
A carbohydrate is a biomolecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen–oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 and thus with the empirical formula Cm(H2O)n, which does not mean the H has covalent bonds with O. However, not all carbohydrates conform to this precise stoichiometric definition, nor are all chemicals that do conform to this definition automatically classified as carbohydrates.
Monosaccharides, also called simple sugars, are the simplest forms of sugar and the most basic units (monomers) from which all carbohydrates are built. Simply, this is the structural unit of carbohydrates.

In organic chemistry, an aldehyde is an organic compound containing a functional group with the structure R−CH=O. The functional group itself can be referred to as an aldehyde but can also be classified as a formyl group. Aldehydes are a common motif in many chemicals important in technology and biology.

In organic chemistry, an acetal is a functional group with the connectivity R2C(OR')2. Here, the R groups can be organic fragments or hydrogen, while the R' groups must be organic fragments not hydrogen. The two R' groups can be equivalent to each other or not. Acetals are formed from and convertible to aldehydes or ketones and have the same oxidation state at the central carbon, but have substantially different chemical stability and reactivity as compared to the analogous carbonyl compounds. The central carbon atom has four bonds to it, and is therefore saturated and has tetrahedral geometry.
In organic chemistry, a nucleophilic addition reaction is an addition reaction where a chemical compound with an electrophilic double or triple bond reacts with a nucleophile, such that the double or triple bond is broken. Nucleophilic additions differ from electrophilic additions in that the former reactions involve the group to which atoms are added accepting electron pairs, whereas the latter reactions involve the group donating electron pairs.

A protecting group or protective group is introduced into a molecule by chemical modification of a functional group to obtain chemoselectivity in a subsequent chemical reaction. It plays an important role in multistep organic synthesis.
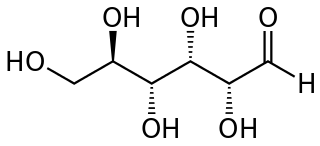
A reducing sugar is any sugar that is capable of acting as a reducing agent. In an alkaline solution, a reducing sugar forms some aldehyde or ketone, which allows it to act as a reducing agent, for example in Benedict's reagent. In such a reaction, the sugar becomes a carboxylic acid.

Cerium(III) chloride (CeCl3), also known as cerous chloride or cerium trichloride, is a compound of cerium and chlorine. It is a white hygroscopic salt; it rapidly absorbs water on exposure to moist air to form a hydrate, which appears to be of variable composition, though the heptahydrate CeCl3·7H2O is known. It is highly soluble in water, and (when anhydrous) it is soluble in ethanol and acetone.
A tetrahedral intermediate is a reaction intermediate in which the bond arrangement around an initially double-bonded carbon atom has been transformed from trigonal to tetrahedral. Tetrahedral intermediates result from nucleophilic addition to a carbonyl group. The stability of tetrahedral intermediate depends on the ability of the groups attached to the new tetrahedral carbon atom to leave with the negative charge. Tetrahedral intermediates are very significant in organic syntheses and biological systems as a key intermediate in esterification, transesterification, ester hydrolysis, formation and hydrolysis of amides and peptides, hydride reductions, and other chemical reactions.

The Claisen rearrangement is a powerful carbon–carbon bond-forming chemical reaction discovered by Rainer Ludwig Claisen. The heating of an allyl vinyl ether will initiate a [3,3]-sigmatropic rearrangement to give a γ,δ-unsaturated carbonyl, driven by exergonically favored carbonyl CO bond formation (Δ = −327 kcal/mol.
Silyl ethers are a group of chemical compounds which contain a silicon atom covalently bonded to an alkoxy group. The general structure is R1R2R3Si−O−R4 where R4 is an alkyl group or an aryl group. Silyl ethers are usually used as protecting groups for alcohols in organic synthesis. Since R1R2R3 can be combinations of differing groups which can be varied in order to provide a number of silyl ethers, this group of chemical compounds provides a wide spectrum of selectivity for protecting group chemistry. Common silyl ethers are: trimethylsilyl (TMS), tert-butyldiphenylsilyl (TBDPS), tert-butyldimethylsilyl (TBS/TBDMS) and triisopropylsilyl (TIPS). They are particularly useful because they can be installed and removed very selectively under mild conditions.
Dioxolane is a heterocyclic acetal with the chemical formula (CH2)2O2CH2. It is related to tetrahydrofuran (THF) by replacement of the methylene group (CH2) at the 2-position with an oxygen atom. The corresponding saturated 6-membered C4O2 rings are called dioxanes. The isomeric 1,2-dioxolane (wherein the two oxygen centers are adjacent) is a peroxide. 1,3-dioxolane is used as a solvent and as a comonomer in polyacetals.

