Related Research Articles
Chlorine trifluoride is an interhalogen compound with the formula ClF3. This colorless, poisonous, corrosive, and extremely reactive gas condenses to a pale-greenish yellow liquid, the form in which it is most often sold. Despite being famous for its extreme oxidation properties and igniting many things, chlorine trifluoride is not combustible itself. The compound is primarily of interest in plasmaless cleaning and etching operations in the semiconductor industry, in nuclear reactor fuel processing, historically as a component in rocket fuels, and various other industrial operations owing to its corrosive nature.
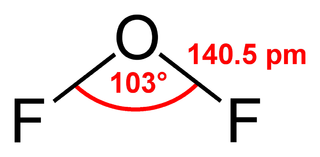
Oxygen difluoride is a chemical compound with the formula OF2. As predicted by VSEPR theory, the molecule adopts a "bent" molecular geometry. It is strong oxidizer and has attracted attention in rocketry for this reason. With a boiling point of -144.75 °C, OF2 is the most volatile (isolable) triatomic compound. The compound is one of many known oxygen fluorides.
Dioxygen difluoride is a compound of fluorine and oxygen with the molecular formula O2F2. It can exist as an orange-colored solid which melts into a red liquid at −163 °C (110 K). It is an extremely strong oxidant and decomposes into oxygen and fluorine even at −160 °C (113 K) at a rate of 4% per day — its lifetime at room temperature is thus extremely short. Dioxygen difluoride reacts vigorously with nearly every chemical it encounters (including ordinary ice) leading to its onomatopoeic nickname FOOF (a play on its chemical structure and its explosive tendencies).
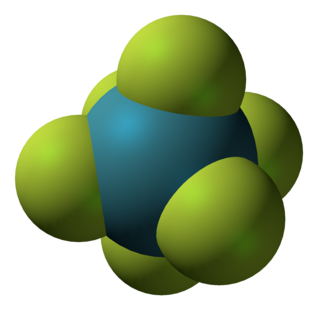
Xenon hexafluoride is a noble gas compound with the formula XeF6. It is one of the three binary fluorides of xenon that have been studied experimentally, the other two being XeF2 and XeF4. All known are exergonic and stable at normal temperatures. XeF6 is the strongest fluorinating agent of the series. It is a colorless solid that readily sublimes into intensely yellow vapors.

Silver(II) fluoride is a chemical compound with the formula AgF2. It is a rare example of a silver(II) compound. Silver usually exists in its +1 oxidation state. It is used as a fluorinating agent.
Perchloryl fluoride is a reactive gas with the chemical formula ClO
3F. It has a characteristic sweet odor that resembles gasoline and kerosene. It is toxic and is a powerful oxidizing and fluorinating agent. It is the acid fluoride of perchloric acid.

Chloryl fluoride is the chemical compound with the formula ClO2F. It is commonly encountered as side-product in reactions of chlorine fluorides with oxygen sources. It is the acyl fluoride of chloric acid.

Fluorine is a chemical element with the symbol F and atomic number 9. It is the lightest halogen and exists at standard conditions as a highly toxic, pale yellow diatomic gas. As the most electronegative reactive element, it is extremely reactive, as it reacts with all other elements except for the light inert gases.
Difluorides are chemical compounds with two fluorine atoms per molecule.

Thiophosphoryl fluoride is an inorganic molecular gas with formula PSF3 containing phosphorus, sulfur and fluorine. It spontaneously ignites in air and burns with a cool flame. The discoverers were able to have flames around their hands without discomfort, and called it "probably one of the coldest flames known". The gas was discovered in 1888.
Fluorine forms a great variety of chemical compounds, within which it always adopts an oxidation state of −1. With other atoms, fluorine forms either polar covalent bonds or ionic bonds. Most frequently, covalent bonds involving fluorine atoms are single bonds, although at least two examples of a higher order bond exist. Fluoride may act as a bridging ligand between two metals in some complex molecules. Molecules containing fluorine may also exhibit hydrogen bonding. Fluorine's chemistry includes inorganic compounds formed with hydrogen, metals, nonmetals, and even noble gases; as well as a diverse set of organic compounds. For many elements the highest known oxidation state can be achieved in a fluoride. For some elements this is achieved exclusively in a fluoride, for others exclusively in an oxide; and for still others the highest oxidation states of oxides and fluorides are always equal.
Krypton hexafluoride is an inorganic chemical compound of krypton and fluorine with the chemical formula KrF6. It is still a hypothetical compound.
Gold hexafluoride is a hypothetical binary inorganic chemical compound of gold and fluorine with the chemical formula AuF6. As of 2023, it is still a hypothetical compound that has never been prepared or observed. In 1999, Neil Bartlett stated, "It should exist, if made at low temperature and kept cold."
Platinum(II) fluoride is a binary chemical compound of platinum and fluorine with the chemical formula PtF
2. Some sources claim that its existence is uncertain.
Lithium hypofluorite is an inorganic compound of lithium, fluorine, and oxygen with the chemical formula of LiFO. This is a lithium salt of hypofluorous acid.
Pentaoxygen difluoride is a binary inorganic compound of fluorine and oxygen with the chemical formula O5F2. The compound is one of many known oxygen fluorides.
Hexaoxygen difluoride is a binary inorganic compound of fluorine and oxygen with the chemical formula O6F2. The compound is one of many known oxygen fluorides.
Periodyl fluoride is an inorganic compound of iodine, fluorine, and oxygen with the chemical formula IO3F. The compound has been initially synthesized around 1950.
Perbromyl fluoride is an inorganic compound of bromine, fluorine, and oxygen with the chemical formula BrO3F.
Oxygen trifluoride is a binary inorganic compound of fluorine and oxygen with the chemical formula OF3. This is one of many known oxygen fluorides.
References
- ↑ Tarendash, Albert S.; Rowe, Frederick J. (2002). AP Chemistry: An Apex Learning Guide. Simon & Schuster. p. 545. ISBN 978-0-7432-2589-2 . Retrieved 20 July 2023.
- ↑ Kuznecov, Vladimir I. (1980). Theory of Valency in Progress. Mir. p. 227. ISBN 978-0-7147-1591-9 . Retrieved 20 July 2023.
- ↑ F Fluorine: Compounds with Oxygen and Nitrogen. Springer Science & Business Media. 29 June 2013. p. 3. ISBN 978-3-662-06339-2 . Retrieved 20 July 2023.
- ↑ Chase, Malcolm W. "NIST-JANAF Thermochemical Tables for the Oxygen Fluorides" (PDF). NIST . Retrieved 20 July 2023.