
Biology – The natural science that studies life. Areas of focus include structure, function, growth, origin, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy.

Ecology is the natural science of the relationships among living organisms and their environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere levels. Ecology overlaps with the closely related sciences of biogeography, evolutionary biology, genetics, ethology, and natural history.

An ecosystem is a system formed by organisms in interaction with their environment. The biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows.

In ecology, a niche is the match of a species to a specific environmental condition. It describes how an organism or population responds to the distribution of resources and competitors and how it in turn alters those same factors. "The type and number of variables comprising the dimensions of an environmental niche vary from one species to another [and] the relative importance of particular environmental variables for a species may vary according to the geographic and biotic contexts".
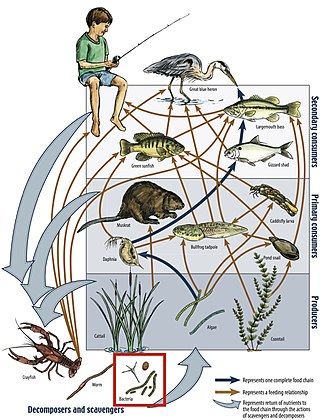
A food web is the natural interconnection of food chains and a graphical representation of what-eats-what in an ecological community. Position in the food web, or trophic level, is used in ecology to broadly classify organisms as autotrophs or heterotrophs. This is a non-binary classification; some organisms occupy the role of mixotrophs, or autotrophs that additionally obtain organic matter from non-atmospheric sources.

Landscape ecology is the science of studying and improving relationships between ecological processes in the environment and particular ecosystems. This is done within a variety of landscape scales, development spatial patterns, and organizational levels of research and policy. Landscape ecology can be described as the science of "landscape diversity" as the synergetic result of biodiversity and geodiversity.

Urban ecology is the scientific study of the relation of living organisms with each other and their surroundings in an urban environment. An urban environment refers to environments dominated by high-density residential and commercial buildings, paved surfaces, and other urban-related factors that create a unique landscape. The goal of urban ecology is to achieve a balance between human culture and the natural environment.

Biological dispersal refers to both the movement of individuals from their birth site to their breeding site and the movement from one breeding site to another . Dispersal is also used to describe the movement of propagules such as seeds and spores. Technically, dispersal is defined as any movement that has the potential to lead to gene flow. The act of dispersal involves three phases: departure, transfer, and settlement. There are different fitness costs and benefits associated with each of these phases. Through simply moving from one habitat patch to another, the dispersal of an individual has consequences not only for individual fitness, but also for population dynamics, population genetics, and species distribution. Understanding dispersal and the consequences, both for evolutionary strategies at a species level and for processes at an ecosystem level, requires understanding on the type of dispersal, the dispersal range of a given species, and the dispersal mechanisms involved. Biological dispersal can be correlated to population density. The range of variations of a species' location determines the expansion range.

An ecosystem engineer is any species that creates, significantly modifies, maintains or destroys a habitat. These organisms can have a large impact on species richness and landscape-level heterogeneity of an area. As a result, ecosystem engineers are important for maintaining the health and stability of the environment they are living in. Since all organisms impact the environment they live in one way or another, it has been proposed that the term "ecosystem engineers" be used only for keystone species whose behavior very strongly affects other organisms.

Charles Sutherland Elton was an English zoologist and animal ecologist. He is associated with the development of population and community ecology, including studies of invasive organisms.

In ecology, habitat refers to the array of resources, physical and biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species habitat can be seen as the physical manifestation of its ecological niche. Thus "habitat" is a species-specific term, fundamentally different from concepts such as environment or vegetation assemblages, for which the term "habitat-type" is more appropriate.
Habitat destruction occurs when a natural habitat is no longer able to support its native species. The organisms once living there have either moved elsewhere, or are dead, leading to a decrease in biodiversity and species numbers. Habitat destruction is in fact the leading cause of biodiversity loss and species extinction worldwide.

The Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia (IBRA) is a biogeographic regionalisation of Australia developed by the Australian government's Department of Sustainability, Environment, Water, Population, and Communities. It was developed for use as a planning tool, for example for the establishment of a national reserve system. The first version of IBRA was developed in 1993–94 and published in 1995.

Reconciliation ecology is the branch of ecology which studies ways to encourage biodiversity in the human-dominated ecosystems of the anthropocene era. Michael Rosenzweig first articulated the concept in his book Win-Win Ecology, based on the theory that there is not enough area for all of earth's biodiversity to be saved within designated nature preserves. Therefore, humans should increase biodiversity in human-dominated landscapes. By managing for biodiversity in ways that do not decrease human utility of the system, it is a "win-win" situation for both human use and native biodiversity. The science is based in the ecological foundation of human land-use trends and species-area relationships. It has many benefits beyond protection of biodiversity, and there are numerous examples of it around the globe. Aspects of reconciliation ecology can already be found in management legislation, but there are challenges in both public acceptance and ecological success of reconciliation attempts.
Spatial ecology studies the ultimate distributional or spatial unit occupied by a species. In a particular habitat shared by several species, each of the species is usually confined to its own microhabitat or spatial niche because two species in the same general territory cannot usually occupy the same ecological niche for any significant length of time.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to ecology:

In ecology, a community is a group or association of populations of two or more different species occupying the same geographical area at the same time, also known as a biocoenosis, biotic community, biological community, ecological community, or life assemblage. The term community has a variety of uses. In its simplest form it refers to groups of organisms in a specific place or time, for example, "the fish community of Lake Ontario before industrialization".
This glossary of geology is a list of definitions of terms and concepts relevant to geology, its sub-disciplines, and related fields. For other terms related to the Earth sciences, see Glossary of geography terms (disambiguation).

A nutrient cycle is the movement and exchange of inorganic and organic matter back into the production of matter. Energy flow is a unidirectional and noncyclic pathway, whereas the movement of mineral nutrients is cyclic. Mineral cycles include the carbon cycle, sulfur cycle, nitrogen cycle, water cycle, phosphorus cycle, oxygen cycle, among others that continually recycle along with other mineral nutrients into productive ecological nutrition.
This glossary of biology terms is a list of definitions of fundamental terms and concepts used in biology, the study of life and of living organisms. It is intended as introductory material for novices; for more specific and technical definitions from sub-disciplines and related fields, see Glossary of cell biology, Glossary of genetics, Glossary of evolutionary biology, Glossary of ecology, Glossary of environmental science and Glossary of scientific naming, or any of the organism-specific glossaries in Category:Glossaries of biology.















