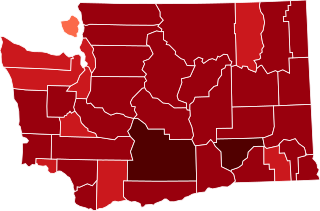
The first confirmed case relating to the COVID-19 pandemic was announced by the state of Washington on January 21, 2020. Washington made the first announcement of a death from the disease in the U.S. on February 29 and later announced that two deaths there on February 26 were also due to COVID-19. Until mid-March, Washington had the highest absolute number of confirmed cases and the highest number per capita of any state in the country, when it was surpassed by New York state. Many of the deceased were residents of a nursing home in Kirkland, an Eastside suburb of Seattle in King County.

The first cases relating to the COVID-19 pandemic in Washington, D.C. were reported on March 7, 2020.

The COVID-19 pandemic was confirmed to have reached the U.S. state of Maryland in March 2020. The first three cases of the virus were reported in Montgomery County on March 5, 2020. As of May 16, 2020, the Maryland Department of Health (MDH) reported 37,968 positive cases and 1,842 deaths in the state, with 2,806 patients released from isolation.
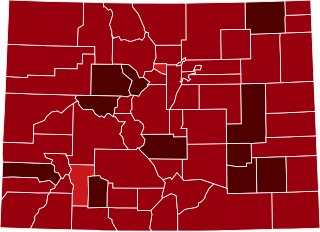
The COVID-19 pandemic reached Colorado on March 5, 2020, when the state's first two cases were confirmed. As of May 16, 2020, the Colorado authorities reported 21,633 confirmed cases of COVID-19 among the state's residents, resulting in 3,866 hospitalized patients and 1192 deaths. All three of these figures are cumulative, beginning on March 5, 2020.

The COVID-19 pandemic was confirmed to have reached the U.S. state of Arkansas in March 2020. The first case in Arkansas was reported on March 11, 2020, in Pine Bluff, Jefferson County.

The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic began in the U.S. state of Illinois on January 24, 2020, when a woman in Chicago, who had just returned from the pandemic's place of origin in Wuhan, Hubei, China, tested positive for the virus. This was the second case of COVID-19 in the United States during the pandemic. The woman's husband was diagnosed with the disease a few days later, the first known case of human-to-human transmission in the United States. Community transmission was not suspected until March 8, when a case with no connection to other cases or recent travel was confirmed.

The COVID-19 pandemic was confirmed to have reached the U.S. state of Kentucky on March 6, 2020, when Governor Andy Beshear's office announced the first confirmed case in Lexington and declared a state of emergency to ensure all entities have the necessary response resources. As of May 13, 2020, 7,080 cases of COVID-19 were confirmed, with 326 deaths.

The COVID-19 pandemic was confirmed to have reached the U.S. state of Montana on March 14, 2020. As of May 16, 2020 the Montana Department of Public Health and Human Services (MDPHHS) has confirmed 468 positive cases and 16 deaths in the state.

The COVID-19 pandemic was confirmed to have reached the U.S. state of Ohio in March 2020.

The COVID-19 pandemic was confirmed to have reached the U.S. state of Pennsylvania in March 2020. As of May 15, 2020, the Pennsylvania Department of Health has confirmed 60,622 cases and 4,342 deaths in the state.

The COVID-19 pandemic was confirmed to have reached the U.S. state of South Carolina in March 2020. As of May 11, 2020, the South Carolina Department of Health and Environmental Control has confirmed 7,792 cases in the state, resulting in 346 deaths. On April 2, 2020, DHEC announced that the virus had spread to all 46 counties in the state.
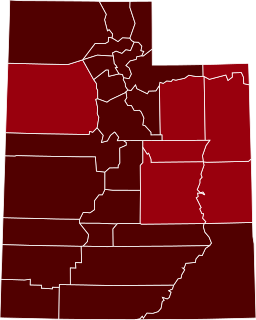
The COVID-19 pandemic began in the U.S. state of Utah in early March with travel-related cases. Residents stockpiled goods, large conferences were cancelled, a state of emergency was declared, and all public universities and colleges switched to online classes. After the first case of community spread was found on March 14, Utah faced a shortage of testing kits, and public schools were ordered closed. Community spread was confirmed in more counties, and the state issued a public health order prohibiting dine-in service in restaurants and gatherings of more than 10 people except in grocery stores. A 5.7-magnitude earthquake struck the Wasatch Front on March 18, hampering the pandemic response. In late March, the state directed all people to voluntarily stay at home as much as possible. Salt Lake, Davis, Weber, Morgan, Tooele, Summit, and Wasatch counties directed people to stay at home except for essential activities. In April, the state briefly ordered all adults entering the state to fill out an online travel declaration. It established phased guidelines for the public to follow and moved from the "red" phase to the "orange" phase at the start of May, advising people to wear face masks in public and stay six feet apart when leaving home.

The COVID-19 pandemic in the U.S. state of Vermont is part of an ongoing worldwide viral pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019, a novel infectious disease caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.

The COVID-19 pandemic in Virginia is part of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. The first confirmed case was reported on March 7, 2020. As of May 16, 2020, there have been 29,683 confirmed cases and 1,007 deaths reported in the U.S. state of Virginia.

The COVID-19 pandemic was confirmed to have reached the U.S. state of Wyoming in March 2020. On April 13, Wyoming became the last state in the U.S. to report its first death from COVID-19. On April 14, Wyoming reported its 2nd COVID-19 related death. As of May 14, Wyoming was the state with the fewest number of deaths from COVID-19.

State, territorial, tribal, and local governments have responded to the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States with various declarations of emergency, closure of schools and public meeting places, lockdowns, and other restrictions intended to slow the progression of the virus.
The following is a timeline of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States.
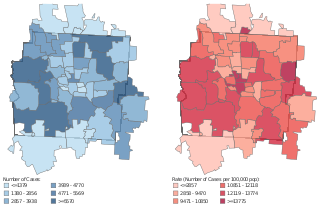
The COVID-19 pandemic is an ongoing viral pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), a novel infectious disease caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The pandemic has affected the city of Columbus, Ohio, as Ohio's stay-at-home order shuttered all nonessential businesses, and is causing event cancellations as well as protests at the Ohio Statehouse, the state capitol building.
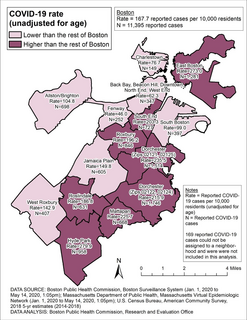
The COVID-19 pandemic in Boston is part of an ongoing pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in the Massachusetts city of Boston. The first confirmed case was reported on February 1, 2020, and the number began to increase rapidly by March 9. The Governor of Massachusetts, Charlie Baker declared a state of emergency on March 10. Boston Mayor, Marty Walsh declared a public health emergency on March 15. By March 21, more than a hundred people in Boston had tested positive for COVID-19. Most early cases were traceable to a company meeting held in late February by the biotechnology firm Biogen in Boston. As of May 16, 2020, there were 11,767 confirmed cases and 570 deaths due to COVID-19. As of May 14, Boston had completed 41,619 tests, 27.3% of which came back positive.
This article is a summary of the social distancing measures related to the COVID-19 pandemic.