
The Mariner program was conducted by the American space agency NASA to explore other planets. Between 1962 and late 1973, NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) designed and built 10 robotic interplanetary probes named Mariner to explore the inner Solar System – visiting the planets Venus, Mars and Mercury for the first time, and returning to Venus and Mars for additional close observations.

Mariner 4 was the fourth in a series of spacecraft intended for planetary exploration in a flyby mode. It was designed to conduct closeup scientific observations of Mars and to transmit these observations to Earth. Launched on November 28, 1964, Mariner 4 performed the first successful flyby of the planet Mars, returning the first close-up pictures of the Martian surface. It captured the first images of another planet ever returned from deep space; their depiction of a cratered, dead planet largely changed the scientific community's view of life on Mars. Other mission objectives were to perform field and particle measurements in interplanetary space in the vicinity of Mars and to provide experience in and knowledge of the engineering capabilities for interplanetary flights of long duration. Initially expected to remain in space for eight months, Mariner 4's mission lasted about three years in solar orbit. On December 21, 1967, communications with Mariner 4 were terminated.

Surveyor 7 was sent to the Moon in 1968 on a scientific and photographic mission as the seventh and last lunar lander of the American uncrewed Surveyor program. With two previous unsuccessful missions in the Surveyor series, and with Surveyor 7's landing success, Surveyor 7 became the fifth and final spacecraft in the series to achieve a lunar soft landing. A total of 21,091 pictures were transmitted from Surveyor 7 back to Earth.

Surveyor 3 is the third lander of the American uncrewed Surveyor program sent to explore the surface of the Moon in 1967 and the second to successfully land. It was the first mission to carry a surface-soil sampling-scoop.

Pioneer 4 was an American spin-stabilized uncrewed spacecraft launched as part of the Pioneer program on a lunar flyby trajectory and into a heliocentric orbit making it the first probe of the United States to escape from the Earth's gravity. Launched on March 3, 1959, it carried a payload similar to Pioneer 3: a lunar radiation environment experiment using a Geiger–Müller tube detector and a lunar photography experiment. It passed within 58,983 km (36,650 mi) of the Moon's surface. However, Pioneer 4 did not come close enough to trigger its photoelectric sensor. The spacecraft was still in solar orbit as of 1969. It was the only successful lunar probe launched by the U.S. in 12 attempts between 1958 and 1963; only in 1964 would Ranger 7 surpass its success by accomplishing all of its mission objectives.

Ranger 1 was a prototype spacecraft launched as part of the Ranger program of uncrewed space missions. Its primary mission was to test the performance of those functions and parts necessary for carrying out subsequent lunar and planetary missions; a secondary objective was to study the nature of particles and fields in the space environment. Due to a launch vehicle malfunction, the spacecraft could reach only Low Earth orbit, rather than the high Earth orbit that had been planned, and was only able to complete part of its mission.

Ranger 2 was a flight test of the Ranger spacecraft system of the NASA Ranger program designed for future lunar and interplanetary missions. Ranger 2 was designed to test various systems for future exploration and to conduct scientific observations of cosmic rays, magnetic fields, radiation, dust particles, and a possible hydrogen gas "tail" trailing the Earth.

Ranger 3 was a space exploration mission conducted by NASA to study the Moon. The Ranger 3 robotic spacecraft was launched January 26, 1962 as part of the Ranger program. Due to a series of malfunctions, the spacecraft missed the Moon by 22,000 mi (35,000 km) and entered a heliocentric orbit.

Ranger 4 was a spacecraft of the Ranger program, launched in 1962. It was designed to transmit pictures of the lunar surface to Earth stations during a period of 10 minutes of flight prior to crashing upon the Moon, to rough-land a seismometer capsule on the Moon, to collect gamma-ray data in flight, to study radar reflectivity of the lunar surface, and to continue testing of the Ranger program for development of lunar and interplanetary spacecraft.

Ranger 5 was a spacecraft of the Ranger program designed to transmit pictures of the lunar surface to Earth stations during a period of 10 minutes of flight prior to impacting on the Moon, to rough-land a seismometer capsule on the Moon, to collect gamma-ray data in flight, to study radar reflectivity of the lunar surface, and to continue testing of the Ranger program for development of lunar and interplanetary spacecraft. Due to an unknown malfunction, the spacecraft ran out of power and ceased operation. It passed within 725 km of the Moon.

