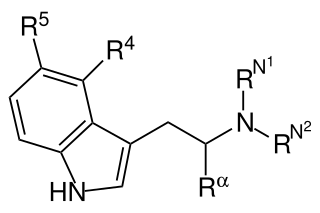
This is a list of agonists of the serotonin receptor subtype 5-HT2A (and other 5-HT2 subtypes to a varying extent) which fall outside the common structural classes. Most agonists at this receptor are either substituted phenethylamine derivatives from the 2C, DOx and 25-NB groups, or substituted tryptamines and related compounds along with more complex derivatives of these such as lysergamides and iboga-type alkaloids. [1] There are however numerous 5-HT2A receptor agonists which do not fall within any of these groups, some representative examples of which are listed below. Ki and EC50 values vary depending on the assay conditions used and so may not be directly comparable between sources. Many of these compounds have been designed to be non-psychoactive derivatives for medical applications, and it should not be assumed that a compound which acts as a 5-HT2A agonist will necessarily be psychedelic in nature. [2]
| Structure | Name | Chemical name | h5-HT2A Ki (EC50) (nM) | PubChem | CAS number | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
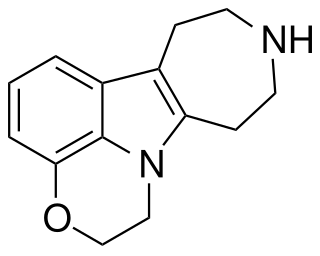
 | Compound 11a | 11-chloro-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1H-[1,4]diazepino[1,7-a]indole | 6.5 | 20726100 | 599173-28-1 | [3] |
 | Compound 23 | 9-Chloro-7-(2-ethoxy-phenyl)-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1H-[1,4]diazepino[1,7-a]indole | 32 | 44315398 | 599173-25-8 | [3] |
 | Compound 10d | 7-Benzyloxy-8-bromo-1-methyl-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1H-3-benzazepine | 22 | 10472780 | 616201-60-6 | [4] |
 | Example 22.67 | 4-(6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-5H-pyrido[2,3-d]azepin-2-yl)thiomorpholine | 21 | 44124494 | [5] | |
 | Compound 3d (N-Bn-THAZ) | 2-benzyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-[1,2]oxazolo[4,5-d]azepin-3-one | (549) | 14515725 | 125115-66-4 | [6] |
 | Compound 11 | (3R)-N,N-diethyl-5-(1H-indol-4-yl)-1-methyl-3,6-dihydro-2H-pyridine-3-carboxamide | (<10) | 156278040 | [7] | |
 | Compound 106 | 6-chloro-1-(2,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole | 4376990 | 528525-37-3 | [8] | |
 | Compound 6c | (6S)-2,3-dichloro-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-6,9-epiminocyclohepta[b]quinoxaline | (400) | [9] | ||
 | Compound 70 | 3-(4-bromo-2-methylpyrazol-3-yl)-N-(4-chlorophenyl)-4-methoxyaniline | 1.77 | 9952456 | [10] | |
 | Compound 22 | 7-(trifluoromethoxy)-2,3,4,10b-tetrahydro-1H-pyrazino[1,2-b]isoindol-6-one | 67 (87) | 11448649 | [10] | |
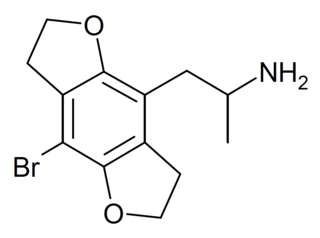
 | Example 1 (ZC-B) | 3-(4-bromo-2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)azetidine | (1.6) | 156337249 | 2641630-65-9 | [11] |
 | 2C-B-aminorex | 5-(4-bromo-2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1,3-oxazol-2-amine | 165360199 | [12] | ||
 | 2-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)morpholine | 2-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)morpholine | 20.6 | 11429275 | [13] | |
 | DM-506 (ibogaminalog) | 3-methyl-2,4,5,6-tetrahydro-1H-azepino[4,5-b]indole | 24183 | 7546-66-9 | [14] | |
 | LPH-5 | (3S)-3-[2,5-dimethoxy-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]piperidine | (3.2) | 156337168 | 2641630-97-7 | [15] |
 | 2C-B-PP | 1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)piperazine | 4738744 | 100939-87-5 | [16] | |
 | cis-urocanic acid (cis-UCA) | (Z)-3-(1H-imidazol-5-yl)prop-2-enoic acid | 4.6 | 1549103 | 7699-35-6 | [17] [18] [19] |
