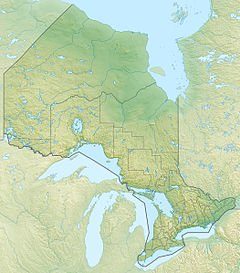
James Bay is a large body of water located on the southern end of Hudson Bay in Canada. It borders the provinces of Quebec and Ontario, and is politically part of Nunavut. Its largest island is Akimiski Island.

Long Point is a sand spit and medium-sized hamlet on the north shore of Lake Erie, part of Norfolk County in the province of Ontario, Canada.

Canada has a large domestic and foreign tourism industry. The second largest country in the world, Canada's wide geographical variety is a significant tourist attractor. Much of the country's tourism is centred in the following regions: Toronto, Montreal, Quebec City, Vancouver/Whistler, Niagara Falls, Vancouver Island, Canadian Rockies, British Columbia's Okanagan Valley, Churchill, Manitoba and the National Capital Region of Ottawa-Gatineau. The large cities are known for their culture, diversity, as well as the many national parks and historic sites.

Churchill is an Arctic port town in northern Manitoba, Canada, on the west shore of Hudson Bay, roughly 140 km (87 mi) from the Manitoba–Nunavut border. It is most famous for the many polar bears that move toward the shore from inland in the autumn, leading to the nickname "Polar Bear Capital of the World" and to the benefit of its burgeoning tourism industry.

The Moose River is a river in the Hudson Plains ecozone of northern Ontario, Canada. The river flows 100 km northeast from the confluence of the Mattagami and Missinaibi Rivers into James Bay. Its drainage basin is 108,500 square kilometres (41,900 sq mi) and it has a mean discharge rate of 1,370 cubic metres (48,000 cu ft). Its full length is 547 kilometres (340 mi) if counted from the head of the Mattagami River.

Lake Superior Provincial Park is one of the largest provincial parks in Ontario, covering about 1,550 square kilometres (600 sq mi) along the northeastern shores of Lake Superior between Sault Ste. Marie and Wawa in Algoma District in Northeastern Ontario, Canada. Ontario Highway 17 now runs through the park. When the park was established by Ontario in 1944, there was no road access.

Lake Nipigon is part of the Great Lakes drainage basin. It is the largest lake entirely within the boundaries of the Canadian province of Ontario.

Quetico Provincial Park is a large wilderness park in Northwestern Ontario, Canada, known for its excellent canoeing and fishing. The 4,760 km2 (1,180,000-acre) park shares its southern border with Minnesota's Boundary Waters Canoe Area Wilderness, which is part of the larger Superior National Forest. These large wilderness parks are often collectively referred to as the Boundary Waters or the Quetico-Superior Country.

Wabakimi Provincial Park is a wilderness park located to the northwest of Lake Nipigon and northwest of Armstrong Station in the province of Ontario, Canada. The park contains a vast and interconnected network of more than 2,000 kilometres of lakes and rivers. The park covers an area of 8,920 square kilometres (3,440 sq mi) and became the second largest park in Ontario and one of the world's largest boreal forest reserves following a major expansion in 1997. A number of local citizen groups and residents, including Bruce Hyer have been instrumental in the creation, expansion, and preservation of this region.

Moose Factory is a community in the Cochrane District, Ontario, Canada. It is located on Moose Factory Island, near the mouth of the Moose River, which is at the southern end of James Bay. It was the first English-speaking settlement in lands now making up Ontario and the second Hudson's Bay Company post to be set up in North America after Fort Rupert. On the mainland, across the Moose River, is the nearby community of Moosonee, which is accessible by water taxi in the summer, ice road in the winter, and chartered helicopter in the off-season.

Wapusk National Park is Canada's 37th national park, established in 1996. The name comes from the Cree word for polar bear (wâpask).
Ontario Parks is a branch of the Ministry of the Environment, Conservation and Parks in Ontario, Canada, that protects significant natural and cultural resources in a system of parks and protected areas that is sustainable and provides opportunities for inspiration, enjoyment and education. The Ontario Parks system covers over 78,000 square kilometres (30,000 sq mi), which is about 10 per cent of the province's surface area or the equivalent of an area approximately equal to Nova Scotia. It falls under the responsibility and mandate of the province's Ministry of the Environment, Conservation and Parks. It was formerly under the mandate of the Ministry of Natural Resources and Forestry.

A provincial park is a park administered by one of the provinces of a country, as opposed to a national park. They are similar to state parks in other countries. They are typically open to the public for recreation. Their environment may be more or less strictly protected.

Killarney Provincial Park is a provincial park in central Ontario, Canada.
Peawanuck is an isolated Cree community in the Kenora District, Ontario, Canada. It is located near the confluence of the Winisk and Shamattawa rivers, about 35 km from the Winisk River's end in Hudson Bay. Its population is 237.

The Winisk River is a river in northern Ontario, Canada, that starts at Wunnummin Lake and flows east to Winisk Lake. From there it continues in a mostly northerly direction to Hudson Bay. The Winisk River is 475 kilometres (295 mi) long and has a drainage basin of 67,300 square kilometres (26,000 sq mi). The name is from Cree origin meaning "groundhog".

Balsam Lake Provincial Park is a provincial park located in south-central Ontario, Canada, on Balsam Lake. The park is situated along the Trent-Severn Waterway, a few kilometres southwest of Coboconk. It is an all-seasons recreation area offering camping, boating and fishing, and while closed in winter it is also used for skiing and snowshoeing.
Opasquia Provincial Park is a provincial park located in northwest Ontario, Canada. Situated alongside the Manitoba border, this remote park is approximately 473,000 hectares in size. The Opasquia park is home to many different species of plants and animals.

The Southern Hudson Bay taiga is a terrestrial ecoregion, as classified by the World Wildlife Fund, which extends along the southern coast of Hudson Bay and resides within the larger taiga biome. The region is nearly coterminous with the Hudson Plain, a Level I ecoregion of North America as designated by the Commission for Environmental Cooperation (CEC) in its North American Environmental Atlas.
The Sutton River is a tributary of the south shore of Hudson Bay, crossing the Kenora District, Northwestern Ontario, Canada.