In organic chemistry, pyranose is a collective term for saccharides that have a chemical structure that includes a six-membered ring consisting of five carbon atoms and one oxygen atom. There may be other carbons external to the ring. The name derives from its similarity to the oxygen heterocycle pyran, but the pyranose ring does not have double bonds. A pyranose in which the anomeric −OH at C(l) has been converted into an OR group is called a pyranoside.
The Rubottom oxidation is a useful, high-yielding chemical reaction between silyl enol ethers and peroxyacids to give the corresponding α-hydroxy carbonyl product. The mechanism of the reaction was proposed in its original disclosure by A.G. Brook with further evidence later supplied by George M. Rubottom. After a Prilezhaev-type oxidation of the silyl enol ether with the peroxyacid to form the siloxy oxirane intermediate, acid-catalyzed ring-opening yields an oxocarbenium ion. This intermediate then participates in a 1,4-silyl migration to give an α-siloxy carbonyl derivative that can be readily converted to the α-hydroxy carbonyl compound in the presence of acid, base, or a fluoride source.
Oligosaccharides and polysaccharides are an important class of polymeric carbohydrates found in virtually all living entities. Their structural features make their nomenclature challenging and their roles in living systems make their nomenclature important.

Organoindium chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing In-C bonds. The main application of organoindium chemistry is in the preparation of semiconducting components for microelectronic applications. The area is also of some interest in organic synthesis. Most organoindium compounds feature the In(III) oxidation state, akin to its lighter congeners Ga(III) and B(III).

Trichloroacetonitrile is an organic compound with the formula CCl3CN. It is a colourless liquid, although commercial samples often are brownish. It is used commercially as a precursor to the fungicide etridiazole. It is prepared by dehydration of trichloroacetamide. As a bifunctional compound, trichloroacetonitrile can react at both the trichloromethyl and the nitrile group. The electron-withdrawing effect of the trichloromethyl group activates the nitrile group for nucleophilic additions. The high reactivity makes trichloroacetonitrile a versatile reagent, but also causes its susceptibility towards hydrolysis.
Fétizon oxidation is the oxidation of primary and secondary alcohols utilizing the compound silver(I) carbonate absorbed onto the surface of celite also known as Fétizon's reagent first employed by Marcel Fétizon in 1968. It is a mild reagent, suitable for both acid and base sensitive compounds. Its great reactivity with lactols makes the Fétizon oxidation a useful method to obtain lactones from a diol. The reaction is inhibited significantly by polar groups within the reaction system as well as steric hindrance of the α-hydrogen of the alcohol.
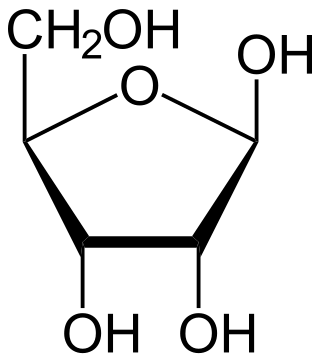
Ribose is a simple sugar and carbohydrate with molecular formula C5H10O5 and the linear-form composition H−(C=O)−(CHOH)4−H. The naturally-occurring form, d-ribose, is a component of the ribonucleotides from which RNA is built, and so this compound is necessary for coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. It has a structural analog, deoxyribose, which is a similarly essential component of DNA. l-ribose is an unnatural sugar that was first prepared by Emil Fischer and Oscar Piloty in 1891. It was not until 1909 that Phoebus Levene and Walter Jacobs recognised that d-ribose was a natural product, the enantiomer of Fischer and Piloty's product, and an essential component of nucleic acids. Fischer chose the name "ribose" as it is a partial rearrangement of the name of another sugar, arabinose, of which ribose is an epimer at the 2' carbon; both names also relate to gum arabic, from which arabinose was first isolated and from which they prepared l-ribose.
D-Ribose pyranase is an enzyme that catalyzes the interconversion of β-D-ribopyranose and β-D-ribofuranose. This enzyme is an isomerase that has only been found in bacteria and viruses. It has two known functions of helping transport ribose into cells and producing β-D-ribofuranose, which can later be used to make ribose 5-phosphate for the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP). D-Ribose pyranase does not have a defined crystal structure but there are two different proposed structures. The active site of D-ribose pyranase is high in histidine residues along with a few other key binding sites.