Surveyor 1 was the first lunar soft-lander in the uncrewed Surveyor program of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration. This lunar soft-lander gathered data about the lunar surface that would be needed for the crewed Apollo Moon landings that began in 1969. The successful soft landing of Surveyor 1 on the Ocean of Storms was the first by an American space probe on any extraterrestrial body, occurring on the first attempt and just four months after the first soft Moon landing by the Soviet Union's Luna 9 probe.

The Ranger program was a series of uncrewed space missions by the United States in the 1960s whose objective was to obtain the first close-up images of the surface of the Moon. The Ranger spacecraft were designed to take images of the lunar surface, transmitting those images to Earth until the spacecraft were destroyed upon impact. A series of mishaps, however, led to the failure of the first six flights. At one point, the program was called "shoot and hope". Congress launched an investigation into "problems of management" at NASA Headquarters and Jet Propulsion Laboratory. After two reorganizations of the agencies, Ranger 7 successfully returned images in July 1964, followed by two more successful missions.

The Lunar Orbiter program was a series of five uncrewed lunar orbiter missions launched by the United States in 1966 and 1967. Intended to help select Apollo landing sites by mapping the Moon's surface, they provided the first photographs from lunar orbit and photographed both the Moon and Earth.
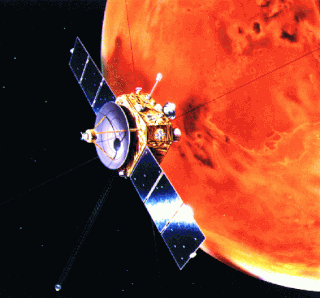
Nozomi was a Japanese Mars orbiter that failed to reach Mars due to electrical failure. It was constructed by the Institute of Space and Astronautical Science, University of Tokyo and launched on July 4, 1998, at 03:12 JST with an on-orbit dry mass of 258 kg and 282 kg of propellant. The Nozomi mission was terminated on December 31, 2003.

Ranger 7 was the first NASA space probe to successfully transmit close-up images of the lunar surface back to Earth. It was also the first completely successful flight of the Ranger program. Launched on July 28, 1964, Ranger 7 was designed to achieve a lunar-impact trajectory and to transmit high-resolution photographs of the lunar surface during the final minutes of flight up to impact.

Ranger 6 was a lunar probe in the NASA Ranger program, a series of robotic spacecraft of the early and mid-1960s to obtain close-up images of the Moon's surface. It was launched on January 30, 1964 and was designed to transmit high-resolution photographs of the lunar terrain during the final minutes of flight until impacting the surface. The spacecraft carried six television vidicon cameras—two wide-angle and four narrow-angle —to accomplish these objectives. The cameras were arranged in two separate chains, or channels, each self-contained with separate power supplies, timers, and transmitters so as to afford the greatest reliability and probability of obtaining high-quality television pictures. No other experiments were carried on the spacecraft. Due to a failure of the camera system, no images were returned.

Ranger 9 was a Lunar probe, launched in 1965 by NASA. It was designed to achieve a lunar impact trajectory and to transmit high-resolution photographs of the lunar surface during the final minutes of flight up to impact. The spacecraft carried six television vidicon cameras—two wide-angle and four narrow-angle —to accomplish these objectives. The cameras were arranged in two separate chains, or channels, each self-contained with separate power supplies, timers, and transmitters so as to afford the greatest reliability and probability of obtaining high-quality television pictures. These images were broadcast live on television to millions of viewers across the United States. No other experiments were carried on the spacecraft.

A Moon landing or lunar landing is the arrival of a spacecraft on the surface of the Moon, including both crewed and robotic missions. The first human-made object to touch the Moon was Luna 2 in 1959.

The Atlas-Agena was an American expendable launch system derived from the SM-65 Atlas missile. It was a member of the Atlas family of rockets, and was launched 109 times between 1960 and 1978. It was used to launch the first five Mariner uncrewed probes to the planets Venus and Mars, and the Ranger and Lunar Orbiter uncrewed probes to the Moon. The upper stage was also used as an uncrewed orbital target vehicle for the Gemini crewed spacecraft to practice rendezvous and docking. However, the launch vehicle family was originally developed for the Air Force and most of its launches were classified DoD payloads.

Explorer 49 was a NASA 328 kg (723 lb) satellite launched on 10 June 1973, for long wave radio astronomy research. It had four 230 m (750 ft) X-shaped antenna elements, which made it one of the largest spacecraft ever built.























