
Zirconium is a chemical element; it has symbol Zr and atomic number 40. First identified in 1789, isolated in impure form in 1824, and manufactured at scale by 1925, pure zirconium is a lustrous transition metal with a greyish-white color that closely resembles hafnium and, to a lesser extent, titanium. It is solid at room temperature, ductile, malleable and corrosion-resistant. The name zirconium is derived from the name of the mineral zircon, the most important source of zirconium. The word is related to Persian zargun. Besides zircon, zirconium occurs in over 140 other minerals, including baddeleyite and eudialyte; most zirconium is produced as a byproduct of minerals mined for titanium and tin.

Palladium(II) chloride, also known as palladium dichloride and palladous chloride, are the chemical compounds with the formula PdCl2. PdCl2 is a common starting material in palladium chemistry – palladium-based catalysts are of particular value in organic synthesis. It is prepared by the reaction of chlorine with palladium metal at high temperatures.

Hafnium(IV) chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula HfCl4. This colourless solid is the precursor to most hafnium organometallic compounds. It has a variety of highly specialized applications, mainly in materials science and as a catalyst.

Titanocene dichloride is the organotitanium compound with the formula (η5-C5H5)2TiCl2, commonly abbreviated as Cp2TiCl2. This metallocene is a common reagent in organometallic and organic synthesis. It exists as a bright red solid that slowly hydrolyzes in air. It shows antitumour activity and was the first non-platinum complex to undergo clinical trials as a chemotherapy drug.

Zirconium(IV) chloride, also known as zirconium tetrachloride, is an inorganic compound frequently used as a precursor to other compounds of zirconium. This white high-melting solid hydrolyzes rapidly in humid air.

Zirconium(IV) fluoride describes members of a family inorganic compounds with the formula ZrF4(H2O)x. All are colorless, diamagnetic solids. Anhydrous Zirconium(IV) fluoride is a component of ZBLAN fluoride glass.
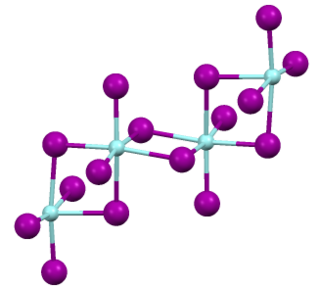
Zirconium(IV) iodide is the chemical compound with the formula ZrI4. It is the most readily available iodide of zirconium. It is an orange-coloured solid that degrades in the presence of water. The compound was once prominent as an intermediate in the purification of zirconium metal.

Dicarbonylbis(cyclopentadienyl)titanium is the chemical compound with the formula (η5-C5H5)2Ti(CO)2, abbreviated Cp2Ti(CO)2. This maroon-coloured, air-sensitive species is soluble in aliphatic and aromatic solvents. It has been used for the deoxygenation of sulfoxides, reductive coupling of aromatic aldehydes and reduction of aldehydes.

Organozirconium chemistry is the science of exploring the properties, structure, and reactivity of organozirconium compounds, which are organometallic compounds containing chemical bonds between carbon and zirconium. Organozirconium compounds have been widely studied, in part because they are useful catalysts in Ziegler-Natta polymerization.

Germanium dichloride is a chemical compound of germanium and chlorine with the formula GeCl2. It is a yellow solid. Germanium dichloride is an example of a compound featuring germanium in the +2 oxidation state.
Zirconocene dichloride is an organozirconium compound composed of a zirconium central atom, with two cyclopentadienyl and two chloro ligands. It is a colourless diamagnetic solid that is somewhat stable in air.

Zirconium(III) chloride is an inorganic compound with formula ZrCl3. It is a blue-black solid that is highly sensitive to air.
In organometallic chemistry, bent metallocenes are a subset of metallocenes. In bent metallocenes, the ring systems coordinated to the metal are not parallel, but are tilted at an angle. A common example of a bent metallocene is Cp2TiCl2. Several reagents and much research is based on bent metallocenes.
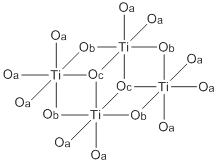
Titanium ethoxide is a chemical compound with the formula Ti4(OCH2CH3)16. It is a commercially available colorless liquid that is soluble in organic solvents but hydrolyzes readily. Its structure is more complex than suggested by its empirical formula. Like other alkoxides of titanium(IV) and zirconium(IV), it finds used in organic synthesis and materials science.

Titanocene pentasulfide is the organotitanium compound with the formula (C5H5)2TiS5, commonly abbreviated as Cp2TiS5. This metallocene exists as a bright red solid that is soluble in organic solvents. It is of academic interest as a precursor to unusual allotropes of elemental sulfur as well as some related inorganic rings.

Zirconium perchlorate is an inorganic compound with the formula Zr(ClO4)4. It is a hygroscopic colorless solid that sublimes in a vacuum at 70 °C. These properties show that the compound is covalently bonded molecule, rather than a salt. It is an example of a transition metal perchlorate complex.

(Cyclopentadienyl)titanium trichloride is an organotitanium compound with the formula (C5H5)TiCl3. It is a moisture sensitive orange solid. The compound adopts a piano stool geometry.
Dysprosium(II) chloride (DyCl2), also known as dysprosium dichloride, is an ionic chemical compound of dysprosium and chlorine. This salt is a reduced compound, as the normal oxidation state of dysprosium in dysprosium compounds is +3.
Carbide chlorides are mixed anion compounds containing chloride anions and anions consisting entirely of carbon. In these compounds there is no bond between chlorine and carbon. But there is a bond between a metal and carbon. Many of these compounds are cluster compounds, in which metal atoms encase a carbon core, with chlorine atoms surrounding the cluster. The chlorine may be shared between clusters to form polymers or layers. Most carbide chloride compounds contain rare earth elements. Some are known from group 4 elements. The hexatungsten carbon cluster can be oxidised and reduced, and so have different numbers of chlorine atoms included.
Hafnium compounds are compounds containing the element hafnium (Hf). Due to the lanthanide contraction, the ionic radius of hafnium(IV) (0.78 ångström) is almost the same as that of zirconium(IV) (0.79 angstroms). Consequently, compounds of hafnium(IV) and zirconium(IV) have very similar chemical and physical properties. Hafnium and zirconium tend to occur together in nature and the similarity of their ionic radii makes their chemical separation rather difficult. Hafnium tends to form inorganic compounds in the oxidation state of +4. Halogens react with it to form hafnium tetrahalides. At higher temperatures, hafnium reacts with oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, boron, sulfur, and silicon. Some compounds of hafnium in lower oxidation states are known.














