External links
| | This article relating to law in the United States or its constituent jurisdictions is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
Title 25 is the portion of the Code of Federal Regulations that governs Government-to-Government relations with Native American tribes within the United States. It is available in digital or printed form.
| Volume | Chapter | Sections | Scope |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | I | 1–299 | Bureau of Indian Affairs (Department of the Interior)
|
| 2 | II | 300–399 | Indian Arts and Crafts Board (Department of the Interior) |
| III | 500–599 | National Indian Gaming Commission (Department of the Interior)
| |
| IV | 700–799 | The Office of Navajo and Hopi Indian Relocation | |
| V | 900 | Bureau of Indian Affairs (Department of the Interior) and Indian Health Service (Department of Health and Human Services) | |
| VI | 1000–1099 | Office of the Assistant Secretary, Indian Affairs (Department of the Interior) | |
| VII | 1200–1299 | Office of the Special Trustee for American Indians (Department of the Interior) |

The United States Code is the official codification of the general and permanent federal statutes of the United States. It contains 53 titles. The main edition is published every six years by the Office of the Law Revision Counsel of the House of Representatives, and cumulative supplements are published annually. The official version of these laws appears in the United States Statutes at Large, a chronological, uncodified compilation.
The Code of Federal Regulations, Telecommunications, containing the U.S. federal regulations for telecommunications can be found under Title 47 of the United States Code of Federal Regulations.
The Federal Aviation Regulations (FARs) are rules prescribed by the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) governing all aviation activities in the United States. The FARs comprise Title 14 of the Code of Federal Regulations. A wide variety of activities are regulated, such as aircraft design and maintenance, typical airline flights, pilot training activities, hot-air ballooning, lighter-than-air aircraft, human-made structure heights, obstruction lighting and marking, model rocket launches, commercial space operations, model aircraft operations, Unmanned Aircraft Systems (UAS) and kite flying. The rules are designed to promote safe aviation, protecting pilots, flight attendants, passengers and the general public from unnecessary risk.

In the law of the United States, the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) is the codification of the general and permanent regulations promulgated by the executive departments and agencies of the federal government of the United States. The CFR is divided into 50 titles that represent broad areas subject to federal regulation.

The Federal Register is the official journal of the federal government of the United States that contains government agency rules, proposed rules, and public notices. It is published every weekday, except on federal holidays. The final rules promulgated by a federal agency and published in the Federal Register are ultimately reorganized by topic or subject matter and codified in the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR), which is updated quarterly.

The Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC) is an independent bureau within the United States Department of the Treasury that was established by the National Currency Act of 1863 and serves to charter, regulate, and supervise all national banks and thrift institutions and the federally licensed branches and agencies of foreign banks in the United States. The acting Comptroller of the Currency is Michael J. Hsu, who took office on May 10, 2021.

Dangerous goods (DG), are substances that when transported are a risk to health, safety, property or the environment. Certain dangerous goods that pose risks even when not being transported are known as hazardous materials. An example for dangerous goods is hazardous waste which is waste that has substantial or potential threats to public health or the environment.
A Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN) is an identifying number used for tax purposes in the United States and in other countries under the Common Reporting Standard. In the United States it is also known as a Tax Identification Number (TIN) or Federal Taxpayer Identification Number (FTIN). A TIN may be assigned by the Social Security Administration (SSA) or by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS).
The Office of the Federal Register is an office of the United States government within the National Archives and Records Administration.

American whiskey is whiskey produced in the United States. American whiskeys made from mashes with at least 51% of their named grains include bourbon whiskey, rye whiskey, rye malt whiskey, malt whiskey, wheat whiskey, Tennessee whiskey, and corn whiskey.
Title 23 of the United States Code is a positive law title of the United States Code with the heading "Highways."
Title 44 of the United States Code outlines the role of public printing and documents in the United States Code.

In aviation, V-speeds are standard terms used to define airspeeds important or useful to the operation of all aircraft. These speeds are derived from data obtained by aircraft designers and manufacturers during flight testing for aircraft type-certification. Using them is considered a best practice to maximize aviation safety, aircraft performance, or both.
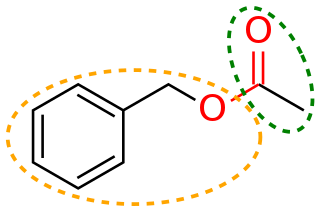
In organic chemistry, a moiety is a part of a molecule that is given a name because it is identified as a part of other molecules as well.

The New York State Department of State (NYSDOS) is the department of the New York state government under the leadership of the Secretary of State of New York. Its regulations are compiled in title 19 of the New York Codes, Rules and Regulations.
Title 1 of the Code of Federal Regulations, titled General Provisions, is a United States federal government regulation.
The California Bureau of Real Estate Appraisers (BREA) is a division of the California Department of Consumer Affairs responsible for real estate appraiser licensing and certification in California.
CFR Title 23 - Highways is one of fifty titles comprising the United States Code of Federal Regulations (CFR), containing the principal set of rules and regulations issued by federal agencies regarding highways. It is available in digital and printed form, and can be referenced online using the Electronic Code of Federal Regulations (e-CFR).