
Empathogens or entactogens are a class of psychoactive drugs that induce the production of experiences of emotional communion, oneness, relatedness, emotional openness—that is, empathy or sympathy—as particularly observed and reported for experiences with 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA). This class of drug is distinguished from the classes of hallucinogen or psychedelic, and amphetamine or stimulants. Major members of this class include MDMA, MDA, MDEA, MDOH, MBDB, 5-APB, 5-MAPB, 6-APB, 6-MAPB, methylone, mephedrone, GHB, αMT, and αET, MDAI among others. Most entactogens are phenethylamines and amphetamines, although several, such as αMT and αET, are tryptamines. When referring to MDMA and its counterparts, the term MDxx is often used. Entactogens are sometimes incorrectly referred to as hallucinogens or stimulants, although many entactogens such as ecstasy exhibit psychedelic or stimulant properties as well.

5-HT receptors, 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors, or serotonin receptors, are a group of G protein-coupled receptor and ligand-gated ion channels found in the central and peripheral nervous systems. They mediate both excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmission. The serotonin receptors are activated by the neurotransmitter serotonin, which acts as their natural ligand.

The serotonin 1A receptor is a subtype of serotonin receptors, or 5-HT receptors, that binds serotonin, also known as 5-HT, a neurotransmitter. 5-HT1A is expressed in the brain, spleen, and neonatal kidney. It is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR), coupled to the Gi protein, and its activation in the brain mediates hyperpolarization and reduction of firing rate of the postsynaptic neuron. In humans, the serotonin 1A receptor is encoded by the HTR1A gene.

5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 1B also known as the 5-HT1B receptor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HTR1B gene. The 5-HT1B receptor is a 5-HT receptor subtype.

5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 1D, also known as HTR1D, is a 5-HT receptor, but also denotes the human gene encoding it. 5-HT1D acts on the central nervous system, and affects locomotion and anxiety. It also induces vasoconstriction in the brain.
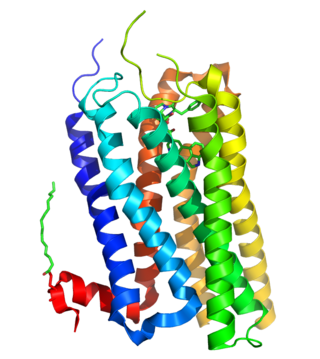
5-Hydroxytryptamine receptor 2B (5-HT2B) also known as serotonin receptor 2B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HTR2B gene. 5-HT2B is a member of the 5-HT2 receptor family that binds the neurotransmitter serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT). Like all 5-HT2 receptors, the 5-HT2B receptor is Gq/G11-protein coupled, leading to downstream activation of phospholipase C.

5-Hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 5A, also known as HTR5A, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HTR5A gene. Agonists and antagonists for 5-HT receptors, as well as serotonin uptake inhibitors, present promnesic (memory-promoting) and/or anti-amnesic effects under different conditions, and 5-HT receptors are also associated with neural changes.

The 5HT6 receptor is a subtype of 5HT receptor that binds the endogenous neurotransmitter serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5HT). It is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that is coupled to Gs and mediates excitatory neurotransmission. HTR6 denotes the human gene encoding for the receptor.

The 5-HT7 receptor is a member of the GPCR superfamily of cell surface receptors and is activated by the neurotransmitter serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT). The 5-HT7 receptor is coupled to Gs (stimulates the production of the intracellular signaling molecule cAMP) and is expressed in a variety of human tissues, particularly in the brain, the gastrointestinal tract, and in various blood vessels. This receptor has been a drug development target for the treatment of several clinical disorders. The 5-HT7 receptor is encoded by the HTR7 gene, which in humans is transcribed into 3 different splice variants.

Xanomeline is a small molecule muscarinic acetylcholine receptor agonist that was first synthesized in a collaboration between Eli Lilly and Novo Nordisk as an investigational therapeutic being studied for the treatment of central nervous system (CNS) disorders.