 | CPD-1 | (3S)-3-Methyl-1-[4-(trifluoromethyl)-1-benzofuran-7-yl]piperazine | 9925822 | 325145-37-7 | [20] | |
 | Efavirenz | (4S)-6-Chloro-4-(2-cyclopropylethynyl)-4-(trifluoromethyl)-2,4-dihydro-1H-3,1-benzoxazin-2-one | 64139 | 154598-52-4 | [21] | |
| GM-2505 | [22] | |||||
 | IHCH-7079 | (6bR,10aS)-8-(2-Methoxyphenethyl)-3-methyl-2,3,6b,7,8,9,10,10a-octahydro-1H-pyrido[3',4':4,5]pyrrolo[1,2,3-de]quinoxaline | 169488014 | 2957888-63-8 | [23] | |
 | IHCH-7113 | (6bR,10aS)-3-methyl-2,3,6b,7,8,9,10,10a-octahydro-1H-pyrido[3',4':4,5]pyrrolo[1,2,3-de]quinoxaline | 21302499 | 313368-85-3 | [23] | |
| ? | ITI-1549 | ? | 10.2 | ? | ? | [24] |
 | NDTDI | N,N-diethyl-3-[methyl(1,3,4,5-tetrahydrobenzo[cd]indol-4-yl)amino]propanamide | 163192742 | [25] | ||
 | Mefloquine | 2,8-bis(trifluoromethyl)quinolin-4-yl-(2-piperidyl)methanol | 40692 | 53230-10-7 | [26] | |
 | ORG-12962 | 1-(5-trifluoromethyl-6-chloropyridin-2-yl)piperazine | 9796408 | 210821-63-9 | [27] | |
 | ORG-37684 | (3S)-3-[(2,3-dihydro-5-methoxy-1H-inden-4-yl)oxy]pyrrolidine | 9794656 | 213007-95-5 | [28] | |
 | OSU-6162 | (3S)-3-[3-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl]-1-propylpiperidine | 9795741 | 156907-84-5 | [29] | |
 | PHA-57378 | 2,7,8,9,10,11-hexahydro-1H-azepino[4,5-b][1,4]oxazino[2,3,4-hi]indole | 4.1 | 10198481 | 303798-94-9 | [3] |
 | P-54 | 2-(5-methoxypyrazolo[1,5-a]pyridin-3-yl)-N,N-dimethylethanamine | 168946740 | [30] | ||
 | I-28 | N-[2-(8-methoxynaphthalen-1-yl)ethyl]-N-methylpropan-2-amine | 170604481 | [31] | ||
 | (R)-69 | 3-[(5R)-5-methyl-1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyridin-3-yl]-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine | 164513426 | [32] | ||
 | RS134-49 | 4-methyl-3-(1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-5-yl)-1H-indole | 168941768 | [33] [34] | ||
 | RH-34 | 3-[2-(2-methoxybenzylamino)ethyl]-1H-quinazoline-2,4-dione | 10041987 | 1028307-48-3 | [35] | |
 | SCHEMBL5334361 | 7-[(3-methoxyphenoxy)methyl]-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1H-3-benzazepine | (0.4) | 59027940 | 959867-47-1 | [36] |
 | Tabernanthalog | 8-methoxy-3-methyl-2,4,5,6-tetrahydro-1H-azepino[4,5-b]indole | 146026994 | 2483829-59-8 | [37] | |
 | TKU-II-100 | [(1S,2S)-2-(2-fluorophenyl)cyclopropyl]methanamine | 0.62 | 44572747 | [38] | |
 | WAY-470 | 1,16-diazatetracyclo[8.8.1.02,9.014,19]nonadeca-2(9),10,12,14(19)-tetraene | 36 | 10037962 | [39] | |
 | WXVL_BT0793LQ2118 | 6-fluoro-4-(1-methyl-1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyridin-3-yl)-1H-indole | [40] | |||
 | Z2825713589 | (4-amino-3,3a,4,5,6,6a-hexahydro-1H-cyclopenta[c]pyrrol-2-yl)-(6-methoxypyrazin-2-yl)methanone | 167788805 | [40] | ||
 | Z2876442907 | ethyl 2-[[2-(4-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)ethylamino]methyl]-1,3-thiazole-5-carboxylate | 167850865 | [40] | ||
 | Z3517967757 | 4-[1-(1-pyrimidin-2-ylethyl)piperidin-3-yl]phenol | 167949972 | [40] | ||
 | Z3881312504 | 2-bromo-4-[2-[methyl-[2-(1,3-thiazol-2-yl)ethyl]amino]ethyl]phenol | 167904469 | [40] | ||
 | Z4154032166 | 2,2,2-trifluoro-1-[6-(1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-5-yl)pyridin-2-yl]ethanol | 167878716 | [40] | ||
 | Z5247692566 | 4-[(3,3-dimethyloxolan-2-yl)methyl]-3-[(1H-indol-3-yl)methyl]morpholine | [40] | |||
 | Z5247692629 | 1-(1-bicyclo[1.1.1]pentanyl)-4-[[5-(4-chlorophenyl)-1H-pyrazol-4-yl]methyl]piperazine | 166358273 | [40] | ||