho and atomic number 67. It is a rare-earth element and the eleventh member of the lanthanide series. It is a relatively soft, silvery, fairly corrosion-resistant and malleable metal. Like many other lanthanides, holmium is too reactive to be found in native form, as pure holmium slowly forms a yellowish oxide coating when exposed to air. When isolated, holmium is relatively stable in dry air at room temperature. However, it reacts with water and corrodes readily, and also burns in air when heated.

Neodymium is a chemical element; it has symbol Nd and atomic number 60. It is the fourth member of the lanthanide series and is considered to be one of the rare-earth metals. It is a hard, slightly malleable, silvery metal that quickly tarnishes in air and moisture. When oxidized, neodymium reacts quickly producing pink, purple/blue and yellow compounds in the +2, +3 and +4 oxidation states. It is generally regarded as having one of the most complex spectra of the elements. Neodymium was discovered in 1885 by the Austrian chemist Carl Auer von Welsbach, who also discovered praseodymium. It is present in significant quantities in the minerals monazite and bastnäsite. Neodymium is not found naturally in metallic form or unmixed with other lanthanides, and it is usually refined for general use. Neodymium is fairly common—about as common as cobalt, nickel, or copper and is widely distributed in the Earth's crust. Most of the world's commercial neodymium is mined in China, as is the case with many other rare-earth metals.

Terbium is a chemical element; it has symbol Tb and atomic number 65. It is a silvery-white, rare earth metal that is malleable, and ductile. The ninth member of the lanthanide series, terbium is a fairly electropositive metal that reacts with water, evolving hydrogen gas. Terbium is never found in nature as a free element, but it is contained in many minerals, including cerite, gadolinite, monazite, xenotime and euxenite.

Praseodymium is a chemical element; it has symbol Pr and the atomic number 59. It is the third member of the lanthanide series and is considered one of the rare-earth metals. It is a soft, silvery, malleable and ductile metal, valued for its magnetic, electrical, chemical, and optical properties. It is too reactive to be found in native form, and pure praseodymium metal slowly develops a green oxide coating when exposed to air.
In chemistry, an aluminate is a compound containing an oxyanion of aluminium, such as sodium aluminate. In the naming of inorganic compounds, it is a suffix that indicates a polyatomic anion with a central aluminium atom.

Holmium(III) oxide, or holmium oxide is a chemical compound of a rare-earth element holmium and oxygen with the formula Ho2O3. Together with dysprosium(III) oxide (Dy2O3), holmium oxide is one of the most powerfully paramagnetic substances known. The oxide, also called holmia, occurs as a component of the related erbium oxide mineral called erbia. Typically, the oxides of the trivalent lanthanides coexist in nature, and separation of these components requires specialized methods. Holmium oxide is used in making specialty colored glasses. Glass containing holmium oxide and holmium oxide solutions have a series of sharp optical absorption peaks in the visible spectral range. They are therefore traditionally used as a convenient calibration standard for optical spectrophotometers.
Cobalt(II) oxide is an inorganic compound that has been described as an olive-green or gray solid. It is used extensively in the ceramics industry as an additive to create blue-colored glazes and enamels, as well as in the chemical industry for producing cobalt(II) salts. A related material is cobalt(II,III) oxide, a black solid with the formula Co3O4.

Manganese(II) oxide is an inorganic compound with chemical formula MnO. It forms green crystals. The compound is produced on a large scale as a component of fertilizers and food additives.

Neodymium(III) oxide or neodymium sesquioxide is the chemical compound composed of neodymium and oxygen with the formula Nd2O3. It forms very light grayish-blue hexagonal crystals. The rare-earth mixture didymium, previously believed to be an element, partially consists of neodymium(III) oxide.

Cerium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ce and atomic number 58. Cerium is a soft, ductile, and silvery-white metal that tarnishes when exposed to air. Cerium is the second element in the lanthanide series, and while it often shows the oxidation state of +3 characteristic of the series, it also has a stable +4 state that does not oxidize water. It is also considered one of the rare-earth elements. Cerium has no known biological role in humans but is not particularly toxic, except with intense or continued exposure.
Praseodymium(III,IV) oxide is the inorganic compound with the formula Pr6O11 that is insoluble in water. It has a cubic fluorite structure. It is the most stable form of praseodymium oxide at ambient temperature and pressure.
Praseodymium(III) fluoride is an inorganic compound with the formula PrF3, being the most stable fluoride of praseodymium.
Praseodymium(III) oxalate is an inorganic compound, a salt of praseodymium metal and oxalic acid with the chemical formula C6O12Pr2. The compound forms light green crystals, insoluble in water, also forms crystalline hydrates.

Praseodymium(IV) fluoride (also praseodymium tetrafluoride) is a binary inorganic compound, a highly oxidised metal salt of praseodymium and fluoride with the chemical formula PrF4.

Neodymium(III) acetate is an inorganic salt composed of a neodymium atom trication and three acetate groups as anions where neodymium exhibits the +3 oxidation state. It has a chemical formula of Nd(CH3COO)3 although it can be informally referred to as NdAc because Ac is an informal symbol for acetate. It commonly occurs as a light purple powder.

Neodymium compounds are compounds formed by the lanthanide metal neodymium (Nd). In these compounds, neodymium generally exhibits the +3 oxidation state, such as NdCl3, Nd2(SO4)3 and Nd(CH3COO)3. Compounds with neodymium in the +2 oxidation state are also known, such as NdCl2 and NdI2. Some neodymium compounds have colors that vary based upon the type of lighting.
Praseodymium compounds are compounds formed by the lanthanide metal praseodymium (Pr). In these compounds, praseodymium generally exhibits the +3 oxidation state, such as PrCl3, Pr(NO3)3 and Pr(CH3COO)3. However, compounds with praseodymium in the +2 and +4 oxidation states, and unlike other lanthanides, the +5 oxidation state, are also known.

Praseodymium(III) iodide is an inorganic salt, consisting of the rare-earth metal praseodymium and iodine, with the chemical formula PrI3. It forms green crystals. It is soluble in water.
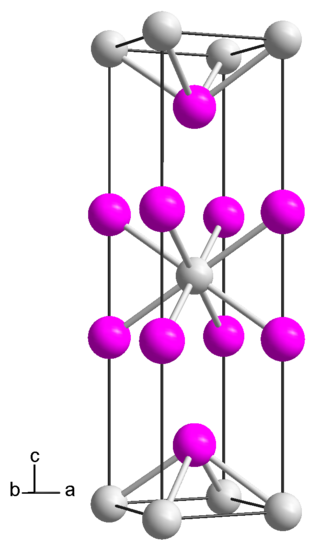
Praseodymium diiodide is a chemical compound with the empirical formula of PrI2, consisting of praseodymium and iodine. It is an electride, with the ionic formula of Pr3+(I−)2e−, and therefore not a true praseodymium(II) compound.
Cerium compounds are compounds containing the element cerium (Ce), a lanthanide. Cerium exists in two main oxidation states, Ce(III) and Ce(IV). This pair of adjacent oxidation states dominates several aspects of the chemistry of this element. Cerium(IV) aqueous solutions may be prepared by reacting cerium(III) solutions with the strong oxidizing agents peroxodisulfate or bismuthate. The value of E⦵(Ce4+/Ce3+) varies widely depending on conditions due to the relative ease of complexation and hydrolysis with various anions, although +1.72 V is representative. Cerium is the only lanthanide which has important aqueous and coordination chemistry in the +4 oxidation state.















