Classification of the Indigenous peoples of the Americas Last updated December 18, 2025
America , Western Hemisphere Cultural regions of North American people at the time of contact Early Indigenous languages in the US Historically, classification of the Indigenous peoples of the Americas is based upon cultural regions, geography, and linguistics. Anthropologists have named various cultural regions, with fluid boundaries, that are generally agreed upon with some variation. These cultural regions are broadly based upon the locations of the Indigenous peoples of the Americas from early European and African contact beginning in the late 15th century. When Indigenous peoples have been forcibly removed by nation-states, they retain their original geographic classification. Some groups span multiple cultural regions. Peoples can also be classified by genetics, technology, and social structure.
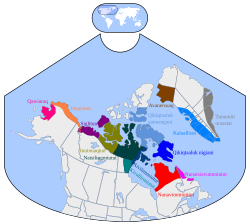
In the United States and Canada , ethnographers commonly classify Indigenous peoples into ten geographical regions with shared cultural traits, called cultural areas. [ 1] Greenland is part of the Arctic region . Some scholars combine the Plateau and Great Basin regions into the Intermontane West, some separate Prairie peoples from Great Plains peoples, while some separate Great Lakes tribes from the Northeastern Woodlands.
Arctic Inuktitut dialect map Early Indigenous languages in Alaska Paleo-Eskimo , precontact cultures, Russia, Alaska, Canada, Greenland, 2500 BCE–1500 CE Arctic small tool tradition , precontact culture, 2500 BCE, Bering Strait Pre-Dorset , eastern Arctic, 2500–500 BCE Saqqaq culture , Greenland, 2500–800 BCE Independence I , northeastern Canada and Greenland, 2400–1800 BCE Independence II culture , northeastern Canada and Greenland, 800–1 BCE) Groswater culture , Labrador and Nunavik, Canada Dorset culture , 500 BCE–1500 CE, Alaska, Canada Aleut (Unangan ), Aleutian Islands of Alaska, and Kamchatka Krai, Russia Inuit , Russia, Alaska, Canada, Greenland Yupik peoples (Yup'ik ), Alaska and Russia Subarctic Ahtna (Ahtena, Nabesna), Alaska Anishinaabe – see also Northeastern Woodlands Oji-Cree (Anishinini, Severn Ojibwa) Ontario, Manitoba Ojibwa (Chippewa , Ojibwe ) Ontario, Manitoba, Michigan, Minnesota, Montana, North Dakota Atikamekw , Quebec Cree , Central and Eastern Canada, North Dakota Dakelh (Carrier ), British Columbia Deg Hit’an (Deg Xinag, Degexit’an, Kaiyuhkhotana), Alaska [ 2] Dena’ina (Tanaina ), Alaska Dene people , Alaska, Yukon, Northwest Territories, British Columbia, Alberta, Saskatchewan, Manitoba Chipewyan , Alaskan interior, Western Canada Tłı̨chǫ (Tlicho ), Northwest Territories Yellowknives (T'atsaot'ine ), Northwest Territories Slavey (Awokanak , Slave , Deh Gah Got'ine , Deh Cho ), Alberta, British Columbia [ 3] Sahtú (North Slavey , Bearlake , Hare , Mountain ), Northwest Territories Gwich'in (Kutchin , Loucheaux ), Alaska, Yukon Dane-zaa (Beaver , Dunneza ), Alberta, British Columbia Hän , Alaska, Yukon Holikachuk , Alaska Innu (Montagnais ), Labrador, Quebec Kaska Dena (Nahane ), Yukon Kolchan (Upper Kuskokwim ) Koyukon , Alaska Naskapi , Quebec, Newfoundland and Labrador Sekani (Tse'khene ), British Columbia Tagish , Yukon Tahltan , British Columbia Tanana Athabaskans (Tanacross ), Alaska Pacific Northwest coast Of the Indigenous peoples of the Northwest Coast, it is widely agreed upon by scholars that that the area north of the Haisla represents a cultural subarea, called the "Northern" or "Northern Maritime" area. However, south of this, there is a deal of disagreement on the existence of any subareas, especially south of Vancouver Island . [ 4] For the purposes of organization, south of the Northern subarea, tribes are grouped by language family.
Northwest Plateau Chelan , WA Coeur d'Alene Tribe , ID, MT, WA Entiat , WA Flathead (Selisch or Salish), ID, MT Kalispel (Pend d'Oreilles ), MT, WA Methow , WA Nespelem , WA Nlaka'pamux (Thompson people), BC Nicola people (Thompson-Okanagan confederacy) Sanpoil , WA Secwepemc , BC (Shuswap people) Sinixt (Lakes), BC, ID, and WA Sinkayuse (Sinkiuse-Columbia ), WA (extinct) Spokane people , WA Syilx (Okanagan ), BC, WA St'at'imc , BC (Upper Lillooet) Wenatchi (Wenatchee), WA Cowlitz , (Upper Cowlitz, Taidnapam), Washington Klickitat , Washington Nez Perce , Idaho Tenino (Tygh, Warm Springs), Oregon Umatilla , Idaho, Oregon Walla Walla , WA Wanapum , WA Wauyukma , WA Wyam (Lower Deschutes), OR Yakama , WA Cayuse , Oregon, Washington Celilo (Wayampam ), Oregon Cowlitz , Washington Kalapuya , northwest Oregon Klamath , Oregon Kutenai (Kootenai , Ktunaxa ), British Columbia, Idaho, and Montana Lower Snake people: Chamnapam , Wauyukma , Naxiyampam , Washington Modoc , formerly California, now Oklahoma and Oregon Molala (Molale), Oregon Nicola Athapaskans (extinct), British Columbia Palus (Palouse), Idaho, Oregon, and Washington Upper Nisqually (Mishalpan ), Washington Great Plains Indigenous peoples of the Great Plains are often separated into Northern and Southern Plains tribes.
Anishinaabeg (Anishinape, Anicinape, Neshnabé, Nishnaabe) (see also Subarctic , Northeastern Woodlands ) Saulteaux (Nakawē), Manitoba, Minnesota and Ontario; later Alberta, British Columbia, Montana, Saskatchewan Odawa people (Ottawa), Ontario, [ 7] Michigan, later Oklahoma Potawatomi , Michigan, [ 7] Ontario, Indiana, Wisconsin, later Oklahoma Apache (see also Southwest ) Arapaho (Arapahoe), formerly Colorado, currently Oklahoma and Wyoming Arikara (Arikaree, Arikari, Ree), North Dakota Atsina (Gros Ventre), Montana Blackfoot Cheyenne , Montana, Oklahoma Comanche , Oklahoma, Texas Plains Cree , Montana Crow (Absaroka, Apsáalooke), Montana Escanjaques , Oklahoma Hidatsa , North Dakota Iowa (Ioway), Kansas, Nebraska, Oklahoma Kaw (Kansa, Kanza), Oklahoma Kiowa , Oklahoma Mandan , North Dakota Métis people (Canada) , North Dakota, Manitoba, Saskatchewan, Alberta Missouri (Missouria), Oklahoma Omaha , Nebraska Osage , Oklahoma, formerly Arkansas, Missouri Otoe (Oto), Oklahoma Pawnee , Oklahoma Ponca , Nebraska, Oklahoma Quapaw , formerly Arkansas, Oklahoma Sioux Dakota , Minnesota, Montana, Nebraska, North Dakota, South Dakota, Manitoba, Saskatchewan Santee , Nebraska Yankton , South Dakota Yanktonai , formerly Minnesota, currently Montana, North Dakota, and South Dakota Lakota (Teton), Montana, North Dakota, South Dakota, Saskatchewan Nakoda (Stoney), Alberta Nakota , Assiniboine (Assiniboin), Montana, Saskatchewan Teyas , Texas Tonkawa , Oklahoma Tsuu T’ina , (Sarcee, Sarsi, Tsuut’ina), Alberta Wichita and Affiliated Tribes (Kitikiti'sh ), Oklahoma, formerly Texas and Kansas Kichai (also related to the Caddo ), Oklahoma, formerly Texas and Kansas Taovayas (Tawehash ), Oklahoma, formerly Texas and Kansas Tawakoni , Oklahoma, formerly Texas and Kansas Waco (Iscani , Yscani ), Oklahoma, formerly Texas Wichita