Appointment
After the election, the President nominate the candidate of the party which gained the most votes to form a government within a month. The nominee must submit its program to the Assembly of the Representatives of the People and get the trust of the majority of its members before being formally appointed the Head of Government by the President. If it fails to form a government or if it does not get the confidence, the President initiates consultations with the political parties to find the best candidate. If, four months after the election, the Assembly did not give confidence in the Head of Government, the President can call new election.

Following the 2011 Tunisian revolution, Elections in Tunisia for the president and the unicameral Assembly of the Representatives of the People are scheduled to be held every five years. The assembly can be dissolved before finishing a full term.

The President of Tunisia, formally known as the President of the Republic of Tunisia, is the head of state of Tunisia. Tunisia is a semi-presidential republic, whereby the president is the head of state and the prime minister is head of government. Under Article 77 of the Constitution of Tunisia, the president is also the commander-in-chief of the Tunisian Armed Forces.
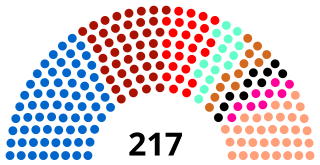
The Assembly of the Representatives of the People is Tunisia's legislative branch of government. The unicameral Assembly replaced the Constituent Assembly and was elected on 26 October 2014. The legislature consists of 217 seats. Before the 2011 revolution, Tunisia's parliament was formerly bicameral and consisted of an upper chamber called the Chamber of Advisors and a lower chamber called the Chamber of Deputies.
The Head of the Government swears to the following oath in the presence of the President:
I swear by Almighty God to work faithfully for the good of Tunisia, to respect its Constitution and laws, scrupulously to their interests and serve loyally.
Constitutional powers
The powers of the Head of Government are established by the current Constitution of Tunisia of 2014. The Head of Government is primarily responsible for domestic policy, while foreign policy, defense and domestic security are handled by the President. [1]

The Constitution of Tunisia is the supreme law of the Tunisian Republic. The constitution is the framework for the organization of the Tunisian government and for the relationship of the federal government with the governorates, citizens, and all people within Tunisia. Tunisia's first modern constitution was the Fundamental Pact of 1857. This was followed by the Constitution of 1861, which was not replaced until after the departure of French administrators in 1956, by the constitution of 1959. It was adopted on 1 June 1959 and amended in 1999 and 2002, after the Tunisian constitutional referendum of 2002.
The Head of Government are responsible for:
- Creating, amending and dissolving ministries (Except ministries of Defence and Foreign Affairs which require the president's approval).
- Creating, amending and dissolving public institutions, public entities and administrative departments.
- Issuing governmental decrees after consulting the Council of Ministers.
- Shall endorse and sign, where appropriate, regulatory orders issued by ministers.
- Request the parliament to give vote of confidence to their government.
The Head of Government, together with the President, represent Tunisia at home and abroad.
In the event the President is temporarily unable to carry out his duties, the Head of Government serves as Acting President for a maximum of 60 days. If the disability is permanent or the result of the President's resignation or death, the President of the Assembly of the Representatives of the People becomes Interim President for a period of 45 to 90 days pending new elections.

The Speaker of the Assembly of the Representatives of the People of Tunisia is the presiding officer of the Assembly of the Representatives of the People, the unicameral legislature of Tunisia.

A prime minister is the head of a cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. A prime minister is not a head of state or chief executive officer of their respective nation, rather they are a head of government, serving typically under a monarch in a hybrid of aristocratic and democratic government forms or a president in a republican form of government.

The Prime Minister of Spain, officially the President of the Government of Spain, is the head of the government of Spain. The office was established in its current form by the Constitution of 1978 and originated in 1823 as a chairmanship of the extant Council of Ministers.
The constructive vote of no confidence is a variation on the motion of no confidence that allows a parliament to withdraw confidence from a head of government only if there is a positive majority for a prospective successor. The principle is intended to ensure that a replacement head of government has enough parliamentary support to govern.

