
A glacier is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. Glaciers slowly deform and flow under stresses induced by their weight, creating crevasses, seracs, and other distinguishing features. They also abrade rock and debris from their substrate to create landforms such as cirques and moraines. Glaciers form only on land and are distinct from the much thinner sea ice and lake ice that forms on the surface of bodies of water.

A valley is a low area between hills or mountains typically with a river running through it. In geology, a valley or dale is a depression that is longer than it is wide. The terms U-shaped and V-shaped are descriptive terms of geography to characterize the form of valleys. Most valleys belong to one of these two main types or a mixture of them, at least with respect to the cross section of the slopes or hillsides.

An inselberg or monadnock is an isolated rock hill, knob, ridge, or small mountain that rises abruptly from a gently sloping or virtually level surrounding plain. In Southern Africa a similar formation of granite is known as a koppie, an Afrikaans word from the Dutch diminutive word kopje. If the inselberg is dome-shaped and formed from granite or gneiss, it can also be called a bornhardt, though not all bornhardts are inselbergs.

In geomorphology, a butte is an isolated hill with steep, often vertical sides and a small, relatively flat top; buttes are smaller landforms than mesas, plateaus, and tablelands. The word butte comes from a French word meaning knoll ; its use is prevalent in the Western United States, including the southwest where mesa is used for the larger landform. Because of their distinctive shapes, buttes are frequently landmarks in plains and mountainous areas. To differentiate, geographers use the rule of thumb that a mesa has a top that is wider than its height, while a butte has a top that is narrower than its height.

A mesa is an isolated, flat-topped elevation, ridge or hill, which is bounded from all sides by steep escarpments and stands distinctly above a surrounding plain. Mesas characteristically consist of flat-lying soft sedimentary rocks capped by a more resistant layer or layers of harder rock, e.g. shales overlain by sandstones. The resistant layer acts as a caprock that forms the flat summit of a mesa. The caprock can consist of either sedimentary rocks such as sandstone and limestone; dissected lava flows; or a deeply eroded duricrust. Unlike plateau, whose usage does not imply horizontal layers of bedrock, e.g. Tibetan Plateau, the term mesa applies exclusively to the landforms built of flat-lying strata. Instead, flat-topped plateaus are specifically known as tablelands.

In geology and physical geography, a plateau, also called a high plain or a tableland, is an area of a highland consisting of flat terrain, that is raised sharply above the surrounding area on at least one side. Often one or more sides have deep hills. Plateaus can be formed by a number of processes, including upwelling of volcanic magma, extrusion of lava, and erosion by water and glaciers. Plateaus are classified according to their surrounding environment as intermontane, piedmont, or continental. A few plateaus may have a small flat top while others have wide ones.
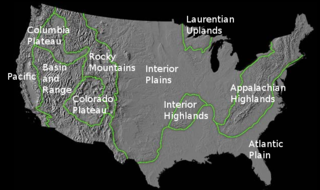
The richly textured landscape of the United States is a product of the dueling forces of plate tectonics, weathering and erosion. Over the 4.5 billion-year history of our Earth, tectonic upheavals and colliding plates have raised great mountain ranges while the forces of erosion and weathering worked to tear them down. Even after many millions of years, records of Earth's great upheavals remain imprinted as textural variations and surface patterns that define distinctive landscapes or provinces.

A ridge or a mountain ridge is a geographical feature consisting of a chain of mountains or hills that form a continuous elevated crest for some distance. The sides of the ridge slope away from narrow top on either side. The lines along the crest formed by the highest points, with the terrain dropping down on either side, are called the ridgelines. Ridges are usually termed hills or mountains as well, depending on size.

A cirque is an amphitheatre-like valley formed by glacial erosion. Alternative names for this landform are corrie and cwm. A cirque may also be a similarly shaped landform arising from fluvial erosion.

The Garibaldi Volcanic Belt is a northwest-southeast trending volcanic chain in the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains that extends from Watts Point in the south to the Ha-Iltzuk Icefield in the north. This chain of volcanoes is located in southwestern British Columbia, Canada. It forms the northernmost segment of the Cascade Volcanic Arc, which includes Mount St. Helens and Mount Baker. Most volcanoes of the Garibaldi chain are dormant stratovolcanoes and subglacial volcanoes that have been eroded by glacial ice. Less common volcanic landforms include cinder cones, volcanic plugs, lava domes and calderas. These diverse formations were created by different styles of volcanic activity, including Peléan and Plinian eruptions.

