
Kuwaykat, also spelled Kuweikat, Kweikat or Kuwaikat, was a Palestinian village located 9 km northeast of Acre. It was depopulated in 1948.

Abu Shusha was a Palestinian Arab village in the Ramle Subdistrict of Mandatory Palestine, located 8 km southeast of Ramle. It was ethnically cleansed in May 1948.

Ra'na was a village located approximately 26 km northwest of Hebron. It was occupied by the Israeli army during Operation Yo'av in October 1948. It was one of 16 villages in the Hebron district that were depopulated.

Abil al-Qamh was a Palestinian village located near the Lebanese border north of Safad. It was depopulated in 1948. It was located at the site of the biblical city of Abel-beth-maachah.

Shahma was a Palestinian Arab village located 15 kilometers (9.3 mi) southwest of Ramla. Depopulated on the eve of the 1948 Arab-Israeli war, the village lands today form part of a fenced-in area used by the Israeli Air Force.
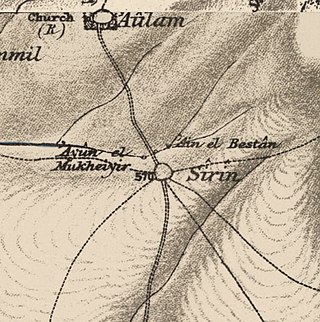
Sirin, was a Palestinian Arab village located 17 kilometers (11 mi) north of Beisan. The village was depopulated and destroyed in 1948. Only the village cemetery and one house remain standing, along with the remains of a mosaic pavement and a vaulted spring dating to the Byzantine period. Mentioned in historical documents, the 1596 census indicated it had 45 households; by 1945, the number of inhabitants had risen to 810.

Abu Shusha was a Palestinian Arab village in the Haifa Subdistrict. It was depopulated during the 1947–48 Civil War in Mandatory Palestine on 9 April 1948 during the Battle of Mishmar HaEmek. The village was inhabited by Turkmens.

Daliyat al-Rawha' was a Palestinian village located 24.5 kilometers (15.2 mi) southeast of Haifa. It was the site of the signing of a ceasefire agreement between the forces of the Mamluks and the Crusaders in the 13th century. A small village of 60 Arab Muslims in the late 19th century, the kibbutz of Dalia was established on land purchased in the village in 1939. The population in 1945 reached 600 people: 280 Arabs and 320 Jews. It was depopulated of its Arab inhabitants in late March during the 1947–1948 civil war in Mandatory Palestine.

Al-Rihaniyya was a Palestinian Arab village in the Haifa Subdistrict. It was depopulated during the 1947–1948 Civil War in Mandatory Palestine on 30 April 1948 as part of the battle of Mishmar HaEmek. It was located 25 km southeast of Haifa and 3 km northwest of Wadi al-Mileh.

Umm al-Shawf or Umm ash Shauf was a Palestinian Arab village located 29.5 km south of Haifa, on the sloping section of Wadi al-Marah. It was depopulated as a result of a military assault between May 12–14, just before the outbreak of the 1948 Arab-Israeli war.

Umm az-Zinat was a Palestinian Arab village in the Haifa Subdistrict. It was depopulated during the 1948 War on May 15, 1948, by Golani Brigade's Fourth Battalion. It was located 20.5 km southeast of Haifa.

Al-'Abbasiyya, also known as al-Yahudiya, was a Palestinian Arab village in the Jaffa Subdistrict. It was attacked under Operation Hametz during the 1948 Palestine War, and finally depopulated under Operation Dani. It was located 13 km east of Jaffa. Some of the remains of the village can be found today in the centre of the modern Israeli city of Yehud.

Bayt Umm al-Mays was a small Palestinian Arab village in the Jerusalem Subdistrict.

Al-Barriyya was a Palestinian village in the Ramle Subdistrict of Mandatory Palestine. It was depopulated during the 1948 Arab–Israeli War on July 10, 1948, as part of Operation Dani. It was located 5.5 km southeast of Ramla, on the eastern bank of Wadi al-Barriyya.

Daniyal was a Palestinian village in the Ramle Subdistrict. It was depopulated during the 1948 Arab–Israeli War on July 10, 1948, by the Yiftach Brigade under the first phase of Operation Dani. It was located 5 km east of Ramla and southeast of Lydda.

Al-Maghar was a Palestinian Arab village in the Ramle Subdistrict of Mandatory Palestine. It was depopulated by the Givati Brigade during Operation Barak on 18 May 1948. It was located 12 km southwest of Ramla, situated north of Wadi al-Maghar.

Al-Mansura was a small Palestinian Arab village in the Ramle Subdistrict, located 10 km south of Ramla. It was depopulated during the 1947–48 Civil War in Mandatory Palestine on April 20, 1948, under Operation Barak.

Arab al-Shamalina also known as Khirbat Abu Zayna was a Palestinian Arab village in the Safad Subdistrict. It was depopulated during the 1947–1948 Civil War in Mandatory Palestine on May 4, 1948, under Operation Matate (Broom), a sub operation of Operation Yiftach. It was located 13 km southeast of Safad near the Jordan River.

Harrawi was a Palestinian Arab village in the Safad Subdistrict. It was depopulated during the 1948 Arab-Israeli War on May 25, 1948, by the Palmach's First Battalion of Operation Yiftach. It was located 18 km northeast of Safad.
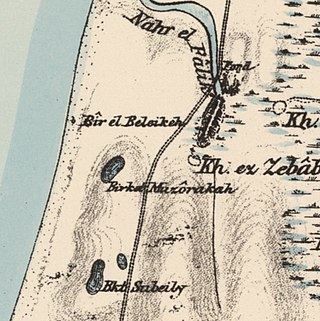
Khirbat al-Zababida was a Palestinian Arab village in the Tulkarm Subdistrict. It was depopulated during the 1948 Arab–Israeli War on May 15, 1948. It was located 20 kilometres (12 mi) southwest of Tulkarm, south of Wadi al-Faliq. Khirbat al-Zababida was mostly destroyed except for four deserted houses.






























