
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are a class of drugs that inhibit the activity of one or both monoamine oxidase enzymes: monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) and monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B). They are best known as effective antidepressants, especially for treatment-resistant depression and atypical depression. They are also used to treat panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, Parkinson's disease, and several other disorders.

Tyramine, also known under several other names, is a naturally occurring trace amine derived from the amino acid tyrosine. Tyramine acts as a catecholamine releasing agent. Notably, it is unable to cross the blood-brain barrier, resulting in only non-psychoactive peripheral sympathomimetic effects following ingestion. A hypertensive crisis can result, however, from ingestion of tyramine-rich foods in conjunction with the use of monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs).

Selegiline, also known as L-deprenyl and sold under the brand names Eldepryl, Zelapar, and Emsam among others, is a medication which is used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease and major depressive disorder. It has also been studied for a variety of other indications, but has not been formally approved for any other use. The medication in the form licensed for depression has modest effectiveness for this condition that is similar to that of other antidepressants. Selegiline is provided as a swallowed tablet or capsule or an orally disintegrating tablet (ODT) for Parkinson's disease and as a patch applied to skin for depression.

Deprenyl, also known by its developmental code name E-250 and as N-propargylmethamphetamine, is the racemic mixture of D-deprenyl and L-deprenyl (selegiline). It was discovered in 1961 in Hungary at Chinoin Pharmaceutical Company by Zoltan Ecseri and József Knoll, was patented in 1962, and was first described in the literature in 1964 or 1965.

Dopaminergic means "related to dopamine", a common neurotransmitter. Dopaminergic substances or actions increase dopamine-related activity in the brain.

Rasagiline, sold under the brand name Azilect among others, is a medication which is used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease. It is used as a monotherapy to treat symptoms in early Parkinson's disease or as an adjunct therapy in more advanced cases. The drug is taken by mouth.

Pargyline, sold under the brand name Eutonyl among others, is a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) medication which has been used to treat hypertension but is no longer marketed. It has also been studied as an antidepressant, but was never licensed for use in the treatment of depression. The drug is taken by mouth.

(–)-Benzofuranylpropylaminopentane is an experimental drug related to selegiline which acts as a monoaminergic activity enhancer (MAE). It is orally active in animals.

1-Phenyl-2-propylaminopentane is an experimental drug related to selegiline which acts as a catecholaminergic activity enhancer (CAE).

Monoamine oxidase B, also known as MAO-B, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MAOB gene.

Levoamphetamine is a stimulant medication which is used in the treatment of certain medical conditions. It was previously marketed by itself under the brand name Cydril, but is now available only in combination with dextroamphetamine in varying ratios under brand names like Adderall and Evekeo. The drug is known to increase wakefulness and concentration in association with decreased appetite and fatigue. Pharmaceuticals that contain levoamphetamine are currently indicated and prescribed for the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), obesity, and narcolepsy in some countries. Levoamphetamine is taken by mouth.
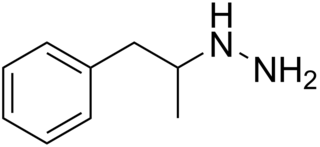
Pheniprazine, formerly sold under the brand names Catron and Cavodil, is an irreversible and non-selective monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine group that was used as an antidepressant to treat depression in the 1960s. It was also used in the treatment of angina pectoris and schizophrenia. Pheniprazine has been largely discontinued due to toxicity concerns such as jaundice, amblyopia, and optic neuritis.

Moussa B. H. Youdim is an Israeli neuroscientist specializing in neurochemistry and neuropharmacology. He is the discoverer of both monoamine oxidase (MAO) B inhibitors l-deprenyl (Selegiline) and rasagiline (Azilect) as anti-Parkinson drugs which possess neuroprotective activities. He is currently professor emeritus at Technion - Faculty of Medicine and President of Youdim Pharmaceuticals.
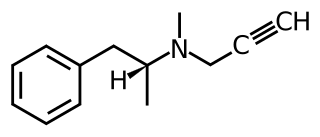
Monoaminergic activity enhancers (MAE), also known as catecholaminergic/serotonergic activity enhancers (CAE/SAE), are a class of compounds that enhance the action potential-evoked release of monoamine neurotransmitters in the nervous system. MAEs are distinct from monoamine releasing agents (MRAs) like amphetamine and fenfluramine in that they do not induce the release of monoamines from synaptic vesicles but rather potentiate only nerve impulse propagation-mediated monoamine release. That is, MAEs increase the amounts of monoamine neurotransmitters released by neurons per electrical impulse.

Desmethylselegiline (DMS), also known as norselegiline or as N-propargyl-L-amphetamine, is an active metabolite of selegiline, a medication used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease and depression.

The pharmacology of selegiline pertains to the pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties of the antiparkinsonian and antidepressant selegiline (L-deprenyl). Selegiline is available in a few different forms, including oral tablets and capsules, orally disintegrating tablets (ODTs), and transdermal patches. These forms have differing pharmacological properties.

Indolylpropylaminopentane (IPAP), also known as α,N-dipropyltryptamine (α,N-DPT), is a monoaminergic activity enhancer (MAE) that is closely related to benzofuranylpropylaminopentane (BPAP) and phenylpropylaminopentane (PPAP). It is a tryptamine derivative and the corresponding analogue of PPAP and BPAP with an indole ring instead of a benzene ring or benzofuran ring, respectively. MAEs are agents that enhance the action potential-mediated release of monoamine neurotransmitters.

(R)-1-Aminoindan ((R)-1-AI; developmental code name TVP-136 or TV-136), or (R)-1-aminoindane, is the major metabolite of the selective MAO-B inhibitor and antiparkinsonian agent rasagiline ((R)-N-propargyl-1-aminoindan). In contrast to rasagiline, it lacks significant monoamine oxidase inhibition. In addition, unlike selegiline and its amphetamine metabolites, it lacks monoamine reuptake-inhibiting and -releasing activities and associated amphetamine-like psychostimulant effects. However, (R)-1-aminoindan retains neuroprotective effects and certain other activities.

1-Aminoindane (1-AI), also known as 1-aminoindan, 1-indanylamine, or 1-indanamine, is an aminoindane. It is a positional isomer of 2-aminoindane. A variety of notable derivatives of 1- and 2-aminoindane are known. The (R)-enantiomer of 1-aminoindan, (R)-1-aminoindan, is pharmacologically active and is an active metabolite of the antiparkinsonian agent rasagiline.
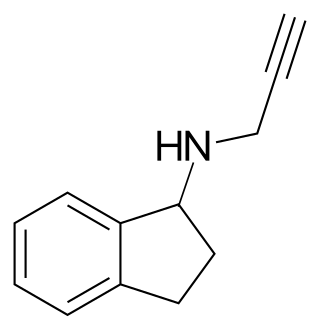
AGN-1135 is a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) that was never marketed. It is the racemic form of rasagiline and is a mixture of the R(+)-enantiomer and S(–)-enantiomer (TVP-1022). Like rasagiline, AGN-1135 is a selective monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B) inhibitor. Virtually all of the MAOI activity of AGN-1135 lies in rasagiline, which is several orders of magnitude more potent as an MAO-B inhibitor than the S(–)-enantiomer. In relation to this, enantiopure rasagiline was developed and marketed for use as a pharmaceutical drug rather than AGP-1135.




