Glacial landforms are landforms created by the action of glaciers. Most of today's glacial landforms were created by the movement of large ice sheets during the Quaternary glaciations. Some areas, like Fennoscandia and the southern Andes, have extensive occurrences of glacial landforms; other areas, such as the Sahara, display rare and very old fossil glacial landforms.
Fluvio refers to things related to rivers and glacial refers to something that is of ice. Fluvio-glacial refers to the meltwater created when a glacier melts. Fluvio-glacial processes can occur on the surface and within the glacier. The deposits that happen within the glacier are revealed after the entire glacier melts or partially retreats. Fluvio-glacial landforms and erosional surfaces include: outwash plains, kames, kame terraces, kettle holes, eskers, varves, and proglacial lakes.

A tuya is a type of distinctive, flat-topped, steep-sided volcano formed when lava erupts through a thick glacier or ice sheet. They are rare worldwide, being confined to regions which were covered by glaciers and had active volcanism during the same period.

U-shaped valleys, trough valleys or glacial troughs, are formed by the process of glaciation. They are characteristic of mountain glaciation in particular. They have a characteristic U shape, with steep, straight sides and a flat or rounded bottom. Glaciated valleys are formed when a glacier travels across and down a slope, carving the valley by the action of scouring. When the ice recedes or thaws, the valley remains, often littered with small boulders that were transported within the ice, called glacial till or glacial erratic.

The geology of the Pacific Northwest includes the composition, structure, physical properties and the processes that shape the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The region is part of the Ring of Fire: the subduction of the Pacific and Farallon Plates under the North American Plate is responsible for many of the area's scenic features as well as some of its hazards, such as volcanoes, earthquakes, and landslides.

The Mount Edziza volcanic complex is a large and potentially active north-south trending complex volcano in Stikine Country, northwestern British Columbia, Canada, located 38 kilometres (24 mi) southeast of the small community of Telegraph Creek. It occupies the southeastern portion of the Tahltan Highland, an upland area of plateau and lower mountain ranges, lying east of the Boundary Ranges and south of the Inklin River, which is the east fork of the Taku River. As a volcanic complex, it consists of many types of volcanoes, including shield volcanoes, calderas, lava domes, stratovolcanoes, and cinder cones.

The Canadian Cascade Arc, also called the Canadian Cascades, is the Canadian segment of the North American Cascade Volcanic Arc. Located entirely within the Canadian province of British Columbia, it extends from the Cascade Mountains in the south to the Coast Mountains in the north. Specifically, the southern end of the Canadian Cascades begin at the Canada–United States border. However, the specific boundaries of the northern end are not precisely known and the geology in this part of the volcanic arc is poorly understood. It is widely accepted by geologists that the Canadian Cascade Arc extends through the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains. However, others have expressed concern that the volcanic arc possibly extends further north into the Kitimat Ranges, another subdivision of the Coast Mountains, and even as far north as Haida Gwaii.

The Mount Cayley volcanic field is a remote volcanic zone on the South Coast of British Columbia, Canada, stretching 31 km (19 mi) from the Pemberton Icefield to the Squamish River. It forms a segment of the Garibaldi Volcanic Belt, the Canadian portion of the Cascade Volcanic Arc, which extends from Northern California to southwestern British Columbia. Most of the Cayley volcanoes were formed during periods of volcanism under sheets of glacial ice throughout the last glacial period. These subglacial eruptions formed steep, flat-topped volcanoes and subglacial lava domes, most of which have been entirely exposed by deglaciation. However, at least two volcanoes predate the last glacial period and both are highly eroded. The field gets its name from Mount Cayley, the largest and most persistent volcano, located at the southern end of the Powder Mountain Icefield. This icefield covers much of the central portion of the volcanic field and is one of the several glacial fields in the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains.
This glossary of geography terms is a list of definitions of terms and concepts used in geography and related fields, which describe and identify spatial dimension, geographic locations, topographical features, natural resources, and the collection, analysis, and visualization of geographic data. For related terms, see Glossary of geology and Glossary of environmental science.