
Manganese dioxide is the inorganic compound with the formula MnO
2. This blackish or brown solid occurs naturally as the mineral pyrolusite, which is the main ore of manganese and a component of manganese nodules. The principal use for MnO
2 is for dry-cell batteries, such as the alkaline battery and the zinc–carbon battery. MnO
2 is also used as a pigment and as a precursor to other manganese compounds, such as KMnO
4. It is used as a reagent in organic synthesis, for example, for the oxidation of allylic alcohols. MnO
2 has an α-polymorph that can incorporate a variety of atoms in the "tunnels" or "channels" between the manganese oxide octahedra. There is considerable interest in α-MnO
2 as a possible cathode for lithium-ion batteries.
Cubane is a synthetic hydrocarbon compound with the formula C8H8. It consists of eight carbon atoms arranged at the corners of a cube, with one hydrogen atom attached to each carbon atom. A solid crystalline substance, cubane is one of the Platonic hydrocarbons and a member of the prismanes. It was first synthesized in 1964 by Philip Eaton and Thomas Cole. Before this work, Eaton believed that cubane would be impossible to synthesize due to the "required 90 degree bond angles". The cubic shape requires the carbon atoms to adopt an unusually sharp 90° bonding angle, which would be highly strained as compared to the 109.45° angle of a tetrahedral carbon. Once formed, cubane is quite kinetically stable, due to a lack of readily available decomposition paths. It is the simplest hydrocarbon with octahedral symmetry.

A protecting group or protective group is introduced into a molecule by chemical modification of a functional group to obtain chemoselectivity in a subsequent chemical reaction. It plays an important role in multistep organic synthesis.

A permanganate is a chemical compound with the manganate(VII) ion, MnO−
4, the conjugate base of permanganic acid. Because the manganese atom has a +7 oxidation state, the permanganate(VII) ion is a strong oxidising agent. The ion is a transition metal ion with a tetrahedral structure. Permanganate solutions are purple in colour and are stable in neutral or slightly alkaline media. The exact chemical reaction depends on the carbon-containing reactants present and the oxidant used. For example, trichloroethane (C2H3Cl3) is oxidised by permanganate ions to form carbon dioxide (CO2), manganese dioxide (MnO2), hydrogen ions (H+), and chloride ions (Cl−).

In inorganic nomenclature, a manganate is any negatively charged molecular entity with manganese as the central atom. However, the name is usually used to refer to the tetraoxidomanganate(2−) anion, MnO2−
4, also known as manganate(VI) because it contains manganese in the +6 oxidation state. Manganates are the only known manganese(VI) compounds.

Sodium oxalate, or disodium oxalate, is a chemical compound with the chemical formula Na2C2O4. It is the sodium salt of oxalic acid. It contains sodium cations Na+ and oxalate anions C2O2−4. It is a white, crystalline, odorless solid, that decomposes above 290 °C.
In chemistry, hypomanganate, also called manganate(V) or tetraoxidomanganate(3−), is a trivalent anion (negative ion) composed of manganese and oxygen, with formula MnO3−
4.
Potassium hypomanganate is the inorganic compound with the formula K3MnO4. Also known as potassium manganate(V), this bright blue solid is a rare example of a salt with the hypomanganate or manganate(V) anion, where the manganese atom is in the +5 oxidation state. It is an intermediate in the production of potassium permanganate and the industrially most important Mn(V) compound.
Oppenauer oxidation, named after Rupert Viktor Oppenauer, is a gentle method for selectively oxidizing secondary alcohols to ketones.
The Rubottom oxidation is a useful, high-yielding chemical reaction between silyl enol ethers and peroxyacids to give the corresponding α-hydroxy carbonyl product. The mechanism of the reaction was proposed in its original disclosure by A.G. Brook with further evidence later supplied by George M. Rubottom. After a Prilezhaev-type oxidation of the silyl enol ether with the peroxyacid to form the siloxy oxirane intermediate, acid-catalyzed ring-opening yields an oxocarbenium ion. This intermediate then participates in a 1,4-silyl migration to give an α-siloxy carbonyl derivative that can be readily converted to the α-hydroxy carbonyl compound in the presence of acid, base, or a fluoride source.
In organic chemistry, a homologation reaction, also known as homologization, is any chemical reaction that converts the reactant into the next member of the homologous series. A homologous series is a group of compounds that differ by a constant unit, generally a methylene group. The reactants undergo a homologation when the number of a repeated structural unit in the molecules is increased. The most common homologation reactions increase the number of methylene units in saturated chain within the molecule. For example, the reaction of aldehydes or ketones with diazomethane or methoxymethylenetriphenylphosphine to give the next homologue in the series.