proper , Guichita , Rayados , Oklahoma, formerly Texas and Kansas Eastern Woodlands Northeastern Woodlands Annamessex , Annemessex, formerly Eastern Shore of Maryland Anishinaabeg (Anishinape, Anicinape, Neshnabé, Nishnaabe) (see also Subarctic , Plains ) Algonquin , [ 9] Quebec, Ontario Nipissing , [ 9] Ontario [ 7] Ojibwe (Chippewa, Ojibwa, Ojibway), Ontario, Michigan, Minnesota, Wisconsin, [ 7] and North Dakota Odawa people (Ottawa), Indiana, Michigan, Ohio, Ontario; [ 7] later Oklahoma Potawatomi , Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, [ 7] Ontario, Wisconsin; later Kansas and Oklahoma Accomac people , formerly Eastern Shore of Virginia Adena culture (1000–200 BCE) formerly Ohio, Indiana, West Virginia, Kentucky, New York, Pennsylvania, and Maryland Assateague , formerly Maryland [ 10] Attawandaron (Neutral Confederacy ), formerly Ontario [ 7] Beothuk , formerly Newfoundland [ 7] Chowanoc , Chowanoke , formerly North Carolina Choptank people , formerly Maryland [ 10] Conoy , Virginia, [ 10] Maryland Fort Ancient culture (1000–1750 CE), formerly Ohio, Kentucky, Indiana, and West Virginia Erie , formerly Pennsylvania, New York [ 7] Etchemin , formerly Maine Ho-Chunk (Winnebago ), southern Wisconsin and Nebraska, formerly northern Illinois, [ 7] Iowa, and Nebraska Honniasont , formerly Pennsylvania, Ohio, and West Virginia Hopewell tradition , formerly Ohio, Illinois, and Kentucky, and Black River region, 200 BCE–500 CE Housatonic , formerly Massachusetts and New York [ 11] Illinois Confederacy (Illiniwek ), formerly Illinois, Iowa, and Missouri [ 7] Cahokia , formerly Illinois, Iowa, Missouri, Arkansas, currently Oklahoma Kaskaskia , formerly Wisconsin, currently Oklahoma Mitchigamea , formerly Illinois, currently Oklahoma Peoria , Illinois, currently Oklahoma Moingona , formerly Illinois, currently Oklahoma Tamaroa , formerly Illinois, currently Oklahoma Iroquois Confederacy [ 9] (Haudenosaunee ), currently Ontario, Quebec, and New York [ 7] Cayuga , currently New York, [ 7] Ontario, and Oklahoma Mohawk , New York, [ 7] Ontario, and Quebec Oneida , New York, [ 7] Ontario, and Wisconsin Onondaga , New York, [ 7] Ontario Seneca , New York, [ 7] Ontario, and Oklahoma Mingo , formerly Pennsylvania, Ohio, West Virginia Tuscarora , formerly North Carolina, currently New York and Ontario Kickapoo , formerly Michigan, [ 7] Illinois, and Missouri; currently Kansas, Oklahoma, Texas, and Mexico Laurentian (St. Lawrence Iroquoians ), formerly New York, Ontario, and Quebec, ca. 1300–1580 CE Lenni Lenape (Delaware ), formerly Pennsylvania, Delaware, New Jersey; currently Ontario, Wisconsin and Oklahoma Munsee -speaking subgroups, formerly Long Island and southeastern New York; [ 12] currently Wisconsin Canarsie (Canarsee ), formerly Long Island New York [ 13] Esopus , formerly New York, [ 12] later Ontario and Wisconsin Hackensack , formerly New York [ 12] Haverstraw (Rumachenanck ), New York [ 14] Kitchawank (Kichtawanks , Kichtawank ), New York [ 14] Minisink , formerly New York [ 12] Navasink , [ 14] formerly north shore of New Jersey Sanhican (Raritan), formerly Monmouth County, New Jersey Sinsink (Sintsink ), formerly Westchester County, New York [ 14] Siwanoy , formerly New York and Connecticut Tappan , formerly New York [ 15] Waoranecks [ 16] Wappinger (Wecquaesgeek , Nochpeem ), formerly New York [ 11] [ 17] Warranawankongs [ 16] Wiechquaeskeck , formerly New York [ 12] Wisquaskeck (Raritan), formerly Westchester County, New York [ 14] Unami -speaking subgroups Mahican (Stockbridge Mahican ) [ 9] formerly Connecticut, Massachusetts, New York, and Vermont [ 7] [ 11] Manahoac , Virginia [ 18] Mascouten , formerly Michigan [ 7] Massachusett , formerly Massachusetts [ 9] [ 19] Meherrin , Virginia, [ 20] North Carolina Menominee , Wisconsin [ 7] Meskwaki (Fox ), formerly Michigan, [ 7] currently Iowa Miami , formerly Illinois, Indiana, and Michigan, [ 7] currently Oklahoma Piankeshaw , formerly Indiana, currently Oklahoma Wea , formerly Indiana, currently Oklahoma Mohegan , [ 9] Connecticut Monacan , Virginia [ 21] Montaukett (Montauk ), [ 9] New York Monyton (Monetons , Monekot, Moheton) (Siouan ), West Virginia and Virginia Nansemond , Virginia Nanticoke , Delaware and Maryland [ 7] Narragansett , Rhode Island [ 9] Niantic , coastal Connecticut [ 9] [ 19] Nipmuc (Nipmuck ), Connecticut, Massachusetts, and Rhode Island [ 19] Noquet , formerly Michigan Nottaway , Virginia [ 20] Occaneechi (Occaneechee ), Virginia, [ 20] [ 22] [ 23] Patuxent , Maryland [ 10] Paugussett , Connecticut [ 9] Pennacook tribe , formerly Massachusetts, New Hampshire [ 24] Pequot , Connecticut [ 9] Petun (Tionontate ), Ontario [ 7] Piscataway , Maryland [ 10] Pocumtuc , western Massachusetts [ 19] Podunk , formerly New York, [ 19] eastern Hartford County, Connecticut Powhatan Confederacy , Virginia [ 10] Appomattoc , Virginia Arrohateck , Virginia Chesapeake , Virginia Chesepian , Virginia Chickahominy , Virginia [ 20] Kiskiack , Virginia Mattaponi , Virginia Nansemond , Virginia [ 20] Paspahegh , Virginia Potomac (Patawomeck ), Virginia Powhatan , Virginia Pamunkey , Virginia [ 20] Quinnipiac , Connecticut, [ 9] eastern New York, northern New Jersey Rappahannock , Virginia Saponi , North Carolina, Virginia, [ 20] later Pennsylvania, New York, and Ontario [ 23] Sauk (Sac ), formerly Michigan, [ 7] currently Iowa, Oklahoma Schaghticoke , western Connecticut [ 9] Shawnee , formerly Ohio, [ 7] Virginia, West Virginia, Pennsylvania, currently Oklahoma Shinnecock , [ 9] Long Island, New York [ 19] Stegarake , formerly Virginia [ 18] Stuckanox (Stukanox ), Virginia [ 20] Conestoga (Susquehannock ), Maryland, Pennsylvania, New York, West Virginia [ 7] Tauxenent (Doeg ), Virginia [ 25] Tunxis (Massaco ), Connecticut [ 9] Tuscarora , formerly North Carolina, Virginia, currently New York Tutelo (Nahyssan ), Virginia, [ 20] [ 22] later Pennsylvania, New York, and Ontario [ 23] Unquachog (Poospatuck ), Long Island, New York [ 19] Wabanaki Confederacy , Maine, New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, Quebec [ 9] Abenaki (Tarrantine ), Quebec, Maine, New Brunswick, New Hampshire, and Vermont Mi'kmaq (Micmac), New Brunswick, Newfoundland and Labrador, Nova Scotia, Prince Edward Island, Quebec, [ 7] and Maine Passamaquoddy , New Brunswick, and Maine [ 7] Penobscot , Maine Wolastoqiyik (Maliseet ), Maine, New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and Quebec [ 7] Wampanoag , Massachusetts [ 9] Wangunk (Mattabeset), formerly Connecticut [ 9] Wawyachtonoc , formerly Connecticut, New York [ 11] Weapemeoc , formerly northern North Carolina Wenro , formerly New York [ 7] [ 9] Wicocomico , formerly Maryland, Virginia Wyandot (Huron ), Ontario south of Georgian Bay , later Kansas and Michigan, and currently Oklahoma and Wendake , Quebec Southeastern Woodlands Most of these no longer exist as tribes.
