This article needs additional citations for verification .(May 2024) |
Vehicle registration plates of Poland indicate the region of registration of the vehicle given the number plate.
This article needs additional citations for verification .(May 2024) |
Vehicle registration plates of Poland indicate the region of registration of the vehicle given the number plate.
This article needs to be updated.(May 2024) |
According to Polish law, the registration plate is tied to the vehicle, not the owner. There is no possibility for the owner to keep the licence number for use on a different car, even if it's a cherished registration. The licence plates are issued by the powiat (county) of the vehicle owner's registered address of residence, in the case of a natural person. If it is owned by a legal person, the place of registration is determined by the person's address. Vehicles leased under operating leases and many de facto finance leases will be registered at the address of the lessor. When a vehicle changes hands, the new owner must apply for new vehicle registration document bearing their name and registered address. The new owner may obtain a new licence plate although it is not necessary. In such a situation the licence plates are usually carried over to the new owner, because the change carries an additional cost. Upon purchasing a vehicle from another person, if the vehicle has an EU plate, the new owner must replace it with a registration for their address and area, and give the EU plate to their powiat licensing authority to free up numbers in the future. If the car has a plate dated before May 1, 2006, the owner is free to do whatever they wish with it, as long as it is legal under Polish law. The plaque cannot be replaced if destroyed. The change of the whole set is required.
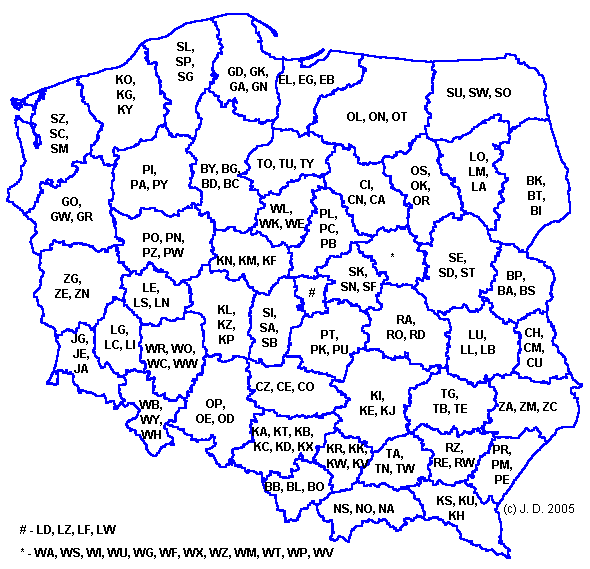
The change in system shown below in 2001 is related to the reduction in the previous year of the number of voivodeships in Poland from 49 to 16, based on the country's historic regions. The pre-2001 licence plates (white letters on black background) can be used indefinitely, but since they are obsolete they have to be replaced in case of change of vehicle's ownership.
In the pre-2001 model, there were not sufficient letters in the Polish alphabet for each of the old voivodeships to have a single letter. Only the standard latin alphabet was used (excluding Q), and the specific Polish characters with diacritics were excluded. Therefore, two letters had to be used to indicate the vehicle's origin (the middle administrative level of powiat was not introduced until 1999). Since the change, the first letter has always denoted the new voivodeship. One additional letter is used in cities with rights of powiat (this applies to 47 of 49 capitals of the old voivodeships, the exceptions being Ciechanów and Sieradz, and numerous major cities). Two additional letters are used in any other powiat.
It is not necessary for EU citizens to immediately re-register the vehicles they have brought with them if they are duly registered and taxed elsewhere in the EU, when living in Poland. This emerges from European law, although local regulations have to date not been changed to reflect the law, leading to officials locally sometimes giving incorrect advice on this point. When in doubt, motorists are recommended to refer to their respective embassies.

The licence plates are invalid without two adhesive stickers with holograms placed on the license plates, and, before 2022, [1] an adhesive plaque bearing the same number as the plates inside the windshield. If the vehicle uses only one licence plate then the second sticker must be attached to the registration documents.

Each powiat uses a unique two or three letter code, with the first letter denoting the voivodeship. The number pools listed below are not used in any particular order, although one pool is usually depleted before the next one is used. A visible gap exists between the area code and series, but there is no possibility of confusion if the number is written down without it.
The following characters are used in licence plate examples:

The letters used in licence plates include all standard Latin alphabet letters outside of Q (not used at all in the Polish language). The letters B, D, I, O, and Z cannot be used in series area (on the right, after the gap), because they could be confused with similarly-looking digits. Custom plates are allowed to include these letters though. The leading 0 in numbers is part of the code and is never omitted.
Due to the pool of license plates combinations possibly running out in some areas, [2] in 2022 the Ministry of Infrastructure issued a directive under which extra leading characters were introduced for several of the voivodeships: [3]
Reportedly, the Warsaw district of Mokotów was the first to start issuing AE registration plates following the new directive. [4]
Format:
The number of available unique numbers with these mentioned formats is 1,100,000 for each two-letter powiat code, and 872,400 for each three-letter powiat code. The combinations "XYZ 1234" and "XYZ 123J" are not used, because they would lead to creation of numbers identical to these in the old system. Also, the two-letter powiat codes must be followed by a leading digit, "XY 1...", to avoid confusion with the "XYZ ..." scheme, as the gap is not significant. Electric vehicles have green background on their license plates.

