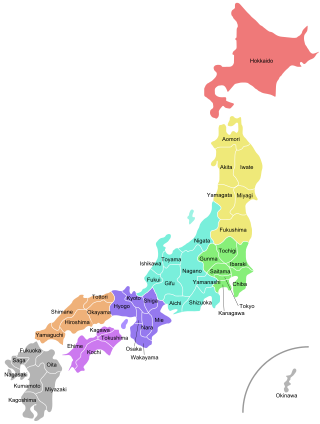
Japan is divided into 47 prefectures, which rank immediately below the national government and form the country's first level of jurisdiction and administrative division. They include 43 prefectures proper, two urban prefectures, one regional prefecture and one metropolis. In 1868, the Meiji Fuhanken sanchisei administration created the first prefectures to replace the urban and rural administrators in the parts of the country previously controlled directly by the shogunate and a few territories of rebels/shogunate loyalists who had not submitted to the new government such as Aizu/Wakamatsu. In 1871, all remaining feudal domains (han) were also transformed into prefectures, so that prefectures subdivided the whole country. In several waves of territorial consolidation, today's 47 prefectures were formed by the turn of the century. In many instances, these are contiguous with the ancient ritsuryō provinces of Japan.

Tochigi Prefecture is a landlocked prefecture of Japan located in the Kantō region of Honshu. Tochigi Prefecture has a population of 1,897,649 and has a geographic area of 6,408 km². Tochigi Prefecture borders Fukushima Prefecture to the north, Gunma Prefecture to the west, Saitama Prefecture to the south, and Ibaraki Prefecture to the southeast.

The Kantō region is a geographical region of Honshu, the largest island of Japan. In a common definition, the region includes the Greater Tokyo Area and encompasses seven prefectures: Gunma, Tochigi, Ibaraki, Saitama, Tokyo, Chiba, and Kanagawa. Slightly more than 45 percent of the land area within its boundaries is the Kantō Plain. The rest consists of the hills and mountains that form land borders with other regions of Japan.
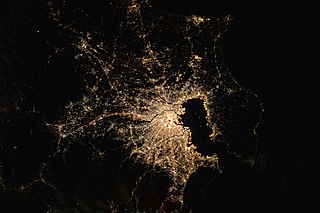
The Greater Tokyo Area is the most populous metropolitan area in the world, consisting of the Kantō region of Japan as well as the prefecture of Yamanashi of the neighboring Chūbu region. In Japanese, it is referred to by various terms, one of the most common being Capital Region.

Nogi is a town located in Tochigi Prefecture, Japan. As of 1 April 2020, the town had an estimated population of 25,050 in 10,153 households, and a population density of 830 persons per km2. The total area of the town is 30.26 square kilometres (11.68 sq mi).
Japanese place names include names for geographic features, present and former administrative divisions, transportation facilities such as railroad stations, and historic sites in Japan. The article Japanese addressing system contains related information on postal addresses.

Chikusei is a city located in Ibaraki Prefecture, Japan. As of 1 January 2024, the city had an estimated population of 98,031 in 39,075 households and a population density of 478 persons per km2. The percentage of the population aged over 65 was 31.2%. The total area of the city is 205.30 square kilometres (79.27 sq mi).
This page lists Japan-related articles with romanized titles beginning with the letter K. For names of people, please list by surname. Please also ignore particles when listing articles.
This page lists Japan-related articles with romanized titles beginning with the letter T. For names of people, please list by surname. Please also ignore articles when listing articles.

The Tokyo Metropolitan Government is the government of the Tokyo Metropolis. One of the 47 prefectures of Japan, the government consists of a popularly elected governor and assembly. The headquarters building is located in the ward of Shinjuku. The metropolitan government administers the special wards, cities, towns and villages that constitute part of the Tokyo Metropolis. With a population closing in on 14 million living within its boundaries, and many more commuting from neighbouring prefectures, the metropolitan government wields significant political power within Japan.

The Kita-Kantō Expressway is a 4-laned national expressway in Japan. It is owned and operated by East Nippon Expressway Company.
The 17th unified local elections in Japan took place in April 2011. In the first phase on April 10, 2011, 12 governors, 41 prefectural assemblies as well as five mayors and 15 assemblies in cities designated by government ordinance were elected. In the second phase on April 24, 2011, mayors and assemblies in hundreds of cities, "special wards" of Tokyo, towns, and villages were up for election. Additionally, a by-election for the National Diet was held in Aichi on April 24.
Events in the year 1905 in Japan. It corresponds to Meiji 38 (明治38年) in the Japanese calendar.
Events in the year 1906 in Japan. It corresponds to Meiji 39 (明治39年) in the Japanese calendar.
The National Governors' Association (NGA) is a national alliance of prefectural governors established under Article 263-3 of the Local Autonomy Law. It mainly makes requests and policy recommendations to the national government regarding local administration and finance. Its abbreviation is NGA. It has organized the Local Autonomy Establishment Measures Council together with the National Association of Prefectural Assembly Speakers, the National Association of City Mayors, the National Association of City Council Speakers, the National Association of Town and Village Speakers, and the National Association of Town and Village Council Speakers.
 Fukushima Prefecture
Fukushima Prefecture  Gunma Prefecture
Gunma Prefecture  Mie Prefecture
Mie Prefecture  Shizuoka Prefecture
Shizuoka Prefecture  Tottori Prefecture
Tottori Prefecture  Yamaguchi Prefecture
Yamaguchi Prefecture 






