Contents
| Friedländer synthesis | |
|---|---|
| Named after | Paul Friedländer |
| Reaction type | Ring forming reaction |
| Identifiers | |
| Organic Chemistry Portal | friedlaender-synthesis |
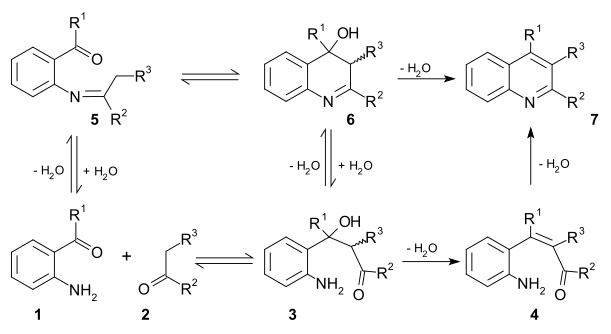
The Friedländer synthesis is a chemical reaction of 2-aminobenzaldehydes [1] with ketones to form quinoline derivatives. [2] [3] It is named after German chemist Paul Friedländer (1857–1923).
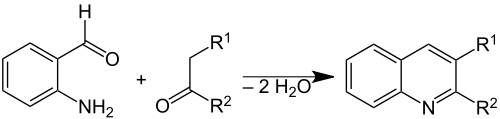
This reaction has been catalyzed by trifluoroacetic acid, [4] toluenesulfonic acid, [5] iodine, [6] and Lewis acids. [7]