Acolapissa (Colapissa), Louisiana and Mississippi [ 26] Ais , eastern coastal Florida [ 27] Alafay (Alafia, Pojoy, Pohoy, Costas Alafeyes, Alafaya Costas), Florida [ 28] Amacano , Florida west coast [ 29] Apalachee , northwestern Florida [ 30] Atakapa (Attacapa), Louisiana west coast and Texas southwestern coast [ 30] Avoyel ("little Natchez"), Louisiana [ 21] [ 26] Bayogoula , southeastern Louisiana [ 21] [ 26] Biloxi , formerly Mississippi, [ 26] [ 30] currently Louisiana Caddo Confederacy , formerly Arkansas, Louisiana, Oklahoma, Texas, [ 30] [ 32] currently Oklahoma Adai (Adaizan, Adaizi, Adaise, Adahi, Adaes, Adees, Atayos), Louisiana and Texas [ 26] Cahinnio , southern Arkansas [ 32] Doustioni , north central Louisiana [ 32] Eyeish (Hais), eastern Texas [ 32] Hainai , eastern Texas [ 32] Hasinai , eastern Texas [ 32] Kadohadacho , northeastern Texas, southwestern Arkansas, northwestern Louisiana [ 32] Nabedache , eastern Texas [ 32] Nabiti , eastern Texas [ 32] Nacogdoche , eastern Texas [ 32] Nacono , eastern Texas [ 32] Nadaco , eastern Texas [ 32] Nanatsoho , northeastern Texas [ 32] Nasoni , eastern Texas [ 32] Natchitoches , Lower: central Louisiana, Upper: northeastern Texas [ 32] Neche , eastern Texas [ 32] Nechaui , eastern Texas [ 32] Ouachita , northern Louisiana [ 32] Tula , western Arkansas [ 32] Yatasi , northwestern Louisiana [ 32] Calusa , southwestern Florida [ 28] [ 30] Cape Fear Indians , North Carolina southern coast [ 26] Capinan (Capina , Moctobi ), Mississippi Catawba (Esaw, Usheree, Ushery, Yssa), [ 33] North Carolina, currently South Carolina [ 30] Chacato (Chatot, Chactoo), Florida panhandle, later southern Alabama and Mississippi, then Louisiana [ 26] Chakchiuma , Alabama and Mississippi, [ 30] merged into Chickasaw, currently Oklahoma Chawasha (Washa), Louisiana [ 26] Cheraw (Chara, Charàh), North Carolina Cherokee , western North Carolina, eastern Tennessee, later Georgia, northwestern South Carolina, northern Alabama, Arkansas, Texas, Mexico, and currently North Carolina and Oklahoma [ 34] Chickanee (Chiquini), North Carolina Chickasaw , Alabama and Mississippi, [ 30] currently Oklahoma [ 34] Chicora , coastal South Carolina [ 21] Chine , Florida Chisca (Cisca), southwestern Virginia [ 21] later in Florida [ 35] Chitimacha , currently Louisiana [ 30] Choctaw , formerly Alabama; currently Mississippi, [ 30] Louisiana, and Oklahoma [ 34] Chowanoc (Chowanoke ), North Carolina Congaree (Canggaree), South Carolina [ 26] [ 36] Coree , North Carolina [ 21] Croatan , North Carolina Cusabo , coastal South Carolina [ 30] Eno , North Carolina [ 26] Grigra (Gris), Mississippi [ 37] Guacata (Santalûces), eastern coastal Florida [ 28] Guacozo , Florida Guale (Cusabo, Iguaja, Ybaja), coastal Georgia [ 26] [ 30] Guazoco , southwestern Florida coast [ 28] Houma , Louisiana and Mississippi [ 30] Jaega (Jobe), eastern coastal Florida [ 27] Jaupin (Weapemoc), North Carolina Jororo , Florida interior [ 28] Keyauwee , North Carolina [ 26] Koasati (Coushatta ), formerly eastern Tennessee, [ 30] currently Louisiana, Oklahoma, and Texas Koroa , Mississippi [ 26] Luca , southwestern Florida coast [ 28] Lumbee , currently North Carolina Machapunga , North Carolina Matecumbe (Matacumbêses, Matacumbe, Matacombe), Florida Keys [ 28] Mayaca , Florida [ 28] Mayaimi (Mayami), interior Florida [ 27] Mayajuaca , Florida Mikasuki (Miccosukee), currently Florida Mobila (Mobile, Movila), northwestern Florida and southern Alabama [ 30] Mocoso , western Florida [ 27] [ 28] Mougoulacha , Mississippi [ 21] Muscogee (Creek) , Tennessee, Georgia, Alabama, Mississippi, Florida; currently Oklahoma and Alabama Abihka , Alabama, [ 31] currently Oklahoma Alabama , formerly Alabama, [ 31] southwestern Tennessee, and northwestern Mississippi, [ 26] [ 30] currently Oklahoma and Texas Pakana (Pacâni, Pagna, Pasquenan, Pak-ká-na, Pacanas), central Alabama, [ 26] later Texas [ 21] Apalachicola Province , (Lower Towns of the Muscogee (Creek) Confederacy), Alabama and Georgia [ 38] Chiaha , Creek Confederacy, Alabama [ 31] Eufaula tribe , Georgia, currently Oklahoma Kialegee Tribal Town , Alabama, currently Oklahoma Osochee (Osochi , Oswichee, Usachi, Oosécha), Creek Confederacy, Alabama [ 26] [ 31] Talapoosa , Creek Confederacy, Alabama [ 31] Thlopthlocco Tribal Town , Alabama, Georgia, currently Oklahoma Tukabatchee , Muscogee Creek Confederacy, Alabama [ 31] Naniaba , northwestern Florida and southern Alabama [ 30] Natchez , Louisiana and Mississippi [ 30] currently Oklahoma Neusiok (Newasiwac, Neuse River Indians), North Carolina [ 26] Norwood culture , Apalachee region, Florida, c. 12,000–4500 BCE Mosopelea (Ofo ), Arkansas and Mississippi, [ 30] eastern Tennessee, [ 26] currently Louisiana Okchai (Ogchay), central Alabama [ 26] Okelousa , Louisiana [ 26] Opelousas , Louisiana [ 26] Pacara, Florida Pamlico , North Carolina Pascagoula , Mississippi coast [ 21] Pee Dee (Pedee ), South Carolina [ 26] [ 39] and North Carolina Pensacola , Florida panhandle and southern Alabama [ 30] Potoskeet , North Carolina Quinipissa , southeastern Louisiana and Mississippi [ 31] Roanoke , North Carolina Saluda (Saludee, Saruti), South Carolina [ 26] Santee (Seretee, Sarati, Sati, Sattees), South Carolina (no relation to Santee Sioux ), South Carolina [ 26] Santa Luces , Florida Saponi , North Carolina, Virginia, [ 20] later Pennsylvania, New York, and Ontario [ 23] Saura , North Carolina Saxapahaw (Sissipahaw , Sissipahua, Shacioes), North Carolina [ 26] Secotan , North Carolina Seminole , currently Florida and Oklahoma [ 34] Sewee (Suye, Joye, Xoye, Soya), South Carolina coast [ 26] Shakori , North Carolina Shoccoree (Haw), North Carolina, [ 26] possibly Virginia Sissipahaw , North Carolina Sugeree (Sagarees, Sugaws, Sugar, Succa), North Carolina and South Carolina [ 26] Surruque , east-central Florida [ 40] Suteree (Sitteree, Sutarees, Sataree), North Carolina Taensa , Mississippi [ 37] Taposa , Mississippi Tawasa , Alabama [ 41] Tequesta , southeastern coastal Florida [ 26] [ 28] Timucua , Florida and Georgia [ 26] [ 28] [ 30] Acuera , central Florida [ 42] Agua Fresca (or Agua Dulce or Freshwater), interior northeast Florida [ 42] Arapaha , north-central Florida and south-central Georgia? [ 42] Cascangue , coastal southeast Georgia [ 42] Icafui (Icafi), coastal southeast Georgia [ 42] Mocama (Tacatacuru), coastal northeast Florida and coastal southeast Georgia [ 42] Northern Utina north-central Florida [ 42] Ocale , central Florida [ 42] Oconi , interior southeast Georgia [ 42] Potano , north-central Florida [ 42] Saturiwa , northeast Florida [ 42] Tacatacuru , coastal southeast Georgia [ 43] Tucururu (or Tucuru), Florida [ 42] Utina (or Eastern Utina), northeast-central Florida [ 44] Yufera , coastal southeast Georgia [ 42] Yui (Ibi), coastal southeast Georgia [ 42] Yustaga , north-central Florida [ 42] Taposa , Mississippi Tiou (Tioux ), Mississippi [ 36] Tocaste , Florida [ 28] Tocobaga , Florida [ 26] [ 28] Tohomé , northwestern Florida and southern Alabama [ 30] Tomahitan , eastern Tennessee Topachula , Florida Tunica , Arkansas and Mississippi, [ 30] currently Louisiana Utiza , Florida [ 27] Uzita , Tampa Bay, Florida [ 45] Vicela , Florida [ 27] Viscaynos , Florida Waccamaw , North Carolina, South Carolina Wateree (Guatari, Watterees), North Carolina [ 26] Waxhaw (Waxsaws, Wisack, Wisacky, Weesock, Flathead), North Carolina and South Carolina [ 26] [ 39] Westo , Virginia and South Carolina, [ 21] extinct Winyah , South Carolina coast [ 26] Woccon , North Carolina [ 26] [ 39] Yamasee , Florida, Georgia [ 21] Yazoo , southeastern tip of Arkansas, eastern Louisiana, Mississippi [ 26] [ 46] Yuchi (Euchee ), central Tennessee, [ 26] [ 30] later northwest Georgia, currently Oklahoma Great Basin Ahwahnechee , Yosemite Valley, California Bannock , Idaho [ 47] Coso People , of Coso Rock Art District in the Coso Range , Mojave Desert California Fremont culture (400 CE–1300 CE), formerly Utah [ 48] Kawaiisu , southern inland California [ 47] Mono , southeastern California Northern Paiute , eastern California, Nevada, Oregon, southwestern Idaho [ 47] Agaideka , Salmon Eaters , Lemhi , Snake River and Lemhi River Valley [ 51] [ 52] Doyahinee' , Mountain people [ 49] Kammedeka , Kammitikka , Jack Rabbit Eaters , Snake River, Great Salt Lake [ 51] Hukundüka , Porcupine Grass Seed Eaters , Wild Wheat Eaters , possibly synonymous with Kammitikka [ 51] [ 53] Tukudeka , Dukundeka' , Sheep Eaters (Mountain Sheep Eaters ), Sawtooth Range, Idaho [ 51] [ 52] Yahandeka , Yakandika , Groundhog Eaters , lower Boise, Payette, and Wiser Rivers [ 51] [ 52] Kuyatikka , Kuyudikka , Bitterroot Eaters , Halleck, Mary's River, Clover Valley, Smith Creek Valley, Nevada [ 53] Mahaguadüka , Mentzelia Seed Eaters , Ruby Valley , Nevada [ 53] Painkwitikka , Penkwitikka , Fish Eaters , Cache Valley, Idaho and Utah [ 53] Pasiatikka , Redtop Grass Eaters , Deep Creek Gosiute , Deep Creek Valley, Antelope Valley [ 53] Tipatikka , Pinenut Eaters , northernmost band [ 53] Tsaiduka , Tule Eaters , Railroad Valley , Nevada [ 53] Tsogwiyuyugi , Elko, Nevada [ 53] Waitikka , Ricegrass Eaters , Ione Valley, Nevada [ 53] Watatikka , Ryegrass Seed Eaters , Ruby Valley , Nevada [ 53] Wiyimpihtikka , Buffalo Berry Eaters [ 53] Southern Paiute , Arizona, Nevada, Utah Timbisha , aka Panamint or Koso, southeastern California Ute , Colorado, Utah, northern New Mexico [ 47] Capote , southeastern Colorado and New Mexico [ 55] Moanunts , Salina, Utah [ 56] Muache , south and central Colorado [ 55] Pahvant , western Utah [ 56] Sanpits , central Utah [ 56] Timpanogots , north central Utah [ 56] Uintah , Utah [ 55] Uncompahgre or Taviwach , central and northern Colorado [ 55] Weeminuche , western Colorado, eastern Utah, northwestern New Mexico [ 55] White River Utes (Parusanuch and Yampa ), Colorado and eastern Utah [ 55] Washo , Nevada and California [ 57] California Nota bene: The California cultural area does not exactly conform to the state of California's boundaries, and many tribes on the eastern border with Nevada are classified as Great Basin tribes and some tribes on the Oregon border are classified as Plateau tribes . [ 58]
