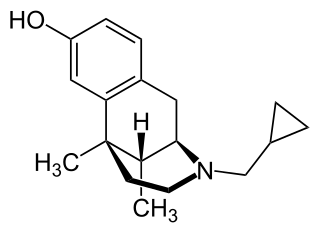
Cyclazocine is a mixed opioid agonist/antagonist related to dezocine, pentazocine and phenazocine. This family of opioid drugs is called the benzomorphans or benzazocines. It is a KOR agonist and MOR partial agonist, and also has high affinity for the DOR.

Ketazocine (INN), also known as ketocyclazocine, is a benzomorphan derivative used in opioid receptor research. Ketazocine, for which the receptor is named, is an exogenous opioid that binds to the κ opioid receptor.
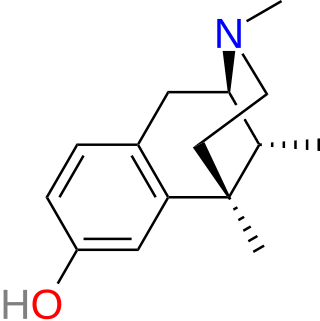
Metazocine is an opioid analgesic related to pentazocine. While metazocine has significant analgesic effects, mediated through a mixed agonist–antagonist action at the mu opioid receptor, its clinical use is limited by dysphoric and hallucinogenic effects which are most likely caused by activity at kappa opioid receptors and/or sigma receptors.

Phenazocine is an opioid analgesic drug, which is related to pentazocine and has a similar profile of effects.

Alazocine, also known more commonly as N-allylnormetazocine (NANM), is a synthetic opioid analgesic of the benzomorphan family related to metazocine, which was never marketed. In addition to its opioid activity, the drug is a sigma receptor agonist, and has been used widely in scientific research in studies of this receptor. Alazocine is described as a potent analgesic, psychotomimetic or hallucinogen, and opioid antagonist. Moreover, one of its enantiomers was the first compound that was found to selectively label the σ1 receptor, and led to the discovery and characterization of the receptor.

Morphan is a chemical compound.

Bremazocine is a κ-opioid receptor agonist related to pentazocine. It has potent and long-lasting analgesic and diuretic effects. It has 200 times the activity of morphine, but appears to have no addictive properties and does not depress breathing. The crystal structure of bremazocine was determined in 1984

Doxpicomine is a mild opioid analgesic drug. The drug acts as a mu-opioid receptor agonist. It is of fairly low potency, with a 400 mg dose of doxpicomine approximately equivalent in pain-killing effect to 8 mg morphine or 100 mg pethidine. It has been used as a lead compound to derive further analogues, although all compounds in this family are comparatively weak mu agonists.
Benzazocine, also known as benzoazocine, is a chemical compound. It consists of a benzene ring bound to an azocine ring. A related compound is benzomorphan.
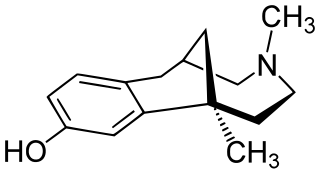
Eptazocine (Sedapain) is an opioid analgesic which was introduced in Japan by Morishita in 1987. It acts as a mixed κ-opioid receptor agonist and μ-opioid receptor antagonist.

Tonazocine (WIN-42,156) is an opioid analgesic of the benzomorphan family which made it to phase II clinical trials for the treatment of postoperative pain, but development was apparently ceased and ultimately it was never marketed. Tonazocine is a partial agonist at both the mu-opioid and delta-opioid receptors, but acting more like an antagonist at the former and more like an agonist at the latter. It lacks most of the side effects of other opioids such as adverse effects on the cardiovascular system and respiratory depression, but it can cause sedation, and in some patients it may induce hallucinations.

Volazocine is an opioid analgesic of the benzomorphan class which was never marketed.

Cogazocine (INN) is an opioid analgesic of the benzomorphan family which was never marketed.

Zenazocine is an opioid analgesic of the benzomorphan family which made it to phase II clinical trials before development was ultimately halted and it was never marketed. It acts as a partial agonist of the μ- and δ-opioid receptors, with less intrinsic activity at the former receptor and more at the latter receptor, and produces antinociceptive effects in animal studies.

Etazocine (NIH-7856) is an opioid analgesic of the benzomorphan family which was never marketed. It acts as a partial agonist of the opioid receptors, with mixed agonist and antagonist effects. In animal studies, it was shown to induce analgesia, dependency, and respiratory depression, with overall effects similar to those of morphine, but with substantially reduced potency in comparison.

Moxazocine (BL-4566) is an opioid analgesic of the benzomorphan family which was never marketed. It acts as a partial agonist or mixed agonist/antagonist of the opioid receptors and binds preferentially to the κ-opioid receptor. Despite its failure to reach the market, clinical studies demonstrated moxazocine to be approximately 10x as potent by weight as morphine as an analgesic.
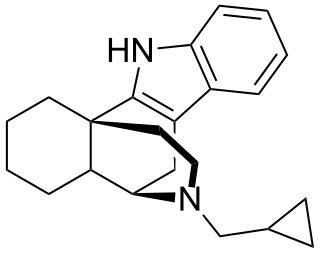
Carbazocine is an opioid analgesic of the benzomorphan family which was never marketed.

Fluorophen, or fluorofen, is a fluorinated analogue of phenazocine, an opioid drug of the benzomorphan group, which was developed as a radioligand for the purpose of labeling opioid receptors during PET scans. Unlike most other benzomorphan derivatives, fluorophen acts as a full agonist of the opioid receptors with preferential affinity for the μ-opioid receptor, similar but slightly lower affinity for the δ-opioid receptor, and very low affinity for the κ-opioid receptor.

Ethylketazocine (WIN-35,197-2), is an opioid drug of the benzomorphan family which has been used extensively in scientific research in the last few decades as a tool to aid in the study of the κ-opioid receptor. However, due to its relatively poor selectivity for the κ-opioid receptor over the μ- and δ-opioid receptors, as well as its relatively poor intrinsic activity at all sites, it has been mostly replaced in recent times by newer and more potent and selective compounds like U-50,488 and ICI-199,441.

Gemazocine (R-15,497), also known as cyclogemine, is a non-selective opioid antagonist of the benzomorphan class. It may have partial agonist properties at some of the opioid receptors, such as at the kappa receptor, but seems to be generally antagonistic in its actions.



















