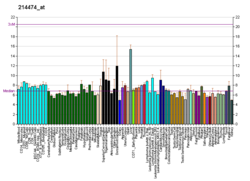
| PRKAB2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | PRKAB2 , protein kinase AMP-activated non-catalytic subunit beta 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 602741; MGI: 1336185; HomoloGene: 38046; GeneCards: PRKAB2; OMA:PRKAB2 - orthologs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
5'-AMP-activated protein kinase subunit beta-2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PRKAB2 gene. [5] [6]
The protein encoded by this gene is a regulatory subunit of the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). AMPK is a heterotrimer consisting of an alpha catalytic subunit, and non-catalytic beta and gamma subunits. AMPK is an important energy-sensing enzyme that monitors cellular energy status. In response to cellular metabolic stresses, AMPK is activated, and thus phosphorylates and inactivates acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) and beta-hydroxy beta-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase (HMGCR), key enzymes involved in regulating de novo biosynthesis of fatty acid and cholesterol. This subunit may be a positive regulator of AMPK activity. It is highly expressed in skeletal muscle and thus may have tissue-specific roles. [6]