Related Research Articles

Phencyclidine or phenylcyclohexyl piperidine (PCP), also known as angel dust among other names, is a dissociative hallucinogenic drug used for its mind-altering effects. PCP may cause hallucinations, distorted perceptions of sounds, and violent behavior. As a recreational drug, it is typically smoked, but may be taken by mouth, snorted, or injected. It may also be mixed with cannabis or tobacco.
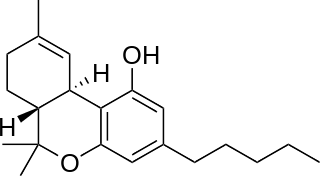
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the principal psychoactive constituent of cannabis and one of at least 113 total cannabinoids identified in the plant. Although the chemical formula for THC (C21H30O2) describes multiple isomers, the term THC usually refers to the Delta-9-THC isomer with chemical name (−)-trans-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol. Like most pharmacologically active secondary metabolites of plants, THC is a lipid found in cannabis, assumed to be involved in the plant's evolutionary adaptation, putatively against insect predation, ultraviolet light, and environmental stress.

A cannabis edible, also known as a cannabis-infused food or simply an edible, is a food product that contain decarboxylated cannabinoids from cannabis extract as an active ingredient. Although edible may refer to either a food or a drink, a cannabis-infused drink may be referred to more specifically as a liquid edible or drinkable. Edibles are a way to consume cannabis. Cannabis edibles may affect people for a longer period of time than smoked cannabis.

The effects of cannabis are caused by chemical compounds in the cannabis plant, including 113 different cannabinoids such as tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and 120 terpenes, which allow its drug to have various psychological and physiological effects on the human body. Different plants of the genus Cannabis contain different and often unpredictable concentrations of THC and other cannabinoids and hundreds of other molecules that have a pharmacological effect, so that the final net effect cannot reliably be foreseen.

Medical cannabis, or medical marijuana (MMJ), is cannabis and cannabinoids that are prescribed by physicians for their patients. The use of cannabis as medicine has not been rigorously tested due to production and governmental restrictions, resulting in limited clinical research to define the safety and efficacy of using cannabis to treat diseases.
Dissociatives are a class of hallucinogen which distort perception of sight and sound and produce feelings of detachment – dissociation – from the environment and/or self. Although many kinds of drugs are capable of such action, dissociatives are unique in that they do so in such a way that they produce hallucinogenic effects, which may include sensory deprivation, dissociation, hallucinations, and dream-like states or anesthesia. Some, which are nonselective in action and affect the dopamine and/or opioid systems, may be capable of inducing euphoria. Many dissociatives have general depressant effects and can produce sedation, respiratory depression, analgesia, anesthesia, and ataxia, as well as cognitive and memory impairment and amnesia.
A depressant, or central depressant, is a drug that lowers neurotransmission levels, which is to depress or reduce arousal or stimulation, in various areas of the brain. Depressants are also occasionally referred to as "downers" as they lower the level of arousal when taken. Stimulants or "uppers" increase mental and/or physical function, hence the opposite drug class of depressants is stimulants, not antidepressants.

Pentazocine, sold under the brand name Talwin among others, is a painkiller used to treat moderate to severe pain. It is believed to work by activating (agonizing) κ-opioid receptors (KOR) and μ-opioid receptors (MOR). As such it is called an opioid as it delivers its effects on pain by interacting with the opioid receptors. It shares many of the side effects of other opioids like constipation, nausea, itching, drowsiness and respiratory depression, but unlike most other opioids it fairly frequently causes hallucinations, nightmares and delusions. It is also, unlike most other opioids, subject to a ceiling effect, which is when at a certain dose no more pain relief, or side effects, is obtained by increasing the dose any further.
Stimulant psychosis is a mental disorder characterized by psychotic symptoms which involves and typically occurs following an overdose or several day 'binge' on psychostimulants; however, it has also been reported to occur in approximately 0.1% of individuals, or 1 out of every 1,000 people, within the first several weeks after starting amphetamine or methylphenidate therapy. Methamphetamine psychosis, or long-term effects of stimulant use in the brain, depend upon genetics and may persist for some time.

Cannabidiol (CBD) is a phytocannabinoid discovered in 1940. It is one of 113 identified cannabinoids in cannabis plants, along with tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), and accounts for up to 40% of the plant's extract. As of 2019, clinical research on CBD included studies related to anxiety, cognition, movement disorders, and pain, but there is insufficient high-quality evidence that cannabidiol is effective for these conditions.