Achomawi , Achumawi , Pit River tribe , northeastern California [ 59] Atsugewi , northeastern California [ 59] Cahuilla , southern California [ 59] Chumash , coastal southern California [ 59] Chilula , northwestern California [ 59] Chimariko , extinct, northwestern California [ 60] Cupeño , southern California [ 59] Eel River Athapaskan peoples Esselen , west-central California [ 59] Hupa , northwestern California [ 59] Juaneño , Acjachemem , southwestern California Karok , northwestern California [ 59] Kato , Cahto , northwestern California [ 59] Kitanemuk , south-central California [ 59] Konkow , northern-central California [ 59] Kumeyaay , Diegueño , Kumiai Ipai , southwestern California [ 59] Tipai , southwestern California and northwestern Mexico [ 59] La Jolla complex , southern California, c. 6050–1000 BCE Luiseño , southwestern California [ 59] Maidu , northeastern California [ 59] Miwok , Me-wuk , central California [ 59] Monache , Western Mono , central California [ 59] Nisenan , eastern-central California [ 59] Nomlaki , northwestern California [ 59] Ohlone , Costanoan , west-central California [ 59] Patwin , central California [ 59] Pauma Complex , southern California, c. 6050–1000 BCE Pomo , northwestern and central-western California [ 59] Salinan , coastal central California [ 59] Serrano , southern California [ 59] Shasta northwestern California [ 59] Tataviam , Allilik (Fernandeño), southern California [ 59] Tolowa , northwestern California [ 59] Tongva , Gabrieleño , Fernandeño , San Clemente tribe , coastal southern California [ 59] Tubatulabal , south-central California [ 59] Wappo , north-central California [ 59] Whilkut , northwestern California [ 59] Wintu , northwestern California [ 59] Wiyot , northwestern California [ 59] Yana , northern-central California [ 59] Yokuts , central and southern California [ 59] Yuki , Ukomno'm , northwestern California [ 59] Yurok , northwestern California [ 59] Southwest This region is also called "Oasisamerica" and includes parts of what is now Arizona , Southern Colorado , New Mexico , Western Texas , Southern Utah , Chihuahua , and Sonora
Southern Athabaskan Chiricahua Apache , New Mexico and Oklahoma Jicarilla Apache , New Mexico Lipan Apache , New Mexico, formerly Texas Mescalero Apache , New Mexico Navajo (Diné ), Arizona and New Mexico San Carlos Apache , Arizona Tonto Apache , Arizona Western Apache (Coyotero Apache), Arizona White Mountain Apache , Arizona Comecrudo , Tamaulipas Cotoname (Carrizo de Camargo ) Genízaro (detribalized Apache, Navajo, and Ute descendants), Arizona, New Mexico Halchidhoma , Arizona and California Hualapai , Arizona Havasupai , Arizona Hohokam , formerly Arizona Karankawa , formerly Texas La Junta , Texas, Chihuahua Mamulique , Texas, Nuevo León Manso , Texas, Chihuahua Mojave , Arizona, California, and Nevada O'odham , Arizona, Sonora Piipaash (Maricopa ), Arizona Pima Bajo Pueblo peoples , Arizona, New Mexico, Western Texas Ancestral Pueblo , formerly Arizona, Colorado, New Mexico, Utah Hopi-Tewa (Arizona Tewa , Hano ), Arizona, joined the Hopi during the Pueblo Revolt Hopi , Arizona Keres people , New Mexico Tewa people , New Mexico Tiwa people , New Mexico Towa people Zuni people (Ashiwi ), New Mexico Quechan (Yuma ), Arizona and California Quems , formerly Coahuila and Texas Solano , Coahuila, Texas Tamique (Aranama ), formerly Texas Toboso , Chihuahua and Coahuila Walapai , Arizona Yaqui (Yoreme ), Arizona, Sonora Yavapai , Arizona Mexico and Mesoamerica The regions of Oasisamerica , Aridoamerica , and Mesoamerica span multiple countries and overlap.
Aridoamerica Aridoamerica region of North America Acaxee Aranama (Hanáma , Hanáme , Chaimamé , Chariname , Xaraname , Taraname ), southeast Texas Coahuiltecan , Texas, northern Mexico Chichimeca Cochimí , Baja California [ 65] Cocopa , Arizona, northern Mexico Garza , Texas, northern Mexico Guachimontone Guamare Guaycura , Baja California Guarijío , Huarijío , Chihuahua, Sonora [ 65] Huichol [ 65] (Wixáritari ), Nayarit, Jalisco, Zacatecas, and Durango Kiliwa , Baja California Mayo , [ 65] Sonora and Sinaloa Monqui , Baja California Paipai , Akwa'ala , Kw'al , Baja California [ 66] Opata Otomi , central Mexico Patiri , southeastern Texas Pericúe , Baja California Pima Bajo [ 65] Seri [ 65] Tarahumara [ 65] Tepecano Tepehuán [ 65] Terocodame , Texas and Mexico Teuchitlan tradition Western Mexico shaft tomb tradition Yaqui , [ 65] Sonora and now southern Arizona Zacateco Mesoamerica Map of Mesoamerica Amuzgos , Mexico Nahua , Guatemala and Mexico Chatinos , Mexico Cora people Cuicatecs Huastec Huave (Wabi ), Juchitán District, Oaxaca Ixcatecos Lenca Maya , Belize , El Salvador , Guatemala , Honduras , and Mexico Mazatec Mixe Mixtec Olmec Otomi Pipil Purépecha , also known as Tarascan Tacuate Tlapanec Trique Xinca Zapotec Zoque Toltec (900–1168 CE), Tula, Hildago Circum-Caribbean Cultural regions of South and Central America at the time of contact (in Spanish) Partially organized per Handbook of South American Indians . [ 67]
Caribbean Anthropologist Julian Steward defined the Antilles cultural area, which includes all of the Antilles and Bahamas , except for Trinidad and Tobago . [ 67]
Arawak Taíno , Greater Antilles, northern Lesser Antilles Igneri , Lesser Antilles, 400–1000 CE Nepoya , Trinidad Suppoya , Trinidad Caquetio , Aruba, Bonaire, Curaçao, and Venezuela Carib , Lesser Antilles Ciboney , Greater Antilles, c. 1000–300 BCE [ 68] Ciguayo , Hispaniola Ortoiroid , c. 5500–200 BCE [ 69] Saladoid culture , 500 BCE–545 CE [ 69] Central America The Central American culture area includes part of El Salvador , most of Honduras , all of Nicaragua , Costa Rica , and Panama , and some peoples on or near the Pacific coasts of Colombia and Ecuador . [ 67]
Bagaces , Costa Rica Bokota , Panama Boruca , Costa Rica Bribri , Costa Rica Cabécar , Costa Rica Cacaopera (Matagalpa , Ulua ), formerly El Salvador [ 70] Cayada , Ecuador Changuena , Panama Embera-Wounaan (Chocó , Wounaan ), Colombia, Panama Choluteca , Honduras Coiba , Costa Rica Coito , Costa Rica Corobici , Costa Rica Desaguadero , Costa Rica Dorasque , Panama Guatuso , Costa Rica Guaymí , Panama Guetar , Costa Rica Guna , Panama and Colombia Lenca , Honduras and El Salvador Mangue , Nicaragua Maribichocoa , Honduras and Nicaragua Miskito , Hondrus, Nicaragua Nagrandah , Nicaragua Ngöbe Buglé , Bocas del Toro, Panama Nicarao , Nicaragua Nicoya , Costa Rica Orotiña , Costa Rica Paparo , Panama Pech , northeastern Honduras Piria, Nicaragua Poton , Honduras and El Salvador Quepo , Costa Rica Rama , Nicaragua Sigua , Panama Subtiaba , Nicaragua Suerre , Costa Rica Sumo (Mayagna ), Honduras and Nicaragua Terraba (Naso , Teribe , Tjër Di ), Panama Tojar , Panama Tolupan (Jicaque), Honduras Ulva , El Salvador, Honduras and Nicaragua Voto , Costa Rica Yasika , Nicaragua Colombia and Venezuela The Colombia and Venezuela culture area includes most of Colombia and Venezuela . Southern Colombia is in the Andean culture area, as are some peoples of central and northeastern Colombia, who are surrounded by peoples of the Colombia and Venezuela culture. Eastern Venezuela is in the Guianas culture area, and southeastern Colombia and southwestern Venezuela are in the Amazonia culture area. [ 67]
