Related Research Articles

Zirconium is a chemical element; it has symbol Zr and atomic number 40. The name zirconium is derived from the name of the mineral zircon, the most important source of zirconium. The word is related to Persian zargun. It is a lustrous, grey-white, strong transition metal that closely resembles hafnium and, to a lesser extent, titanium.

Zirconium(IV) chloride, also known as zirconium tetrachloride, is an inorganic compound frequently used as a precursor to other compounds of zirconium. This white high-melting solid hydrolyzes rapidly in humid air.
Zirconium(IV) bromide is the inorganic compound with the formula ZrBr4. This colourless solid is the principal precursor to other Zr–Br compounds.

Zirconium(IV) fluoride describes members of a family inorganic compounds with the formula (ZrF4(H2O)x. All are colorless, diamagnetic solids. Anhydrous Zirconium(IV) fluoride' is a component of ZBLAN fluoride glass.
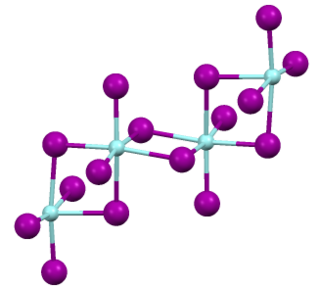
Zirconium(IV) iodide is the chemical compound with the formula ZrI4. It is the most readily available iodide of zirconium. It is an orange-coloured solid that degrades in the presence of water. The compound was once prominent as an intermediate in the purification of zirconium metal.

Zirconium(IV) sulfide is the inorganic compound with the formula ZrS2. It is a violet-brown solid. It adopts a layered structure similar to that of cadmium iodide.

Zirconium(III) chloride is an inorganic compound with formula ZrCl3. It is a blue-black solid that is highly sensitive to air.

Neodymium(II) iodide or neodymium diiodide is an inorganic salt of iodine and neodymium the formula NdI2. Neodymium uses the +2 oxidation state in the compound.

Praseodymium(III) iodide is an inorganic salt, consisting of the rare-earth metal praseodymium and iodine, with the chemical formula PrI3. It forms green crystals. It is soluble in water.

Zirconium(III) bromide is an inorganic compound with the formula ZrBr3.
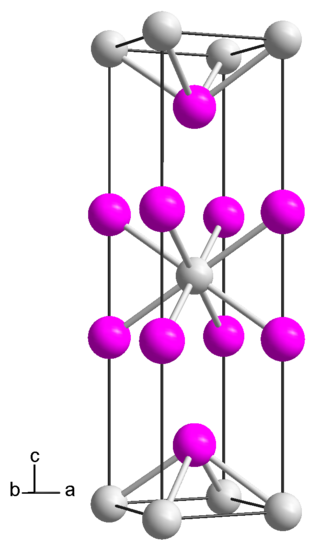
Praseodymium diiodide is a chemical compound with the empirical formula of PrI2, consisting of praseodymium and iodine. It is an electride, with the ionic formula of Pr3+(I−)2e−, and therefore not a true praseodymium(II) compound.

Zirconium(III) iodide is an inorganic compound with the formula ZrI3.

Lanthanum diiodide is an iodide of lanthanum, with the chemical formula of LaI2. It is an electride, actually having a chemical formula of La3+[(I−)2e−].

Cerium diiodide is an iodide of cerium, with the chemical formula of CeI2.

Disulfur diiodide is an unstable inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula S2I2. It is a red-brown solid that decomposes above −30 °C to elemental sulfur and iodine.
Einsteinium(II) iodide is a binary inorganic chemical compound of einsteinium and iodide with the chemical formula EsI2.
Zirconium dichloride is an inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula ZrCl2.
Zirconium difluoride is an inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula ZrF2.

Zirconium trifluoride is an inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula ZrF3. This is a salt of zirconium and hydrofluoric acid, forms black crystals.
Zirconium dibromide is an inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula ZrBr2.
References
- ↑ "Zirconium(II) Iodide". American Elements . Retrieved 19 July 2024.
- ↑ Mines, United States Bureau of (1984). Bulletin. U.S. Government Printing Office. p. 247. Retrieved 19 July 2024.
- ↑ Clark, R. J. H.; Bradley, D. C.; Thornton, P. (12 March 2018). The Chemistry of Titanium, Zirconium and Hafnium: Pergamon Texts in Inorganic Chemistry. Elsevier. p. 433. ISBN 978-1-4831-5921-8 . Retrieved 19 July 2024.