
The United States House of Representatives elections in California, 1998 was an election for California's delegation to the United States House of Representatives, which occurred as part of the general election of the House of Representatives on November 3, 1998. Democrats gained the 1st district but lost the 3rd and 36th districts for a net loss of one seat.

The United States House of Representatives elections in California, 1994 was an election for California's delegation to the United States House of Representatives, which occurred as part of the general election of the House of Representatives on November 8, 1994. As in much of the country during the Republican Revolution, Republicans made gains in California's House delegation, gaining three seats. In a December 12, 1995, special election former Rep. Tom Campbell won Rep. Norman Mineta's old seat and tied the delegation at 26 seats a piece. This would be the last time that Republicans defeated an incumbent Democrat in a general election in California until 2020. As of 2022 this is the last time Republicans won the house popular vote in California.
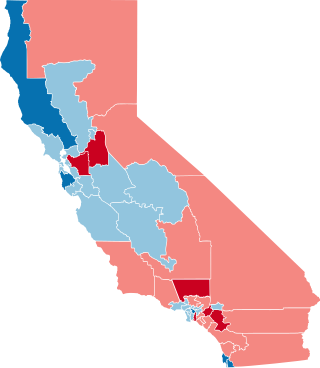
The United States House of Representatives elections in California, 1992 was an election for California's delegation to the United States House of Representatives, which occurred as part of the general election of the House of Representatives on November 3, 1992. California gained seven seats after the 1990 census, five of which were won by Republicans and two by Democrats. Of California's already-existing seats, Democrats won three Republican-held seats while Republicans won one Democratic-held seat.

The United States House of Representatives elections in California, 1982 was an election for California's delegation to the United States House of Representatives, which occurred as part of the general election of the House of Representatives on November 2, 1982. California gained two seats, both of which were won by Democrats, as a result of the 1980 census, and Democrats picked up three Republican-held districts.

The United States House of Representatives elections in California, 1978 was an election for California's delegation to the United States House of Representatives, which occurred as part of the general election of the House of Representatives on November 7, 1978. Republicans knocked off three Democratic incumbents. 11th district Congressman Leo Ryan was re-elected, but was murdered while investigating the Peoples Temple in Guyana following the election.

The United States House of Representatives elections in California, 1972 was an election for California's delegation to the United States House of Representatives, which occurred as part of the general election of the House of Representatives on November 7, 1972. California gained 5 seats as a result of the 1970 census, three of which were won by Democrats and two by Republicans. Of California's existing House seats, none switched parties.

The United States House of Representatives elections in California, 1966 was an election for California's delegation to the United States House of Representatives, which occurred as part of the general election of the House of Representatives on November 8, 1966. Republicans gained three seats from the Democrats. There was a mid-decade redistricting of the California districts in 1966.

The United States House of Representatives elections in California, 1962 was an election for California's delegation to the United States House of Representatives, which occurred as part of the general election of the House of Representatives on November 6, 1962. California gained eight districts as a result of the 1960 census, seven of which were won by Democrats and one by a Republican. Of California's existing districts, Democrats picked up three and lost one.

The United States House of Representatives elections in California, 1958 was an election for California's delegation to the United States House of Representatives, which occurred as part of the general election of the House of Representatives on November 4, 1958. Democrats picked up three seats, taking a majority of the delegation, which they would keep ever since except for a brief tie with the Republicans in the 104th Congress.

The United States House of Representatives elections in California, 1942 was an election for California's delegation to the United States House of Representatives, which occurred as part of the general election of the House of Representatives on November 3, 1942. California gained three districts as a result of the 1940 census, two of which were won by Democrats and one by Republicans. Of California's existing seats, Democrats and Republicans each swapped one district.

The United States House of Representatives elections in California, 1936 was an election for California's delegation to the United States House of Representatives, which occurred as part of the general election of the House of Representatives on November 3, 1936. Democrats gained two Republican-held districts and the Progressive Party gained one Republican-held district.