Abibe , northwestern Colombia Aburrá , central Colombia Achagua (Axagua ), eastern Colombia, western Venezuela Agual , western Colombia Amaní , central Colombia Ancerma , western Colombia Andaqui (Andaki ), Huila Department, Colombia Andoque , Andoke , southeastern Colombia Antiochia , Colombia Arbi , western Colombia Arma , western Colombia Atunceta , western Colombia Auracana , northeastern Colombia Buriticá , western Colombia Caquetio , western Venezuela Calamari , northwestern Colombia Calima culture , western Colombia, 200 BCE–400 CE Caramanta , western Columbia Carate , northeastern Colombia Carare , northeastern Colombia Carex , northwestern Colombia Cari , western Colombia Carrapa , western Colombia Cartama , western Colombia Cauca , western Colombia Corbago , northeastern Colombia Cosina , northeastern Colombia Catio , northwestern Colombia Cenú , northwestern Colombia Cenufaná , northwestern Colombia Chanco , western Colombia Coanoa , northeastern Colombia Cuiba , east Colombia west Venezuela Cuica , western Venezuela Cumanagoto , eastern Venezuela Evéjito , western Colombia Fincenú , northwestern Colombia Gorrón , western Colombia Guahibo (Guajibo ), eastern Colombia, southern Venezuela Guambía , western Colombia Guanes , Colombia, pre-Columbian culture Guanebucan , northeastern Colombia Guazuzú , northwestern Colombia Hiwi , western Colombia, eastern Venezuela Jamundí , western Colombia Kari'ña , eastern Venezuela Kogi , northern Colombia Lile , western Colombia Lache , central Colombia Mariche , central Venezuela Maco (Mako, Itoto, Wotuja, or Jojod), northeastern Colombia and western Venezuela Mompox , northwestern Colombia Motilone , northeastern Colombia and western Venezuela Naura , central Colombia Nauracota , central Colombia Noanamá (Waunana, Huaunana, Woun Meu), northwestern Colombia and Panama Nutabé , northwestern Colombia Opón , northeastern Colombia Pacabueye , northwestern Colombia Pancenú , northwestern Colombia Patángoro , central Colombia Paucura , western Colombia Pemed , northwestern Colombia Pequi people , western Colombia Picara people , western Colombia Pozo , western Colombia Pumé (Yaruro ), Venezuela Quimbaya , central Colombia, 4th–7th centuries CE Quinchia , western Colombia Sutagao , central Colombian Tahamí , northwestern Colombia Tairona , northern Colombia, pre-Columbian culture, 1st–11th centuries CE Tamalameque , northwestern Colombia Mariche , central Venezuela Timba , western Colombia Timote , western Venezuela Tinigua , Caquetá Department, Colombia Tolú , northwestern Colombia Toro , western Colombia Tupe , northeastern Colombia Turbaco people , northwestern Colombia Urabá , northwestern Colombia Urezo , northwestern Colombia U'wa , eastern Colombia, western Venezuela Waikerí , eastern Venezuela Wayuu (Wayu, Wayúu, Guajiro, Wahiro), northeastern Colombia and northwestern Venezuela Xiriguana , northeastern Colombia Yamicí , northwestern Colombia Yapel , northwestern Colombia Yarigui , northeastern Colombia Yukpa , Yuko , northeastern Colombia Zamyrua , northeastern Colombia Zendagua , northwestern Colombia Zenú , northwestern Colombia, pre-Columbian culture, 200 BCE–1600 CE Zopia , western Colombia Guianas The Guianas in northern South America The position of the Guianas in the Neotropical realm in northern South America This region includes northern parts Colombia , French Guiana , Guyana , Suriname , Venezuela , and parts of the Amazonas , Amapá , Pará , and Roraima States in Brazil.
Acawai (6N 60W) Acokwa (3N 53W) Acuria (Akurio , Akuriyo ), 5N 55W, Suriname Akawaio , Roraima, Brazil, Guyana, and Venezuela Amariba (2N 60W) Amicuana (2N 53W) Apalaí (Apalai ), Amapá, Brazil Apirua (3N 53W) Apurui (3N 53W) Aracaret (4N 53W) Aramagoto (2N 54W) Aramisho (2N 54W) Arebato (7N 65W) Arekena (2N 67W) Arhuaco , northeastern Colombia Arigua Arinagoto (4N 63W) Aruã (1N 50W) Aruacay , Venezuela Atorai (2N 59W) Atroahy (1S 62W) Auaké , Brazil and Guyana Baniwa (Baniva) (3N 68W), Brazil, Colombia and Venezuela Baraüana (1N 65W) Bonari (3S 58W) Baré (3N 67W) Caberre (4N 71 W) Cadupinago Cariaya (1S 63 W) Carib (Kalinago), Venezuela Carinepagoto , Trinidad Chaguan , Venezuela Chaima , Venezuela Cuaga , Venezuela Cuacua , Venezuela Cumanagoto , Venezuela Guayano , Venezuela Guinau (4N 65W) Hixkaryána , Amazonas, Brazil Hodï , Venezuela Inao (4N 65W) Ingarikó , Brazil, Guyana and Venezuela Jaoi (Yao), Guyana, Trinidad and Venezuela Kali'na , Brazil, Guyana, French Guiana, Suriname, Venezuela Lokono (Arawak, Locono), Guyana, Trinidad, Venezuela Macapa (2N 59W) Macushi , Brazil and Guyana Maipure (4N 67W) Maopityan (2N 59W) Mapoyo (Mapoye), Venezuela Marawan (3N 52W) Mariusa , Venezuela Marourioux (3N 53W) Nepuyo (Nepoye), Guyana, Trinidad and Venezuela Orealla , Guyana Palengue , Venezuela Palikur , Brazil, French Guiana Parauana (2N 63W) Parauien (3S 60W) Pareco , Venezuela Paria , Venezuela Patamona , Roraima, Brazil Pauishana (2N 62W) Pemon (Arecuna), Brazil, Guyana, and Venezuela Piapoco (3N 70W) Piaroa , Venezuela Pino (3N 54W) Piritú , Venezuela Purui (2N 52W) Saliba (Sáliva ), Venezuela Sanumá , Venezuela, Brazil Shebayo , Trinidad Sikiana (Chikena , Xikiyana ), Brazil, Suriname Tagare , Venezuela Tamanaco , Venezuela Tarumá (3S 60W) Tibitibi , Venezuela Tiriyó (Tarëno ), Brazil, Suriname Tocoyen (3N 53W) Tumuza , Venezuela Wai-Wai , Amazonas, Brazil and Guyana Wapishana , Brazil and Guyana Warao (Warrau), Guyana and Venezuela Wayana (Oyana ), Pará, Brazil Ya̧nomamö (Yanomami ), Venezuela and Amazonas, Brazil Ye'kuana , Venezuela, Brazil Eastern Brazil This region includes parts of the Ceará , Goiás , Espírito Santo , Mato Grosso , Mato Grosso do Sul , Pará , and Santa Catarina states of Brazil
Apinajé (Apinaye Caroyo ), [ 9] Rio Araguiaia Arara , Pará Atikum , Bahia and Pernambuco Bororo , [ 9] Mato Grosso Botocudo (Lakiãnõ ) Carijo Guaraní [ 9] East Brazilian tradition , Precolumbian culture [ 9] Guató (Guato ), Mato Grosso Kadiwéu (Guaicuru ), [ 9] Mato Grosso do Sul Kaingang Karajá (Iny , Javaé ), [ 9] Goiás, Mato Grosso, Pará, and Tocantins Kaxixó , Minas Gerais Kayapo (Cayapo , Mebêngôkre ), [ 9] Mato Grosso and Pará Laklãnõ , [ 9] Santa Catarina Mehim (Krahô , Crahao ), [ 9] Rio Tocantins Ofayé , Mato Grosso do Sul Parakatêjê (Gavião ), [ 9] Pará Pataxó , Bahia Potiguara (Pitigoares ), [ 9] Ceará Tabajara , Ceará Tapirapé (Tapirape) Terena , Mato Gross and Mato Grosso do Sul, Brazil Tupiniquim , Espírito Santo Umutina (Barbados ) [ 9] Xakriabá (Chakriaba , Chikriaba , or Shacriaba ), Minas Gerais Xavánte (Shavante ), [ 9] Mato Grosso Xerénte (Sherente ), [ 9] Goiás Xucuru , Pernambuco Andes The Tawantinsuyu , or fullest extent of the Inca Empire , which includes much of the Andean cultural region Andean Hunting-Collecting tradition , Argentina, 11,000–4,000 CE Awa-Kwaiker , northern Ecuador, southern Colombia Aymara , Bolivia, [ 71] Chile, Peru Callawalla (Callahuaya ), Bolivia [ 71] Cañari , Ecuador Capulí culture , Ecuador, 800–1500 CE Cerro Narrio (Chaullabamba ) (Precolumbian culture) Chachapoyas , Amazonas, Peru Chachilla (Cayapas ) Chanka (Chanca ), Peru Chavín , northern Peru, 900–200 BCE Chincha people , Peru (Precolumbian culture) Chipaya , Oruro Department, Bolivia [ 71] Chuquibamba culture (Precolumbian culture) Conchucos Diaguita Guangaia (Precolumbian culture) Ichuña microlithic tradition (Precolumbian culture) Inca Empire (Inka), based in Peru Jama-Coaque (Precolumbian culture) Killke culture , Peru, 900–1200 CE Kogi Kolla (Colla ), Argentina, Bolivia, Chile La Tolita (Precolumbian culture) Las Vegas culture , coastal Ecuador, 8000 BCE–4600 BCE Lauricocha culture , Peru, 8000–2500 BCE Lima culture , Peru, 100–650 CE Maina , Ecuador, Peru Manteño-Huancavilca (Precolumbian culture) Milagro (Precolumbian culture) Mollo culture , Bolivia, 1000–1500 CE Muisca , Colombian highlands (Precolumbian culture) Pachacama (Precolumbian culture) Paez (Nasa culture ), Colombian highlands (Precolumbian culture) Panzaleo (Precolumbian culture) Pasto Pijao , Colombia Quechua (Kichua , Kichwa ), Bolivia [ 71] Quitu culture , 2000 BCE–1550 CE Salinar (Precolumbian culture) Saraguro Tiwanaku culture (Tiahuanaco ), 400–1000 CE, Bolivia Tsáchila (Colorado ), Ecuador Tuza-Piartal (Precolumbian culture) Uru , Bolivia, [ 71] Peru Wari culture , central coast and highlands of Peru, 500–1000 CE Pacific lowlands Amotape complex , northern coastal Peru, 9,000–7,100 BCE Atacameño (Atacama , Likan Antaí ), Chile Awá , Colombia and Ecuador Bara , Colombia Cara culture , coastal Ecuador, 500 BCE–1550 CE Bahía , Ecuador, 500 BCE–500 CE Casma culture , coastal Peru, 1000–1400 CE Chancay , central coastal Peru, 1000–1450 CE Chango , coastal Peru, northern Chile Chimú , north coastal Peru, 1000–1450 CE Cupisnique (Precolumbian culture), 1000–200 BCE, coastal Peru Lambayeque (Sican culture ), north coastal Peru, 750–1375 CE Machalilla culture , coastal Ecuador, 1500–1100 BCE Manteño civilization , western Ecuador, 850–1600 CE Moche (Mochica), north coastal Peru, 1–750 CE Nazca culture (Nasca ), south coastal Peru, 1–700 CE Norte Chico civilization (Precolumbian culture), coastal Peru Paiján culture , northern coastal Peru, 8,700–5,900 BCE Paracas , south coastal Peru, 600–175 BCE Recuay culture , Peru (Precolumbian culture) Tallán (Precolumbian culture), north coastal Peru Valdivia culture , Ecuador, 3500–1800 BCE Virú culture , Piura Region, Peru, 200 BCE–300 CE Wari culture (Huari culture ), Peru, 500–1000 CE Yukpa (Yuko ), Colombia Yurutí , Colombia Amazon Northwestern Amazon This region includes Amazonas in Brazil ; the Amazonas and Putumayo Departments in Colombia ; Cotopaxi , Los Rios , Morona-Santiago , Napo , and Pastaza Provinces and the Oriente Region in Ecuador ; and the Loreto Region in Peru .