SB-271046 is a drug which is used in scientific research. It was one of the first selective 5-HT6 receptor antagonists to be discovered, and was found through high-throughput screening of the SmithKline Beecham Compound Bank using cloned 5-HT6 receptors as a target, with an initial lead compound being developed into SB-271046 through a structure-activity relationship (SAR) study. SB-271046 was found to be potent and selective in vitro and had good oral bioavailability in vivo, but had poor penetration across the blood–brain barrier, so further SAR work was then conducted, which led to improved 5-HT6 antagonists such as SB-357,134 and SB-399,885.

AR-A000002 is a drug which is one of the first compounds developed to act as a selective antagonist for the serotonin receptor 5-HT1B, with approximately 10x selectivity for 5-HT1B over the closely related 5-HT1D receptor. It has been shown to produce sustained increases in levels of serotonin in the brain, and has anxiolytic effects in animal studies.

SB-204741 is a drug which acts as a potent and selective antagonist at the serotonin 5-HT2B receptor, with around 135x selectivity over the closely related 5-HT2C receptor, and even higher over the 5-HT2A receptor and other targets. It is used in scientific research for investigating the functions of the 5-HT2B receptor.

SB-269970 is a drug and research chemical developed by GlaxoSmithKline used in scientific studies. It is believed to act as a selective 5-HT7 receptor antagonist (EC50 = 1.25 nM) (or possibly inverse agonist). A subsequent study in guinea pig at a concentration of 10 μM showed that it also blocks the α2-adrenergic receptor. The large difference in test concentrations however confirms the selectivity of SB-269970 for the 5-HT7 receptor.
A serenic, or anti-aggressive drug, is a type of drug which reduces the capacity for aggression.
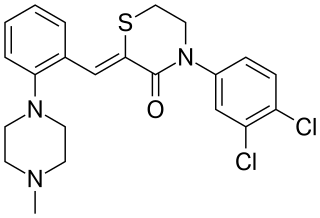
Elzasonan (CP-448,187) is a selective 5-HT1B and 5-HT1D receptor antagonist that was under development by Pfizer for the treatment of depression but was discontinued, possibly due to poor efficacy. By preferentially blocking 5-HT1B and 5-HT1D autoreceptors, elzasonan is thought to enhance serotonergic innervations originating from the raphe nucleus, thereby improving signaling to limbic regions like the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex and ultimately resulting in antidepressant effects.

SB-206553 is a drug which acts as a mixed antagonist for the 5-HT2B and 5-HT2C serotonin receptors. It has anxiolytic properties in animal studies and interacts with a range of other drugs. It has also been shown to act as a positive allosteric modulator of α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Modified derivatives of SB-206553 have been used to probe the structure of the 5-HT2B receptor.

S32212 is a drug which is under preclinical investigation as a potential antidepressant medicine. It behaves as a selective, combined 5-HT2C receptor inverse agonist and α2-adrenergic receptor antagonist (at all three subtypes—α2A, α2B, and α2C) with additional 5-HT2A and, to a lesser extent, 5-HT2B receptor antagonistic properties, and lacks any apparent affinity for the monoamine reuptake transporters or for the α1-adrenergic, H1, or mACh receptors. This profile of activity is compatible with the definition of a noradrenergic and specific serotonergic antidepressant (NaSSA), and as such, S32212 could in turn be classified as a NaSSA.
Hyperlocomotion, also known as locomotor hyperactivity, hyperactivity, or increased locomotor activity, is an effect of certain drugs in animals in which locomotor activity is increased. It is induced by certain drugs like psychostimulants and NMDA receptor antagonists and is reversed by certain other drugs like antipsychotics and certain antidepressants.

GR-55562 is a selective serotonin 5-HT1B and 5-HT1D receptor antagonist. It is one of several selective serotonin 5-HT1B receptor antagonists used in scientific research.
















