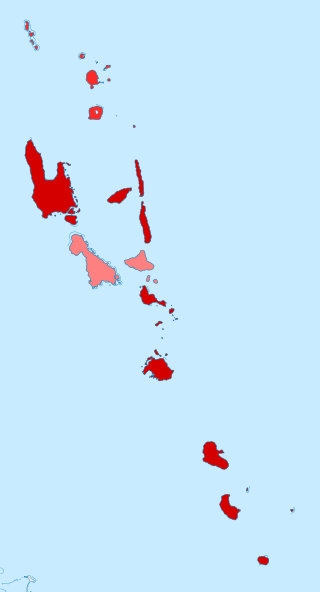
The COVID-19 pandemic in Vanuatu is part of the ongoing worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. The virus was confirmed to have reached Vanuatu on 11 November 2020.
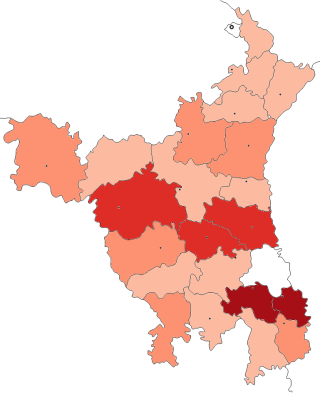
The first case of the COVID-19 pandemic in the Indian state of Haryana was reported on 4 March 2020. The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare has confirmed a total of 2,64,955 positive cases as of 10 January 2021 out of which 2,510 are still active and 2,950 deaths so far. The recovery rate in Haryana is 97.9%.
The first case of the COVID-19 pandemic in India was reported on 30 January 2020, originating from China. Slowly, the pandemic spread to various states and union territories including the state of Tripura. The first case was recorded in this region on 6 April.
The first case of the COVID-19 pandemic in India was reported on 30 January 2020, originating from China. Slowly, the pandemic spread to various states and union territories including the state of Meghalaya. The first case was recorded in this region on 14 April.

The first case of the COVID-19 pandemic in India was reported on 30 January 2020, originating from China. Slowly, the pandemic spread to various states and union territories including the state of Chhattisgarh. The first case was recorded in this region on 19 March 2020.
The first case of the COVID-19 pandemic in India was reported on 30 January 2020, originating from China. Slowly, the pandemic spread to various states and union territories including the Indian-administered union territory of Jammu and Kashmir. Two suspected cases with high virus load were detected and isolated on 4 March in Government Medical College, Jammu. One of them became the first confirmed positive case on 9 March 2020. Both individuals had a travel history to Iran.
The first case of the COVID-19 pandemic in India was reported on 30 January 2020, originating from China. Slowly, the pandemic spread to various states and union territories including the state of Himachal Pradesh. The first case was recorded in this region on 20 March 2020.
The first case of the COVID-19 pandemic in India was reported on 30 January 2020, originating from China. Slowly, the pandemic spread to various states and union territories of India including the union territory of Ladakh. The first case was recorded in this region on 18 March.
The first case of the COVID-19 pandemic in India was reported on 30 January 2020. Slowly, the pandemic spread to various states and union territories including the state of Uttarakhand. The first case was recorded in this region on 15 March.
The first case of the COVID-19 pandemic in India was reported on 30 January 2020, originating from China. Slowly, the pandemic spread to various states and union territories including the union territory of Chandigarh. The first case was recorded in this region on 19 March 2020. As on 24 May, total number of cases in Chandigarh was 225. This contains 43 active cases as 179 successfully recovered from it and three died from the virus.
The first case of the COVID-19 pandemic in India was reported on 30 January 2020, originating from China. Slowly, the pandemic spread to various states and union territories including the union territory of Andaman and Nicobar Islands. The first case was recorded in this region on 26 March 2020. The islands have pursued a strategy of zero COVID-19 transmission, which, except for three flareups in August 2020, May 2021, and January 2022, which were swiftly contained, have resulted in no community outbreaks. The islands have successfully managed the outbreaks, and the union territory has the lowest case count of any region of India, both in total cases and infection rate.
The first case of the COVID-19 pandemic in India was reported on 30 January 2020, originating from China. Slowly, the pandemic spread to various states and union territories including the union territory of Puducherry. The first case was recorded in this region on 17 March.
The COVID-19 pandemic reached the state of Nagaland on 22 May 2020, with its first case confirmed on 25 May 2020. Officially, Nagaland is the last of the northeastern states after Sikkim to report COVID-19 positive cases.
The first case of the COVID-19 pandemic in India was reported on 30 January 2020, originating from China. Slowly, the pandemic spread to various states and union territories including the state of Manipur. The first case was recorded in this region on 24 March 2020.
The first case of the COVID-19 pandemic in India was reported on 30 January 2020, originating from China. Slowly, the pandemic spread to various states and union territories including the state of Arunachal Pradesh. The first case was recorded in this region on 2 April 2020.

The first case of the COVID-19 pandemic in India was reported on 30 January 2020, originating from China. Slowly, the pandemic spread to various states and union territories including the state of Mizoram. The first case was recorded in this region on 24 March 2020, and the first death was recorded on 28 October 2020.
The first case of the COVID-19 pandemic in India was reported on 30 January 2020, originating from China. Slowly, the pandemic spread to various states and union territories including the union territory of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu. The first case was recorded in this region on 10 April 2020.
The first case of the COVID-19 pandemic in India was reported on 30 January 2020, originating from China. Slowly, the pandemic spread to various states and union territories including the state of Sikkim.

India began administration of COVID-19 vaccines on 16 January 2021. As of 4 March 2023, India has administered over 2.2 billion doses overall, including first, second and precautionary (booster) doses of the currently approved vaccines. In India, 95% of the eligible population (12+) has received at least one shot, and 88% of the eligible population (12+) is fully vaccinated.
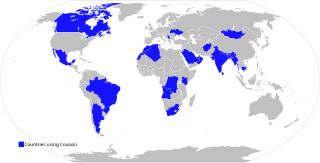
Vaccine Maitri is a humanitarian initiative undertaken by the Indian government to provide COVID-19 vaccines to countries around the world. The government started providing vaccines from 20 January 2021. As of 21 February 2022, India had delivered around 16.29 crore doses of vaccines to 96 countries. Of these, 1.43 crore doses were gifted to 98 countries by the Government of India. The remaining 10.71 crore were supplied by the vaccine producers under its commercial and 4.15 crore were supplied by COVAX obligations. In late March 2021, the Government of India temporarily froze exports of the Covishield, citing India's own COVID crisis and the domestic need for these vaccines. The Health Minister of India, Mansukh Mandaviya announced in September that India will resume the export of vaccines from October to the rest of the world.