Arabela , Loreto Region, Peru Arapaso (Arapaco ), Amazonas, Brazil Baniwa Barbudo , Loreto Region, Peru Bora , Loreto Region, Peru Candoshi-Shapra (Chapras ), Loreto Region, Peru Carútana (Arara ), Amazonas, Brazil Chayahuita (Chaywita ) Loreto Region, Peru Cocama , Loreto Region, Peru Cofán (Cofan ), Putumayo Department, Colombia and Ecuador Cubeo (Kobeua ), Amazonas, Brazil and Colombia Dâw , Rio Negro, Brazil Flecheiro Huaorani (Waorani , Waodani , Waos ), Ecuador Hupda (Hup ), Brazil, Colombia Jibito , Loreto Region, Peru Jivaroan peoples , Ecuador and Peru Achuar , Morona-Santiago Province and Oriente Region, Ecuador and Loreto Region, Peru Aguaruna (Aguarana ), Ecuador, Peru Huambisa , Peru Shuar , Morona-Santiago Province and Oriente Region, Ecuador and Loreto Region, Peru Kachá (Shimaco , Urarina ), Loreto Region, Peru Kamsá (Sebondoy ), Putumayo Department, Colombia Kanamarí , Amazonas, Brazil Kichua (Quichua ) Korubu , Amazonas, Brazil Kugapakori-Nahua Macaguaje (Majaguaje ), Río Caquetá, Colombia Machiguenga , Peru Marubo Matsés (Mayoruna , Maxuruna ), Brazil and Peru Mayoruna (Maxuruna ) Miriti , Amazonas Department, Colombia Murato , Loreto Region, Peru Mura , Amazonas, Brazil Pirahã (Mura-pirarrã), Amazonas, Brazil Nukak (Nukak-Makú ), eastern Colombia Ocaina , Loreto Region, Peru Omagua (Cambeba , Kambeba , Umana ), Amazonas, Brazil Orejón (Orejon ), Napo Province, Ecuador Panoan , western Brazil, Bolivia, Peru Sharpas Siona (Sioni ), Amazonas Department, Colombia Siriano , Brazil, Colombia Siusi , Amazonas, Brazil Tariano (Tariana ), Amazonas, Brazil Tsohom Djapá Tukano (Tucano ), Brazil, Colombia Waikino (Vaikino ), Amazonas, Brazil Waimiri-Atroari (Kinja , Uaimiri-Atroari ), Amazonas and Roraima, Brazil Wanano (Unana , Vanana ), Amazonas, Brazil Witoto Yagua (Yahua ), Loreta Region, Peru Yaminahua (Jaminawa , Yamanawa , Yaminawá ), Pando Department, Bolivia [ 71] Yora Záparo (Zaparo ), Pastaza Province, Ecuador Zuruahã (Suruahá , Suruwaha ), Amazonas, Brazil Eastern Amazon This region includes Amazonas , Maranhão , and parts of Pará States in Brazil.
Amanayé (Ararandeura ), Brazil Araweté (Araueté , Bïde ), Pará, Brazil Awá (Guajá) , Brazil Ch'unchu , Peru Ge Guajajára (Guajajara ), Maranhão, Brazil Guaraní , Paraguay Ka'apor , Maranhão, Brazil Kuruaya , Pará, Brazil Marajoara , Precolumbian culture, Pará, Brazil Panará , Mato Grosso and Pará, Brazil Parakanã (Paracana ) Suruí do Pará , Pará, Brazil Tembé Turiwára Wayampi Zo'é people , Pará, Brazil Southern Amazon This region includes southern Brazil (Mato Grosso , Mato Grosso do Sul , parts of Pará , and Rondônia ) and Eastern Bolivia (Beni Department ).
Aikanã , Rondônia, Brazil Akuntsu , Rondônia, Brazil Apiacá (Apiaká ), Mato Grosso and Pará, Brazil [ 72] Assuriní do Toncantins (Tocantins ) Aweti (Aueto ), Mato Grosso, Brazil Bakairí (Bakairi ) Chácobo (Chacobo ), northwest Beni Department, Bolivia [ 71] Chiquitano (Chiquito , Tarapecosi ), Brazil and Santa Cruz, Bolivia [ 71] Cinta Larga , Mato Grosso, Brazil Enawene Nawe , Mato Grosso, Brazil Gavião of Rondônia Guarayu (Guarayo ), Bolivia [ 71] Ikpeng (Xicao ), Mato Grosso, Brazil Itene , Beni Department, Bolivia [ 71] Irántxe (Iranche ) Juma (Kagwahiva ), Rondônia, Brazil Jurúna (Yaruna , Juruna , Yudjá ), Mato Grosso, Brazil Kaiabi (Caiabi , Cajabi , Kajabi, Kayabi ), Mato Grosso, Brazil Kalapálo (Kalapalo ), Mato Grosso, Brazil Kamayurá (Camayura ), Mato Grosso, Brazil Kanoê (Kapixaná ), Rondônia, Brazil Karipuná (Caripuna ) Karitiâna (Caritiana ), Brazil Kayapo , Mato Grosso, Brazil Kuikuro , Mato Grosso, Brazil Matipu , Mato Grosso, Brazil Mehináku (Mehinacu , Mehinako ), Mato Grosso, Brazil Moxo (Mojo ), Bolivia Nahukuá (Nahuqua ), Mato Grosso, Brazil Nambikuára (Nambicuara , Nambikwara ), Mato Grosso, Brazil Pacahuara (Pacaguara , Pacawara ), northwest Beni Department, Bolivia [ 71] Pacajá (Pacaja ) Panará , Mato Grosso and Pará, Brazil Parecís (Paressi ) Rikbaktsa (Erikbaksa ), Mato Grosso, Brazil Rio Pardo people , Mato Grosso, Brazil Sateré-Mawé (Maue ), Brazil Suyá (Kisedje ), Mato Grosso, Brazil Tacana (Takana ), Beni and Madre de Dios Rivers, Bolivia [ 71] Tapajó (Tapajo ) Tenharim Trumai , Mato Grosso, Brazil Tsimané (Chimané , Mosetén , Pano ), Beni Department, Bolivia [ 71] Uru-Eu-Wau-Wau , Rondônia, Brazil Wari' (Pacanawa , Waricaca' ), Rondônia, Brazil Wauja (Waurá , Waura ), Mato Grosso, Brazil Wuy jugu (Mundurucu , Munduruku ) Yawalapiti (Iaualapiti ), Mato Grosso, Brazil Southwestern Amazon This region includes the Cuzco , Huánuco Junín , Loreto , Madre de Dios , and Ucayali Regions of eastern Peru , parts of Acre , Amazonas , and Rondônia , Brazil , and parts of the La Paz and Beni Departments of Bolivia .
