Related Research Articles

Chlorine is a chemical element with the symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between them. Chlorine is a yellow-green gas at room temperature. It is an extremely reactive element and a strong oxidising agent: among the elements, it has the highest electron affinity and the third-highest electronegativity on the revised Pauling scale, behind only oxygen and fluorine.

The halogens are a group in the periodic table consisting of six chemically related elements: fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), astatine (At), and tennessine (Ts), though some authors would exclude tennessine as its chemistry is unknown and is theoretically expected to be more like that of gallium. In the modern IUPAC nomenclature, this group is known as group (XVII) or group (VII).

Fluorocarbons are chemical compounds with carbon-fluorine bonds. Compounds that contain many C-F bonds often have distinctive properties, e.g., enhanced stability, volatility, and hydrophobicity. Several fluorocarbons and their derivatives are commercial polymers, refrigerants, drugs, and anesthetics.
A period 2 element is one of the chemical elements in the second row of the periodic table of the chemical elements. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring (periodic) trends in the chemical behavior of the elements as their atomic number increases; a new row is started when chemical behavior begins to repeat, creating columns of elements with similar properties.
In chemistry, halogenation is a chemical reaction that entails the introduction of one or more halogens into a compound. Halide-containing compounds are pervasive, making this type of transformation important, e.g. in the production of polymers, drugs. This kind of conversion is in fact so common that a comprehensive overview is challenging. This article mainly deals with halogenation using elemental halogens. Halides are also commonly introduced using salts of the halides and halogen acids. Many specialized reagents exist for and introducing halogens into diverse substrates, e.g. thionyl chloride.
In chemistry, an interhalogen compound is a molecule which contains two or more different halogen atoms and no atoms of elements from any other group.
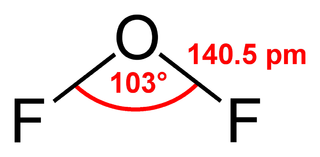
Oxygen difluoride is a chemical compound with the formula OF2. As predicted by VSEPR theory, the molecule adopts a "bent" molecular geometry. It is strong oxidizer and has attracted attention in rocketry for this reason. With a boiling point of -144.75 °C, OF2 is the most volatile (isolable) triatomic compound. The compound is one of many known oxygen fluorides.

Oxygen fluorides are compounds of elements oxygen and fluorine with the general formula OnF2, where n = 1 to 6. Many different oxygen fluorides are known:
Dioxygen difluoride is a compound of fluorine and oxygen with the molecular formula O2F2. It can exist as an orange-colored solid which melts into a red liquid at −163 °C (110 K). It is an extremely strong oxidant and decomposes into oxygen and fluorine even at −160 °C (113 K) at a rate of 4% per day — its lifetime at room temperature is thus extremely short. Dioxygen difluoride reacts vigorously with nearly every chemical it encounters (including ordinary ice) leading to its onomatopoeic nickname FOOF (a play on its chemical structure and its explosive tendencies).

Bromine pentafluoride, BrF5, is an interhalogen compound and a fluoride of bromine. It is a strong fluorinating agent.

Silver(II) fluoride is a chemical compound with the formula AgF2. It is a rare example of a silver(II) compound. Silver usually exists in its +1 oxidation state. It is used as a fluorinating agent.
Organofluorine chemistry describes the chemistry of organofluorine compounds, organic compounds that contain a carbon–fluorine bond. Organofluorine compounds find diverse applications ranging from oil and water repellents to pharmaceuticals, refrigerants, and reagents in catalysis. In addition to these applications, some organofluorine compounds are pollutants because of their contributions to ozone depletion, global warming, bioaccumulation, and toxicity. The area of organofluorine chemistry often requires special techniques associated with the handling of fluorinating agents.

Chloryl fluoride is the chemical compound with the formula ClO2F. It is commonly encountered as side-product in reactions of chlorine fluorides with oxygen sources. It is the acyl fluoride of chloric acid.

Hypofluorous acid, chemical formula HOF, is the only known oxyacid of fluorine and the only known oxoacid in which the main atom gains electrons from oxygen to create a negative oxidation state. The oxidation state of the oxygen in hypofluorites is 0. It is also the only hypohalous acid that can be isolated as a solid. HOF is an intermediate in the oxidation of water by fluorine, which produces hydrogen fluoride, oxygen difluoride, hydrogen peroxide, ozone and oxygen. HOF is explosive at room temperature, forming HF and O2:

The carbon–fluorine bond is a polar covalent bond between carbon and fluorine that is a component of all organofluorine compounds. It is one of the strongest single bonds in chemistry, and relatively short, due to its partial ionic character. The bond also strengthens and shortens as more fluorines are added to the same carbon on a chemical compound. As such, fluoroalkanes like tetrafluoromethane are some of the most unreactive organic compounds.
Dioxygenyl hexafluoroplatinate is a compound with formula O2PtF6. It is a hexafluoroplatinate of the unusual dioxygenyl cation, O2+, and is the first known compound containing this cation. It can be produced by the reaction of dioxygen with platinum hexafluoride. The fact that PtF
6 is strong enough to oxidise O
2, whose first ionization potential is 12.2 eV, led Neil Bartlett to correctly surmise that it might be able to oxidise xenon (first ionization potential 12.13 eV). This led to the discovery of xenon hexafluoroplatinate, which proved that the noble gases, previously thought to be inert, are able to form chemical compounds.

The oxidation state of oxygen is −2 in almost all known compounds of oxygen. The oxidation state −1 is found in a few compounds such as peroxides. Compounds containing oxygen in other oxidation states are very uncommon: −1⁄2 (superoxides), −1⁄3 (ozonides), 0, +1⁄2 (dioxygenyl), +1, and +2.

Fluorine perchlorate, also called perchloryl hypofluorite is the rarely encountered chemical compound of fluorine, chlorine, and oxygen with the chemical formula ClO
4F or FOClO
3. It is an extremely unstable gas that explodes spontaneously and has a penetrating odor.

Rhodium hexafluoride, also rhodium(VI) fluoride, (RhF6) is the inorganic compound of rhodium and fluorine. A black volatile solid, it is a highly reactive material, and a rare example of a rhodium(VI) compound. It is one of seventeen known binary hexafluorides.
Fluorine forms a great variety of chemical compounds, within which it always adopts an oxidation state of −1. With other atoms, fluorine forms either polar covalent bonds or ionic bonds. Most frequently, covalent bonds involving fluorine atoms are single bonds, although at least two examples of a higher order bond exist. Fluoride may act as a bridging ligand between two metals in some complex molecules. Molecules containing fluorine may also exhibit hydrogen bonding. Fluorine's chemistry includes inorganic compounds formed with hydrogen, metals, nonmetals, and even noble gases; as well as a diverse set of organic compounds. For many elements the highest known oxidation state can be achieved in a fluoride. For some elements this is achieved exclusively in a fluoride, for others exclusively in an oxide; and for still others the highest oxidation states of oxides and fluorides are always equal.
References
- ↑ F Fluorine: Compounds with Oxygen and Nitrogen. Springer Science & Business Media. 29 June 2013. p. 3. ISBN 978-3-662-06339-2 . Retrieved 20 July 2023.