Dithietanes are saturated heterocyclic compounds that contain two divalent sulfur atoms and two sp3-hybridized carbon centers. Two isomers are possible for this class of organosulfur compounds:
The Hofmann–Löffler reaction (also referred to as Hofmann–Löffler–Freytag reaction, Löffler–Freytag reaction, Löffler–Hofmann reaction, as well as Löffler's method) is an organic reaction in which a cyclic amine 2 (pyrrolidine or, in some cases, piperidine) is generated by thermal or photochemical decomposition of N-halogenated amine 1 in the presence of a strong acid (concentrated sulfuric acid or concentrated CF3CO2H). The Hofmann–Löffler–Freytag reaction proceeds via an intramolecular hydrogen atom transfer to a nitrogen-centered radical and is an example of a remote intramolecular free radical C–H functionalization.
A hydroxynaphthoquinone is any of several organic compounds that can be viewed as derivatives of a naphthoquinone through replacement of one hydrogen atom (H) by a hydroxyl group (-OH).

Mary Peters Fieser was an American chemist best known for the many books she wrote with her husband Louis Fieser.
Alcohol oxidation is a collection of oxidation reactions in organic chemistry that convert alcohols to aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, and esters where the carbon carries a higher oxidation state. The reaction mainly applies to primary and secondary alcohols. Secondary alcohols form ketones, while primary alcohols form aldehydes or carboxylic acids.

1,4-Naphthoquinone or para-naphthoquinone is a quinone derived from naphthalene. It forms volatile yellow triclinic crystals and has a sharp odor similar to benzoquinone. It is almost insoluble in cold water, slightly soluble in petroleum ether, and more soluble in polar organic solvents. In alkaline solutions it produces a reddish-brown color. Vitamin K is a derivative of 1,4-naphthoquinone. It is a planar molecule with one aromatic ring fused to a quinone subunit. It is an isomer of 1,2-naphthoquinone.
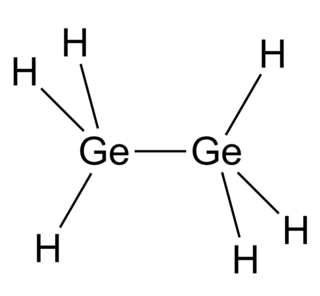
Digermane is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ge2H6. One of the few hydrides of germanium, it is a colourless liquid. Its molecular geometry is similar to ethane.

N-Hydroxyphthalimide is the organic compound with the formula C6H4(CO)2NOH. A white or yellow solid, it is a derivative of phthalimide. The compound is as a catalyst in the synthesis of other organic compounds. It is soluble in water and organic solvents such as acetic acid, ethyl acetate and acetonitrile.

2-Carboxybenzaldehyde is a chemical compound. It consists of a benzene ring, with an aldehyde and a carboxylic acid as substituents that are ortho to each other. The compound exhibits ring–chain tautomerism: the two substituents can react with each other to form 3-hydroxyphthalide, a cyclic lactol. This lactol reacts readily with Grignard reagents, forming alkyl- and aryl-substituted phthalides. Other benzo-fused heterocyclic compounds can be derived from 2-carboxybenzaldehyde, including isoindolinones and phthalazinones, with a variety of pharmacological properties, such as the antihistamine azelastine.