Aguano (Santacrucino, Uguano), Peru Amahuaca , Brazil, Peru Apurinã (Popũkare ), Amazonas and Acre Asháninka (Campa , Chuncha ), Acre, Brazil and Junín, Pasco, Huánuco, and Ucayali, Peru Banawá (Jafí , Kitiya ), Amazonas, Brazil Cashibo (Carapache ), Huánuco Region, Peru Conibo (Shipibo-Conibo ), Peru and Amazonas, Brazil Ese Ejja (Chama ), Beni Department, Bolivia [ 71] Harakmbut , Madre de Dios, Peru Amarakaeri , Madre de Dios Region, Peru Huachipaeri , Madre de Dios Region, Peru Arasairi , Madre de Dios Region, Peru Manuquiari , Madre de Dios Region, Peru Puikiri (Puncuri ), Madre de Dios Region, Peru Sapiteri , Madre de Dios Region, Peru Toyeri , Madre de Dios Region, Peru [ 73] Hi-Merimã , Himarimã , Amazonas, Brazil Jamamadi , Acre and Amazonas, Brazil Kaxinawá (Cashinahua , Huni Kuin ), Peru and Acre, Brazil Kulina (Culina ), Peru Kwaza (Coaiá , Koaiá ), Rondônia, Brazil Latundê , Rondônia, Brazil Machinere , Bolivia [ 71] and Peru Mashco-Piro , Peru Matís (Matis ), Brazil Matsés (Mayoruna , Maxuruna ), Brazil, Peru Parintintin (Kagwahiva’nga ), Brazil Shipibo , Loreto Region, Peru Sirionó (Chori , Miá ), Beni and Santa Cruz Departments, Bolivia Ticuna (Tucuna ), Brazil, Colombia, Peru Toromono (Toromona ), La Paz Department, Bolivia [ 71] Yanesha' (Amuesha ), Cusco Region, Peru Yawanawa (Jaminawá , Marinawá , Xixinawá ), Acre, Brazil; Madre de Dios, Peru; and Bolivia Yine (Contaquiro , Simiranch , Simirinche ), Cuzco Region, Peru Yuqui (Bia , Yuki ), Cochabamba Department, Bolivia [ 71] Yuracaré (Yura), Beni and Cochabamba Departments, Bolivia [ 71] Gran Chaco Approximate region of the Gran Chaco Abipón , Argentina, historic group Angaite (Angate), northwestern Paraguay Ayoreo [ 74] (Ayoré , Moro , Morotoco , Pyeta , Yovia , [ 71] Zamuco ), Bolivia and Paraguay Chamacoco (Zamuko ), [ 74] Paraguay Chané , Argentina and Bolivia Chiquitano (Chiquito, Tarapecosi), eastern Bolivia Chorote (Choroti , [ 74] Iyo'wujwa , [ 71] Iyojwa'ja Chorote , Manjuy ), Argentina, Bolivia, and Paraguay Guana [ 74] (Kaskihá), Paraguay Guaraní , [ 74] Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, and Paraguay Guaycuru peoples , Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, and Paraguay Kaiwá , [ 74] Argentina and Brazil Lengua people (Enxet ), [ 74] Paraguay Lulé (Pelé, Tonocoté), Argentina Maká [ 74] (Towolhi), Paraguay Nivaclé (Ashlushlay , [ 74] Chulupí , Chulupe, Guentusé), Argentina and Paraguay Sanapaná [ 74] (Quiativis), Paraguay Vilela , Argentina Wichí (Mataco ), [ 74] Argentina and Tarija Department, Bolivia [ 71] Southern Cone Patagonian languages at the time of European/African contact Aché , southeastern Paraguay Chaná (extinct ), formerly Uruguay Chandule (Chandri ) Charrúa , southern Brazil and Uruguay Comechingon (Henia-Camiare ), Argentina Haush (Manekʼenk , Mánekenk , Aush ), Tierra del Fuego Het (Querandí ) (extinct ), formerly Argentinian Pampas Huarpe (Warpes ), Argentina, Chile Mapuche (Araucanian ), southwestern Argentina and Chile Mbeguá (extinct ), formerly Paraná River, Argentina Minuane (extinct ), formerly Uruguay Puelche (Guennaken, Pamba) (later Araucanized ) (extinct), Argentinian and Chilean Andes [ 75] Tehuelche (later Araucanized ), Patagonia Teushen (Tehues ), extinct , formerly Tierra del Fuego Selkʼnam (Ona), Tierra del Fuego Yaro (Jaro ) Fjords and channels of Patagonia Writing Before European contact:
After European contact, some distinct writing systems have been used for Indigenous languages:
Empires Arising before European contact:
Comancheria (1770-1850) has also been described by some scholars as a Native American empire which arose after European contact.
Technological and social periods The Andes, Mesoamerica, and eastern North America are considered centers that independently developed agriculture, a process known globally as the Neolithic Revolution .
The technological and social development of pre-Columbian cultures are conventionally classified into five archaeological stages :
Lithic stage or Paleo-Indian - hunter-gatherers using stone tools and weapons Archaic stage - first settlements, first crops, subsistence Formative stage - pottery, weaving, sedentary agriculture, ceremonial centers Classic stage - metallurgy, craft specialization, urbanism, theocracy Post-Classic stage - advanced metallurgy, complex urbanism, militarism, secularization In North America, the later stages are grouped instead into the Woodland period and Mississippian culture .
Metallurgy in pre-Columbian America included for some cultures equivalents to Eurasian Copper Age and Bronze Age technology:
The Iron Age in Eurasia is defined by the production of iron tools via smelting ; iron smelting was never developed natively in the Americas. Unsmelted iron was used Andeana and Mesoamerican cultures for mirrors, decorative and ceremonial items, starting fires, and small hammers. Iron magnets were apparently used by the Olmec and Chavin to align monuments. Smelted iron from shipwrecked East Asian vessels was used in the Pacific Northwest before European contact.
Notes ↑ "Culture Areas Index" . the Canadian Museum of Civilization . Archived from the original on 2013-11-04. Retrieved 2009-08-18 . ↑ "Dena'ina." Archived 2016-11-15 at the Wayback Machine ↑ "Slavey" . The Canadian Encyclopedia . Historica Canada. Archived from the original on 13 January 2017. Retrieved 10 December 2016 . ↑ Suttles, Wayne (1990). "Introduction". Northwest Coast . Vol. 7. Washington, DC: Smithsonian Institution. pp. 9– 12. ↑ Krauss, Michael E. (1970). Eyak Dictionary . University of Alaska and Massachusetts Institute of Technology . ↑ Campbell, Lyle (1997). American Indian Languages : The Historical Linguistics of Native America . Oxford: Oxford University Press . pp. 396 n. 29. ISBN 978-0-19-514050-7 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 Sturtevant and Trigger ix 1 2 3 4 "Preamble." Constitution of the Pawnee Nation of Oklahoma Archived 2013-10-07 at the Wayback Machine 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 "Cultural Thesaurus" Archived 2010-06-24 at the Wayback Machine National Museum of the American Indian . Accessed 8 April 2014. 1 2 3 4 5 6 Sturtevant and Trigger 241 1 2 3 4 Sturtevant and Trigger 198 1 2 3 4 5 Goddard 72 ↑ Goddard 72 and 237 1 2 3 4 5 Goddard 237 ↑ Goddard 72, 237–38 1 2 3 Goddard 238 ↑ Goddard 72 and 238 1 2 Sturtevant and Fogelson, 290 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Sturtevant and Trigger 161 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Sturtevant and Fogelson, 293 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Sturtevant and Fogelson, 81–82 1 2 Sturtevant and Fogelson, 291 1 2 3 4 Vest, Jay Hansford C. (Winter–Spring 2005). "An Odyssey among the Iroquois: A History of Tutelo Relations in New York" . American Indian Quarterly . 29 (1/2): 124– 55. doi :10.1353/aiq.2005.0072 . JSTOR 4138803 . ↑ Brooks, Rebecca Beatrice. "Native American Tribes in Massachusetts" . History of Massachusetts . Retrieved 15 November 2021 . ↑ Sturtevant and Trigger 255 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 Sturtevant and Fogelson, 69 1 2 3 4 5 6 Sturtevant and Fogelson, 205 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Sturtevant and Fogelson, 214 ↑ Sturtevant and Fogelson, 673 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 Sturtevant and Fogelson, ix 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Sturtevant and Fogelson, 374 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Sturtevant, 617 ↑ Folgelson, ed. (2004), p. 315 1 2 3 4 Frank, Andrew K. "Indian Removal" . The Encyclopedia of Oklahoma History and Culture . Retrieved 28 April 2024 . ↑ Hann, John H. (2006). The Native American World Beyond Apalachee . University Press of Florida. pp. 53– 56. ISBN 978-0-8130-2982-5 1 2 Sturtevant and Fogelson, 188 1 2 Sturtevant and Fogelson, 598–99 1 2 3 4 5 Hann, John H. (2006). The Native American World Beyond Apalachee . University Press of Florida. p. 87. ISBN 978-0-8130-2982-5 1 2 3 Sturtevant and Fogelson, 302 ↑ Hann 1993 ↑ Sturtevant and Fogelson, 78, 668 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Hann 1996, 5–13 ↑ Milanich 1999, p. 49. ↑ Milanich 1996, p. 46. ↑ Hann 2003:11 ↑ Sturtevant and Fogelson, 190 1 2 3 4 5 6 D'Azevedo, ix ↑ D'Azevedo, 161–62 1 2 3 Loether, Christopher. "Shoshones" Archived 2014-11-10 at the Wayback Machine Encyclopedia of the Great Plains . Retrieved 20 Oct 2013. 1 2 3 Shimkin 335 1 2 3 4 5 6 Murphy and Murphy 306 1 2 3 Murphy and Murphy 287 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Thomas, Pendleton, and Cappannari 280–83 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Pritzker, 230 1 2 3 4 5 6 D'Azevedo, 339 1 2 3 4 D'Azevedo, 340 ↑ Nicholas, Walter S. "A Short History of Johnsondale" . RRanch.org. Archived from the original on 2010-10-31. Retrieved 2010-06-04 . ↑ Pritzker 112 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 Heizer ix ↑ Heizer 205–07 ↑ Heizer 190 ↑ Heizer 593 ↑ Heizer 769 ↑ Heizer 249 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 "Mexico: Map" . Ethnologue. Archived from the original on 25 September 2015. Retrieved 16 November 2015 . ↑ "Paipai Language (Akwa'ala)" Archived 2010-09-26 at the Wayback Machine Native Languages of the Americas . Retrieved 10 Sept 2010. 