
Hartnup disease is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder affecting the absorption of nonpolar amino acids. Niacin is a precursor to nicotinamide, a necessary component of NAD+.

ATP-binding cassette sub-family A member 12 also known as ATP-binding cassette transporter 12 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCA12 gene.

Excitatory amino-acid transporter 5 (EAAT5) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC1A7 gene.

b(0,+)-type amino acid transporter 1, also known as b(0,+)AT1, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the SLC7A9 gene.

Neutral and basic amino acid transport protein rBAT is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC3A1 gene.

Aminomethyltransferase is an enzyme that catabolizes the creation of methylenetetrahydrofolate. It is part of the glycine decarboxylase complex.

Sialin, also known as H(+)/nitrate cotransporter and H(+)/sialic acid cotransporter, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the SLC17A5 gene.

Neutral amino acid transporter B(0) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC1A5 gene.

Y+L amino acid transporter 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC7A7 gene.

Large neutral amino acids transporter small subunit 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC7A8 gene.

Cationic amino acid transporter 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC7A3 gene.

Vesicular inhibitory amino acid transporter is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC32A1 gene.

Sodium-coupled neutral amino acid transporter 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC38A1 gene.

Hypertryptophanemia is a rare autosomal recessive metabolic disorder that results in a massive buildup of the amino acid tryptophan in the blood, with associated symptoms and tryptophanuria.
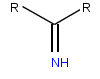
Iminoglycinuria is an autosomal recessive disorder of renal tubular transport affecting reabsorption of the amino acid glycine, and the imino acids proline and hydroxyproline. This results in excess urinary excretion of all three acids.

Solute carrier family 6, member 18 also known as SLC6A18 is a protein which in humans is encoded by the SLC6A18 gene.

Solute carrier family 6, member 20 also known as SLC6A20 is a protein which in humans is encoded by the SLC6A20 gene.

Proton-coupled amino acid transporter 2 is a protein which in humans is encoded by the SLC36A2 gene.

Asc-type amino acid transporter 1 (Asc-1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC7A10 gene.

Sodium-dependent neutral amino acid transporter B(0)AT2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC6A15 gene.
