Format:
Cars – reduced size

Format:
The plates are designed for cars imported from USA and Japan. Reduced size plates are the same width as US plates.


Format:
These plates use black text on yellow background with an additional picture of a vintage car on the right side. Vehicles are required to meet three criteria: [5]
These criteria, however, can be waived for special cases, such as prototype vehicles that were never mass-produced, cars of considerable historical value, cars being part of museum exhibition or models representing technological breakthroughs. As such, issuing of these plates is always handled on a case-by-case basis by the conservation officer. Registered classic cars are not required to undergo yearly technical checkup unless used for transportation services, such as taxi.

Format:
These plates use red text on a white background. The plates wear a seal with month and year of validation. The windshield plaque is not issued with it.

Introduced on 1 January 2020, they are issued to battery-electric and hydrogen vehicles. They are similar to regular plates but the background colour is light green instead of white. Such vehicles are allowed to drive on bus lanes, therefore visibly different registration plates allow the police to establish whether a vehicle is doing so legally. Electric plates are also used in "American" plates with reduced space. [6]

Format:
These plates use red text on a white background. The last character is always the letter B (which stands for badawcza, or "research type"). Only car manufacturers and automobile R&D centres are issued these plates.

Format:
These plates use standard black letters on a white background. Each custom number starts with the letter denoting voivodeship and a single digit, followed by the gap. This digit and next characters can be picked by the owner. Outside the availability the following constrains are used:

Format:
Since July 2019 dealers of new cars can apply for special number plates with green letters on white background specifically for doing test drives. Those plates are issued exclusively for the company itself and not for a specific vehicle. This means they can be applied to multiple vehicles when needed. Only car retailers can obtain these and such cars can be driven only by the car dealer, owner of the company, their employees or customers, but only when accompanied by an employee.

Format:
White symbols on dark blue background. The leading character is reserved for voivodeship, but in practice all vehicles are issued W and registered by the Masovian voivode. [7] The first three digits indicate a country or organization as listed in the table below.
On top of the origin of the diplomatic mission, the vehicle's function can also be determined by the latter three digits: [8]
Diplomatic vehicles are also required to carry a sticker with CD (corps diplomatique) or CC (corps consulaire). [9]


Format:
Vehicles utilised used by the Polish Ministry of Internal Affairs and Administration use licence plates beginning with "H", instead of the voivodeship code. The second letter denotes the service, for example "HP" is used by the Polish Police. Any standard Latin letter outside Q can be used (unlike common licence plates). These services are also allowed to use common licence plates.
Codes:


Format:
The Polish military uses licence plates beginning with "U" instead of the voivodeship code. The following letter denotes the usage of the vehicle. For example, military trucks have licence plates beginning with "UC". The trailing T in the number denotes a tracked vehicle. The military are not obliged to use the standard licence plates on tracked vehicles, armoured cars and armoured personnel carriers — they can be painted on the vehicle itself or applied as a sticker.
Codes:



From July 1922 Polish car number plates had two letters denoting voivodeship (being an abbreviation of its name), or single letter W denoting capital city of Warsaw, and up to five digits. Except for letter identifier, each voivodeship had own range of numbers (except for autonomic Silesian Voivodeship, which used ŚL identifier and own numbers from 1). Plates were white, with red letters and black digits, separated with red dash.
There were also temporary plates with PR letters and presidential plates with WZK letters (for President of Poland chancellery). Military plates had only four white digits on black background.
From 1937 there was a new different system of registration numbers introduced, with white letters on black plates. There was one letter denoting vehicle type, two-digit number denoting voivodeship, and three-digit individual number after a dash. Letters A, B, C, D, E, H, K, L, X, Y, Z were used for cars, trucks and buses, T for taxicabs, M, N, P, R, S, U for motorcycles and W for military vehicles. A range of numbers 00 to 19 meant capital city of Warsaw, 20 to 24 indicated Białostok Voivodeship, and so on, in alphabetical order, up to 95 to 99 for Wołyńskie Voivodeship.
During World War II there were plates introduced by occupants.
From 1946 Polish car number plates had the LNN-NNN format, with L being a letter and N being a digit. The full name of the province was located at the bottom. [10]

From June 19, 1956, Polish car number plates had 2 letters and 4 digits, and after May 13, 1964, letters could stand after digits.[ citation needed ]
Individual elements meant:
Codes of voivodeships:[ citation needed ]
Codes of special forces:


Plates from the 1976–2000 series are still valid. They have white letters on black background. The coding used was three letters and four digits (XYZ 1234) or three letters, three digits and one letter (XYZ 123A), although at the beginning the configuration with a letter in the end was used for public cars only.
The following coding was used for the 49 regions of the country:
The following codes were used for special forces:
Special plates:
Since the year 2000 Polish car plates have black letters pressed onto white reflective blanks with an EU stripe and country code. The switch was made to conform with other EU countries and to increase visibility. The licence plates issued until May 1, 2006, bear a Polish national flag. Plates issued after that date have the 12 EU stars instead of the Polish flag.[ dubious – discuss ]