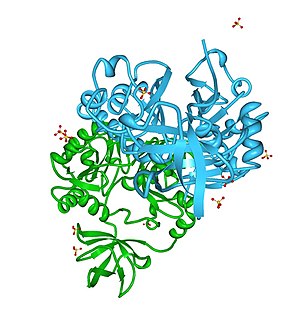
Aminomethyltransferase is an enzyme that catabolizes the creation of methylenetetrahydrofolate. It is part of the glycine decarboxylase complex.

Sodium/glucose cotransporter 1 (SGLT1) also known as solute carrier family 5 member 1 is a protein in humans that is encoded by the SLC5A1 gene which encodes the production of the SGLT1 protein to line the absorptive cells in the small intestine and the epithelial cells of the kidney tubules of the nephron for the purpose of glucose uptake into cells. Through the use of the sodium glucose cotransporter 1 protein, cells are able to obtain glucose which is further utilized to make and store energy for the cell.

Concentrative nucleoside transporter 2 (CNT2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC28A2 gene.

Proton-coupled amino acid transporter 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC36A1 gene.

Neutral amino acid transporter A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC1A4 gene.

Y+L amino acid transporter 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC7A7 gene.

Large neutral amino acids transporter small subunit 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC7A8 gene.

Sodium/bile acid cotransporter also known as the Na+-taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide (NTCP) or liver bile acid transporter (LBAT) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC10A1 (solute carrier family 10 member 1) gene.
An amino acid transporter is a membrane transport protein that transports amino acids. They are mainly of the solute carrier family.

Vesicular inhibitory amino acid transporter is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC32A1 gene.

Sodium-coupled neutral amino acid transporter 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC38A1 gene.

Sodium-dependent neutral amino acid transporter B(0)AT1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC6A19 gene.
Iminoglycinuria, is an autosomal recessive disorder of renal tubular transport affecting reabsorption of the amino acid glycine, and the imino acids proline and hydroxyproline. This results in excess urinary excretion of all three acids.

Solute carrier family 6, member 18 also known as SLC6A18 is a protein which in humans is encoded by the SLC6A18 gene.

Solute carrier family 6, member 20 also known as SLC6A20 is a protein which in humans is encoded by the SLC6A20 gene.

Y+L amino acid transporter 2, also known as cationic amino acid transporter, y+ system, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC7A6 gene.

Asc-type amino acid transporter 1 (Asc-1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC7A10 gene.

Monocarboxylate transporter 10, also known as aromatic amino acid transporter 1 and T-type amino acid transporter 1 (TAT1) and solute carrier family 16 member 10 (SLC16A10), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC16A10 gene. SLC16A10 is a member of the solute carrier family.

Sodium-dependent neutral amino acid transporter B(0)AT2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC6A15 gene.
Proton-coupled amino acid transporters belong to the SLC26A5 family; they are protein receptors whose main function is the transmembrane movement of amino acids and their derivatives. This family of receptors is most commonly found within the luminal surface of the small intestine as well as in some lysosomes. The solute carrier family (SLC) of genes includes roughly 400 membrane proteins that are characterized by 66 families in total. The SLC36 family of genes maps to chromosome 11. The diversity of these receptors is vast, with the ability to transport both charged and uncharged amino acids along with their derivatives. In research and practice, SLC36A1/2 are both targets for drug-based delivery systems for a wide range of disorders.
