The prime minister of Albania, officially styled Prime Minister of the Republic of Albania, is the head of government of the Republic of Albania and as well the most powerful and influential person in Albanian politics. The prime minister holds the executive power of the nation and represents the Council of Ministers and chairs its meetings.

The president of Romania is the head of state of Romania. The president is directly elected by a two-round system for a five-year term. An individual may serve two terms. During his or her term in office, the president may not be a member of any political party.

The President of the Arab Republic of Egypt is the head of state of Egypt. Under the various iterations of the Constitution of Egypt, the president is also the Supreme Commander of the Armed Forces and head of the executive branch of the Egyptian government. The current president is Abdel Fattah el-Sisi, in office since 8 June 2014.

The Reichspräsident was the German head of state under the Weimar constitution, which was officially in force from 1919 to 1945. In English he was usually simply referred to as the President of Germany. The German title Reichspräsident literally means President of the Reich.

The President of the Portuguese Republic is the executive head of state of Portugal. The powers, functions and duties of prior presidential offices, and their relation with the Prime Minister and cabinets have over time differed with the various Portuguese constitutions.

The Prime Minister of Georgia is the head of government and chief executive of Georgia. The Prime Minister organizes, directs, and controls the functions of the Government and signs the legal acts of the government. They appoint and dismiss ministers in the government. The Prime Minister represents Georgia in foreign relations and concludes international treaties on behalf of Georgia. They are accountable for the activities of the Government before the Parliament of Georgia.
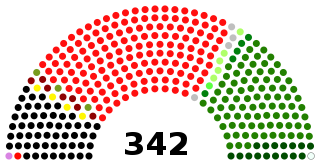
The National Assembly is the lower house of the bicameral Majlis-e-Shura, which also comprises the Senate of Pakistan. The National Assembly and the Senate both convene at Parliament House in Islamabad. The National Assembly is a democratically elected body consisting of a total of 336 members, before 25th amendment they used to be 342' who are referred to as Members of the National Assembly (MNAs), of which 272 are directly elected members and 70 reserved seats for women and religious minorities. A political party must secure 137 seats to obtain and preserve a majority.

The Parliament of Egypt, officially the House of Representatives is currently a unicameral legislature.

The Constitution of the Arab Republic of Egypt was the former constitution of Egypt. It was adopted on 11 September 1971 through a public referendum. It was later amended in 1980, 2005, and 2007. It was proclaimed to update the democratic representative system in assertion of the rule of law, independence of the judiciary, and party plurality. On 13 February 2011, the Constitution was suspended following the resignation of President Hosni Mubarak as a result of the 2011 Egyptian Revolution. On 30 March 2011, it was officially voided after a new provisional constitution was passed by the country's ruling Supreme Council of the Armed Forces.

The Prime Minister of the Kingdom of Cambodia is the head of government of Cambodia. The prime minister is also the chairman of the Cabinet and leads the executive branch of the Royal Cambodian Government. The prime minister is a member of parliament, and is appointed by the monarch for a term of five years. Since 1945, 36 individuals have served as prime minister; 32 as official prime ministers, and 4 in acting capacities.

The Government of Romania forms one half of the executive branch of the government of Romania. It is headed by the Prime Minister of Romania, and consists of the ministries, various subordinated institutions and agencies, and the 42 prefectures. The seat of the Romanian Government is at Victoria Palace in Bucharest.

The Cabinet of Ministers of the Republic of Mauritius is the official council which advises the President of the Republic in the making of major decisions. It is led by the Prime Minister and a total of 23 ministers and the Attorney General, who is considered to be a cabinet member. The constitution of the Republic provides a cabinet under the leadership of the Prime Minister that must be appointed by the President after each general elections.

There have been eight Prime Ministers of Slovenia, officially President of the Government of the Republic of Slovenia, since the country gained parliamentary democracy in 1989 and independence in 1991.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.

























































