
Containerization is a system of intermodal freight transport using intermodal containers. Containerization, also referred as container stuffing or container loading, is the process of unitization of cargoes in exports. Containerization is the predominant form of unitization of export cargoes today, as opposed to other systems such as the barge system or palletization. The containers have standardized dimensions. They can be loaded and unloaded, stacked, transported efficiently over long distances, and transferred from one mode of transport to another—container ships, rail transport flatcars, and semi-trailer trucks—without being opened. The handling system is mechanized so that all handling is done with cranes and special forklift trucks. All containers are numbered and tracked using computerized systems.

A container ship is a cargo ship that carries all of its load in truck-size intermodal containers, in a technique called containerization. Container ships are a common means of commercial intermodal freight transport and now carry most seagoing non-bulk cargo.

Mitsui O.S.K. Lines is a Japanese transport company headquartered in Toranomon, Minato, Tokyo, Japan. It is one of the largest shipping companies in the world.

American President Lines, LLC, is an American container shipping company that is a subsidiary of French shipping company CMA CGM. It operates an all-container ship fleet, including nine U.S. flagged container vessels.

The Container Security Initiative (CSI) a.k.a. the 24-Hour Rule was launched in 2002 by the U.S. Bureau of Customs and Border Protection (CBP), an agency of the Department of Homeland Security. Its purpose was to increase security for container cargo shipped to the United States. As the CBP puts it, the intent is to "extend [the] zone of security outward so that American borders are the last line of defense, not the first."

China Ocean Shipping Company was a former shipping corporation from 1961 to 2016, owned by the State Council of China. The company merged with China Shipping Group Company to form China COSCO Shipping Corporation in January 2016.

The Port of Hong Kong located by the South China Sea, is a deepwater seaport dominated by trade in containerised manufactured products, and to a lesser extent raw materials and passengers. A key factor in the economic development of Hong Kong, the natural shelter and deep waters of Victoria Harbour provide ideal conditions for berthing and the handling of all types of vessels. It is one of the busiest ports in the world, in the three categories of shipping movements, cargo handled and passengers carried. This makes Hong Kong a Large-Port Metropolis.

COSCO Shipping Development Co., Ltd., stylized as COSCO SHIPPING Development is a financial services company based in Shanghai, China.

Orient Overseas Container Line, commonly known as OOCL, is a container shipping and logistics service company with headquarters in Hong Kong. The company is incorporated in Hong Kong as Orient Overseas Container Line Limited and separately incorporated as Orient Overseas Container Line Inc. in Liberia. The latter was also re-domiciled to the Marshall Islands.

Malcom Purcell McLean was an American businessman who invented the modern intermodal shipping container, which revolutionized transport and international trade in the second half of the twentieth century. Containerization led to a significant reduction in the cost of freight transportation by eliminating the need for repeated handling of individual pieces of cargo, and also improved reliability, reduced cargo theft, and cut inventory costs by shortening transit time. Containerization is a major driver of globalization.

China Merchants Port Holdings Company Limited is a major conglomerate based in Hong Kong and is involved in a range of businesses such as port operations, general and bulk cargo transportation, container and shipping business, air cargo, logistics park operations and paint products. China Merchants Port is considered as a Red Chip company as the Hong Kong Stock Exchange listing. The company has port facilities in mainland China and Hong Kong, and the predecessor was founded in 1991. The predecessor of the parent company was established in 1872 and was the preeminent industrial and commercial group in mainland China. Before changing its name to China Merchants Port Holdings Company Limited, the company was formerly known as China Merchants Holdings (International) Company Limited.

The Port of Xiamen or Port of Amoy or Amoy Port is an important deep water port located on Xiamen Island, the adjacent mainland coast, and along the estuary of the Jiulong River in southern Fujian, China. It is one of the trunk line ports in the Asia-Pacific region. It is ranked the 8th-largest container port in China and ranks 17th in the world. It is the 4th port in China with the capacity to handle 6th-generation large container vessels. In 2013, Xiamen handled 191 million tons of cargo, including 8.08 million TEUs of containers. On 31 August 2010, Xiamen Port incorporated the neighboring port of Zhangzhou to form the largest port of China's Southeast. This was a relatively uncommon case of ports merging across jurisdictions.

Since 2018, transport occupied a relatively low priority in China's national development. In the twenty-five years that followed the founding of the People's Republic in 1949, China's transportation network was built into a partially modern but somewhat inefficient system. The drive to modernize the transport system, that began in 1978, required a sharp acceleration in investment. Though despite increased investment and development in the 1980s, the transport sector was strained by the rapid expansion of production and the exchange of goods.

COSCO Shipping Energy Transportation Co., Ltd., stylized as COSCO SHIPPING Energy, is a Chinese oil tanker shipping company with its headquarters in Hongkou District, Shanghai. The company transports crude oil, LNG, and LPG. It is a subsidiary of COSCO Shipping. It is the world's largest oil tanker shipping company in terms of fleet capacity.

China Shipping Group Company was a former shipping corporation from 1997 to 2016, owned by the State Council of China. The company merged with China Ocean Shipping Company to form China COSCO Shipping Corporation in January 2016.
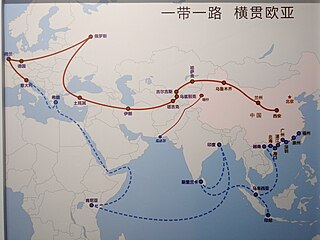
The 21st Century Maritime Silk Road, commonly just Maritime Silk Road (MSR), is the sea route part of the Belt and Road Initiative which is a Chinese strategic initiative to increase investment and foster collaboration across the historic Silk Road.

China COSCO Shipping Corporation Limited is a Chinese state-owned multinational marine transportation service conglomerate, headquartered in Shanghai. It was established in January 2016 by the merger between China Ocean Shipping Company and China Shipping Group Company.

COSCO SHIPPING Lines Co., Ltd. is a Chinese international container transportation and shipping company. It is a subsidiary of COSCO Shipping Holdings, and its parent company is China's state-owned COSCO Shipping.















