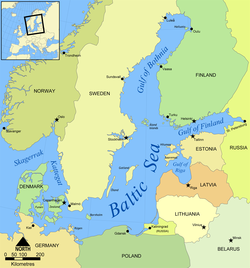
The Baltic Sea Region, alternatively the Baltic Rim countries (or simply the Baltic Rim), and the Baltic Sea countries/states, refers to the general area surrounding the Baltic Sea, including parts of Northern, Central and Eastern Europe. [1] [2] [3] Unlike the "Baltic states", the Baltic region includes all countries that border the sea.