The first cases of the COVID-19 pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 in North America were reported in the United States on 23 January 2020. Cases were reported in all North American countries after Saint Kitts and Nevis confirmed a case on 25 March, and in all North American territories after Bonaire confirmed a case on 16 April.

The COVID-19 pandemic in Mexico is part of the ongoing worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.

The COVID-19 pandemic in California began earlier than in some other parts of the United States. Ten of the first 20 confirmed COVID-19 infections in the United States were detected in California, and the first infection was confirmed on January 26, 2020. All of the early confirmed cases were persons who had recently travelled to China, as testing was restricted to this group, but there were some other people infected by that point. A state of emergency was declared in the state on March 4, 2020. A mandatory statewide stay-at-home order was issued on March 19, 2020; it was ended on January 25, 2021. On April 6, 2021, the state announced plans to fully reopen the economy by June 15, 2021.
The COVID-19 pandemic in Costa Rica was a part of the ongoing worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. The virus was confirmed to have spread to Costa Rica on 6 March 2020, after a 49-year-old woman tourist from New York, United States, tested positive for the virus.

The COVID-19 pandemic in Bolivia was a part of the worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. The virus was confirmed to have spread to Bolivia on 10 March 2020, when its first two cases were confirmed in the departments of Oruro and Santa Cruz.
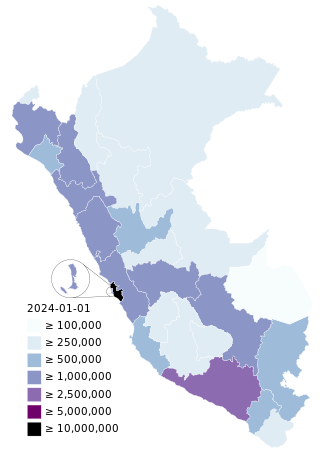
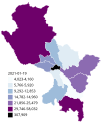
The COVID-19 pandemic in Peru has resulted in 4,524,748 confirmed cases of COVID-19 and 220,831 deaths. The virus spread to Peru on 6 March 2020, when a 25-year-old man who had travelled to Spain, France, and the Czech Republic tested positive. On 15 March 2020, President Martín Vizcarra announced a country-wide lockdown, closing borders, restricting domestic flights, and forbidding nonessential business operations, excluding health facilities, grocery stores, pharmacies, and banks. As of May 2023, Peru has the highest COVID-19 death rate in the world, with over 6,400 deaths per one million citizens.
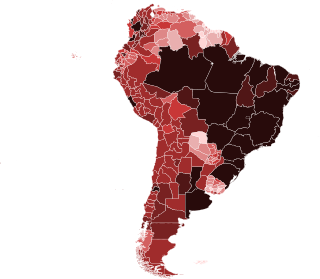
The COVID-19 pandemic was confirmed to have reached South America on 26 February 2020 when Brazil confirmed a case in São Paulo. By 3 April, all countries and territories in South America had recorded at least one case.
The COVID-19 pandemic in Honduras was a part of the worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. The virus was first confirmed to have spread to Honduras on 10 March 2020, when two women tested positive for the virus after one of them landed on Toncontín International Airport in a flight from Madrid, Spain, and the other on Ramón Villeda Morales International Airport in a flight from Geneva, Switzerland. Confirmed cases have been reported in all 18 departments of the country, with the majority of cases located in Cortés and Francisco Morazán.

The COVID-19 pandemic in Puerto Rico was an ongoing viral pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), a novel infectious disease caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). It is part of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic.
The COVID-19 pandemic in El Salvador was a part of the worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. The virus was confirmed to have reached El Salvador on 18 March 2020. As of 19 September 2021, El Salvador reported 102,024 cases, 3,114 deaths, and 84,981 recoveries. As of that date El Salvador had arrested a total of 2,424 people for violating quarantine orders, and 1,268,090 people had been tested for the virus. On 31 March 2020, the first COVID-19 death in El Salvador was confirmed.
The COVID-19 pandemic in Nicaragua was a part of the worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. The virus was shown to have spread to Nicaragua when the first case, a Nicaraguan citizen who had returned to the country from Panama, was confirmed on 18 March 2020.

Operation Broadshare is the code name for the British military operation to address the COVID-19 pandemic overseas, primarily in the British Overseas Territories (BOTs) and British overseas military bases. The operation runs in parallel to a similar military operation in the United Kingdom, named Operation Rescript.
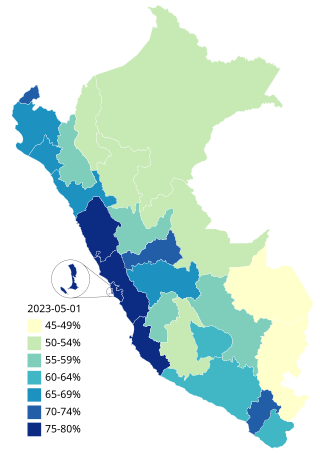
The COVID-19 vaccination program in Peru is the national vaccination strategy to protect the population against SARS-CoV-2 employing vaccines developed for the COVID-19 pandemic in Peru. Vaccination began on 9 February 2021, after three days of arrival of first vaccines. On a nation message, the head of state Francisco Sagasti confirmed the purchase of 38 millions of vaccines, being one million of vaccines for health personnel.

This article presents official statistics gathered during the COVID-19 pandemic in Peru.

The Lambda variant, also known as lineage C.37, is a variant of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. It was first detected in Peru in August 2020. On 14 June 2021, the World Health Organization (WHO) named it Lambda variant and designated it as a variant of interest. It has spread to at least 30 countries around the world and is known to be more resistant to neutralizing antibodies compared to other strains. There is evidence that suggests the Lambda variant is both more infectious and resistant to vaccines than the Alpha and/or Gamma variant.

Elizabeth Zulema Tomás Gonzales is a Peruvian cardiovascular anaesthesiologist. She served as the country's Minister of Health from 7 January to 15 November 2019.

The Mu variant, also known as lineage B.1.621 or VUI-21JUL-1, is one of the variants of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. It was first detected in Colombia in January 2021 and was designated by the WHO as a variant of interest on August 30, 2021. The WHO said the variant has mutations that indicate a risk of resistance to the current vaccines and stressed that further studies were needed to better understand it. Outbreaks of the Mu variant were reported in South America and Europe. The B.1.621 lineage has a sublineage, labeled B.1.621.1 under the PANGO nomenclature, which has already been detected in more than 20 countries worldwide.

The 2022–2023 mpox outbreak in Peru is a part of the outbreak of human mpox caused by the West African clade of the monkeypox virus. The outbreak reached Peru on 26 June 2022.