The United States House of Representatives elections in California, 1932 was an election for California's delegation to the United States House of Representatives, which occurred as part of the general election of the House of Representatives on November 8, 1932. This election began the transition of California from a solidly Republican state to a swing state, which it would be for the next 60 years. California gained nine seats as a result of the 1930 census; it would have been six if the House seats were reapportioned in 1920 since California would have had 14 seats as a result of the 1920 census. Democrats won six of those seats while Republicans won three. Of California's existing seats, Democrats won four Republican-held seats.

The United States House of Representatives elections in California, 1922 was an election for California's delegation to the United States House of Representatives, which occurred as part of the general election of the House of Representatives on November 7, 1922. The districts were not reapportioned after the 1920 census, so the state's delegation remained at 11 representatives, and the partisan makeup remained unchanged, at 9 Republicans and 2 Democrats.

The United States House of Representatives elections in California, 1904 was an election for California's delegation to the United States House of Representatives, which occurred as part of the general election of the House of Representatives on November 8, 1904. Republicans won the three Democratic-held districts, giving California an all-Republican House delegation, which it would maintain until 1910.
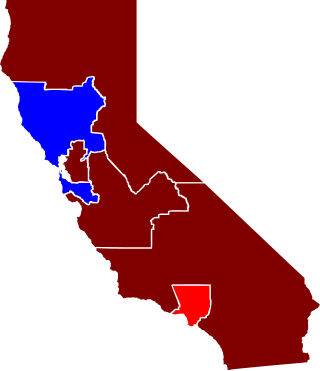
An election was held for California's delegation to the United States House of Representatives as part of the general election of the House of Representatives on November 4, 1902. California gained one seat as a result of the 1900 census, which Republicans won. However, of the existing districts, Democrats won three Republican-held districts.
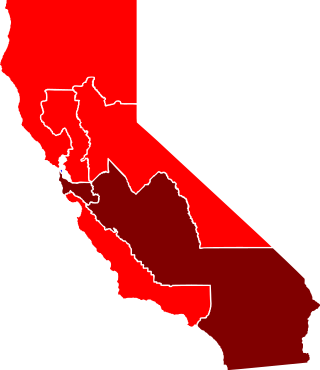
The United States House of Representatives elections in California, 1894 was an election for California's delegation to the United States House of Representatives, which occurred as part of the general election of the House of Representatives on November 6, 1894. Republicans picked up three Democratic-held districts and the lone Populist open seat.

The United States House of Representatives elections in California, 1884 was an election for California's delegation to the United States House of Representatives, which occurred as part of the general election of the House of Representatives on November 4, 1884. Republicans won both newly created districts and three of the four existing districts.

The United States House of Representatives elections in California, 1879 were elections for California's delegation to the United States House of Representatives, which occurred on September 3, 1879. California's delegation remained unchanged, at three Republicans and one Democrat.
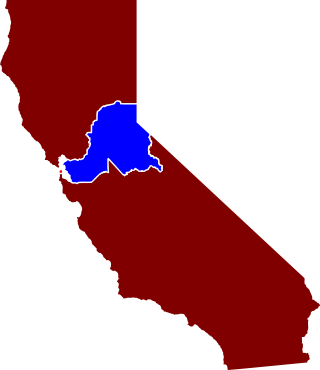
The United States House of Representatives elections in California, 1872 was an election for California's delegation to the United States House of Representatives, which occurred as part of the general election of the House of Representatives on November 5, 1872. California gained one seat as a result of the 1870 census, which the Republicans won. The Democrats, however, gained a Republican-held district.
The United States House of Representatives elections in California, 1864 were elections for California's delegation to the United States House of Representatives, which occurred as part of the general election of the House of Representatives on November 8, 1864. California's all-Republican delegation was unchanged. This was the first election in which California was divided into districts. Formerly, all three seats were elected at-large.