Cannabis, also known as marijuana among other names, is a psychoactive drug from the Cannabis plant. Native to Central and South Asia, the cannabis plant has been used as a drug for both recreational and entheogenic purposes and in various traditional medicines for centuries. Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the main psychoactive component of cannabis, which is one of the 483 known compounds in the plant, including at least 65 other cannabinoids, including cannabidiol (CBD). Cannabis can be used by smoking, vaporizing, within food, or as an extract.
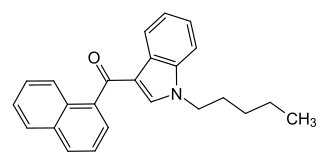
JWH-018 (1-pentyl-3-(1-naphthoyl)indole) or AM-678 is an analgesic chemical from the naphthoylindole family that acts as a full agonist at both the CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors, with some selectivity for CB2. It produces effects in animals similar to those of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), a cannabinoid naturally present in cannabis, leading to its use in synthetic cannabis products that in some countries are sold legally as "incense blends".
A hallucinogen is a psychoactive agent that often or ordinarily causes hallucinations, perceptual anomalies, and other substantial subjective changes in thought, emotion, and consciousness that are not typically experienced to such degrees with other drug classifications. The term hallucinogen almost invariably refers to any drug which causes what is called a "trip". The common classifications for hallucinogens are psychedelics, dissociatives and deliriants. Although hallucinogens all can induce altered states of consciousness with some overlap in effects, there are quantifiable as well as vast qualitative differences in the induced subjective experiences between the different classes of hallucinogens due to differing and distinct pharmacological mechanisms. Contemporarily, certain potentially hallucinogenic GABAergic drugs such as muscimol, gaboxadol and zolpidem may be grouped into a distinct, separate or new category of hallucinogens that may be referred to as hypnotics despite many hypnotic and GABAergic drugs not being hallucinogenic like the three previously mentioned compounds. Additionally, cannabinergic compounds may also be considered distinct from the other categories as well despite sharing characteristics; specifically with both the psychedelic and dissociative classes.

Synthetic cannabinoids are a class of designer drug molecules that bind to the same receptors to which cannabinoids in cannabis plants attach. These novel psychoactive substances should not be confounded with synthetic phytocannabinoids or synthetic endocannabinoids from which they are in many aspects distinct.

The long-term effects of cannabis have been the subject of ongoing debate. Because cannabis is illegal in most countries, clinical research presents a challenge and there is limited evidence from which to draw conclusions. In 2017, the U.S. National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine issued a report summarizing much of the published literature on health effects of cannabis, into categories regarded as conclusive, substantial, moderate, limited and of no or insufficient evidence to support an association with a particular outcome.
Substance-induced psychosis is a form of psychosis that is attributed to substance use. It is a psychosis that results from the effects of chemicals or drugs, including those produced by the body itself. Various psychoactive substances have been implicated in causing or worsening psychosis in users.

Cannabis use disorder (CUD), also known as cannabis addiction or marijuana addiction, is defined in the fifth revision of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) and ICD-10 as the continued use of cannabis despite clinically significant impairment.

Harris Isbell was an American pharmacologist and the director of research for the NIMH Addiction Research Center at the Public Health Service Hospital in Lexington, Kentucky from 1945 to 1963. He did extensive research on the physical and psychological effects of various drugs on humans. Early work investigated aspects of physical dependence with opiates and barbiturates, while later work investigated psychedelic drugs, including LSD. The research was extensively reported in academic journals such as the Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, Psychopharmacologia, and the AMA Archives of Neurology and Psychiatry.

Delta-8-tetrahydrocannabinol is a psychoactive cannabinoid found in the Cannabis plant. It is an isomer of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol, the compound commonly known as THC. ∆8-THC is under preliminary research for its biological properties.
References
- ↑ Pfeiffer (1986). "Psychotomimesis mediated by kappa opiate receptors". Science. 233 (4765): 774–776. Bibcode:1986Sci...233..774P. doi:10.1126/science.3016896. PMID 3016896.
- ↑ Musacchio JM (1990). "The psychotomimetic effects of opiates and the sigma receptor". Neuropsychopharmacology. 3 (3): 191–200. PMID 2163646.
- ↑ Sewell R. A.; Ranganathan M.; D'Souza D. C. (2009). "Cannabinoids and psychosis". International Review of Psychiatry . 21 (2): 152–162. doi:10.1080/09540260902782802. PMID 19367509.
- ↑ D'Souza DC, Perry E, MacDougall L, Ammerman Y, Cooper T, Wu YT, Braley G, Gueorguieva R, Krystal JH (2004). "The psychotomimetic effects of intravenous delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol in healthy individuals: implications for psychosis" (PDF). Neuropsychopharmacology. 29 (8): 1558–1572. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1300496 . PMID 15173844.
- ↑ Brenneisen R. Chemistry and analysis of phytocannabinoids and other Cannabis constituents. In: ElSohly MA (ed). Marijuana and the cannabinoids. Humana Press Inc: Totowa, New Jersey, 2007.
- ↑ Sagan, Carl. "Mr. X". Marijuana-Uses.com. Retrieved November 8, 2012.