1 2 3 4 Steward, Julian H. (1948) Editor. Handbook of South American Indians. Volume 4 The Circum-Caribbean Tribes . Smithsonian Institution Bureau of American Ethnology Bulletin 143. ↑ "Aboriginal Roots of Cuban Culture" Archived 2012-03-26 at the Wayback Machine 1 2 3 4 "Prehistory of the Caribbean Culture Area" Archived 2011-08-05 at the Wayback Machine Southeast Archaeological Center . (retrieved 9 July 2011) ↑ "Cacaopera" Archived 2019-09-13 at the Wayback Machine 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 "Languages of Bolivia" Archived 2012-10-02 at the Wayback Machine Ethnologue . Retrieved 23 Oct 2012. ↑ "Apiaká: Introduction" Archived 2012-03-30 at the Wayback Machine ↑ "Huachipaeri" Archived 2011-11-16 at the Wayback Machine Ethnologue . Retrieved 18 Feb 2012. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 "Cultural Thesaurus" Archived 2011-04-29 at the Wayback Machine ↑ "Puelche" . Encyclopædia Britannica . Archived from the original on 1 December 2016. Retrieved 1 December 2016 . ↑ Gordon, Raymond G., Jr. (Ed.). (2005). Ethnologue: Languages of the world (15th ed.). Dallas, TX: SIL International. ISBN 1-55671-159-X ↑ "Y-Chromosome Evidence for Differing Ancient Demographic Histories in the Americas" (PDF) . Department of Biology, University College, London; Departamento de Gene´tica, Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul, Porto Alegre, Brazil; Instituto Venezolano de Investigaciones Cientı´ficas, Caracas, Venezuela; Departamento de Gene´tica, Universidade Federal do Parana´, Curitiba, Brazil; 5Department of Anthropology, University of New Mexico, Albuquerque; 6Laboratorio de Gene´tica Humana, Universidad de los Andes, Bogota´; Victoria Hospital, Prince Albert, Canada; Subassembly of Medical Sciences, Mongolian Academy of Sciences, Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia; Laboratorio de Gene´tica Molecular, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad de Antioquia, Medellı´n, Colombia; Université de Montréal . University College London 73:524–539. 2003. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2019-04-30. Retrieved 2010-01-22 . ↑ Orgel L (2004). "Prebiotic chemistry and the origin of the RNA world" (PDF) . Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol . 39 (2): 99– 123. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.537.7679 . doi :10.1080/10409230490460765 . PMID 15217990 . Archived (PDF) from the original on 2018-11-13. Retrieved 2010-01-19 . 1 2 Tymchuk, Wendy (2008). "Learn about Y-DNA Haplogroup Q" . Genebase Systems. Archived from the original (Verbal tutorial possible) on 2010-06-22. Retrieved 2009-11-21 . Haplogroups are defined by unique mutation events such as single nucleotide polymorphisms, or SNPs. These SNPs mark the branch of a haplogroup, and indicate that all descendants of that haplogroup at one time shared a common ancestor. The Y-DNA SNP mutations were passed from father to son over thousands of years. Over time, additional SNPs occur within a haplogroup, leading to new lineages. These new lineages are considered subclades of the haplogroup. Each time a new mutation occurs, there is a new branch in the haplogroup, and therefore a new subclade. Haplogroup Q, possibly the youngest of the 20 Y-chromosome haplogroups, originated with the SNP mutation M242 in a man from Haplogroup P that likely lived in Siberia approximately 15,000 to 20,000 years before present ↑ Wells, Spencer; Read, Mark (2002). The Journey of Man – A Genetic Odyssey (Digitised online by Google books) . Random House . ISBN 0-8129-7146-9 Archived from the original on 2016-05-18. Retrieved 2009-11-21 . ↑ "First Americans Endured 20,000-Year Layover – Jennifer Viegas, Discovery News" . Archived from the original on 2012-10-10. Retrieved 2009-11-18 . Archaeological evidence, in fact, recognizes that people started to leave Beringia for the New World around 40,000 years ago, but rapid expansion into North America didn't occur until about 15,000 years ago, when the ice had literally broken page 2 Archived March 13, 2012, at the Wayback Machine ↑ Than, Ker (2008). "New World Settlers Took 20,000-Year Pit Stop" . National Geographic Society . Archived from the original on 2011-01-19. Retrieved 2010-01-23 . Over time descendants developed a unique culture—one that was different from the original migrants' way of life in Asia but which contained seeds of the new cultures that would eventually appear throughout the Americas ↑ "Summary of knowledge on the subclades of Haplogroup Q" . Genebase Systems. 2009. Archived from the original on 2011-05-10. Retrieved 2009-11-22 . ↑ Ruhlen M (November 1998). "The origin of the Na-Dene" . Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America . 95 (23): 13994– 96. Bibcode :1998PNAS...9513994R . doi : 10.1073/pnas.95.23.13994 . PMC 25007 . PMID 9811914 . ↑ Zegura SL, Karafet TM, Zhivotovsky LA, Hammer MF (January 2004). "High-resolution SNPs and microsatellite haplotypes point to a single, recent entry of Native American Y chromosomes into the Americas" . Molecular Biology and Evolution . 21 (1): 164– 75. doi : 10.1093/molbev/msh009 . PMID 14595095 . ↑ Juliette Saillard; Peter Forster; Niels Lynnerup; Hans-Jürgen Bandelt; Søren Nørby (2000). "mtDNA Variation among Greenland Eskimos. The Edge of the Beringian Expansion" . Laboratory of Biological Anthropology, Institute of Forensic Medicine, University of Copenhagen, Copenhagen, McDonald Institute for Archaeological Research, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, University of Hamburg, Hamburg . Archived from the original on 2011-08-11. Retrieved 2009-11-22 . The relatively lower coalescence time of the entire haplogroup A2 including the shared sub-arctic branches A2b (Siberians and Inuit) and A2a (Eskimos and Na-Dené) is probably due to secondary expansions of haplogroup A2 from the Beringia area, which would have averaged the overall internal variation of haplogroup A2 in North America. ↑ A. Torroni; T. G. Schurr; C. C. Yang; EJE. Szathmary; R. C. Williams; M. S. Schanfield; G. A. Troup; W. C. Knowler; D. N. Lawrence; K. M. Weiss; D. C. Wallace (January 1992). "Native American Mitochondrial DNA Analysis Indicates That the Amerind and the Nadene Populations Were Founded by Two Independent Migrations" . Center for Genetics and Molecular Medicine and Departments of Biochemistry and Anthropology, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, Georgia . 130 (1). Genetics Society of America: 153– 62. Archived from the original on 2009-02-20. Retrieved 2009-11-28 . The divergence time for the Nadene portion of the HaeIII np 663 lineage was about 6,000–10,000 years. Hence, the ancestral Nadene migrated from Asia independently and considerably more recently than the progenitors of the Amerinds References D'Azevedo, Warren L., volume editor. Handbook of North American Indians , Volume 11: Great Basin . Washington, DC: Smithsonian Institution, 1986. ISBN 978-0-16-004581-3 Hann, John H. "The Mayaca and Jororo and Missions to Them", in McEwan, Bonnie G. ed. The Spanish Missions of "La Florida" . Gainesville, Florida: University Press of Florida. 1993. ISBN 0-8130-1232-5 Hann, John H. A History of the Timucua Indians and Missions . Gainesville, Florida: University Press of Florida, 1996. ISBN 0-8130-1424-7 Hann, John H. (2003). Indians of Central and South Florida: 1513–1763 . University Press of Florida. ISBN 0-8130-2645-8 Heizer, Robert F., volume editor. Handbook of North American Indians, Volume 8: California . Washington, DC: Smithsonian Institution, 1978. ISBN 978-0-16-004574-5 Milanich, Jerald (1999). The Timucua ISBN 0-631-21864-5 . Retrieved June 11, 2010 . Pritzker, Barry M. A Native American Encyclopedia: History, Culture, and Peoples . Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2000. ISBN 978-0-19-513877-1 Steward, Julian H., editor. Handbook of South American Indians , Volume 4: The Circum-Caribbean Tribes . Smithsonian Institution, 1948. Sturtevant, William C., general editor and Bruce G. Trigger, volume editor. Handbook of North American Indians: Northeast . Volume 15. Washington DC: Smithsonian Institution, 1978. ASIN B000NOYRRA . Sturtevant, William C., general editor and Raymond D. Fogelson, volume editor. Handbook of North American Indians: Southeast . Volume 14. Washington DC: Smithsonian Institution, 2004. ISBN 0-16-072300-0
Pre-history Mythology/Religion North America Mesoamerica
South America
Culture
European Modern groups
Related topics
Archaeological Archaeological Human Miscellaneous
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.